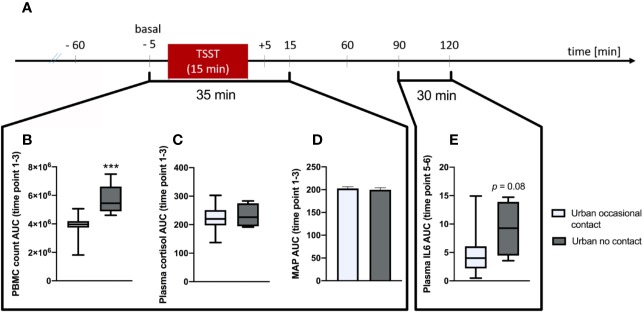
Figure 3.
Analysis of Trier Social Stress Test (TSST)-induced alterations on immunological and physiological parameters between urban participants growing up with no animal contact at all vs. urban participants growing up with “occasional” animal contact until the 15th birthday, respectively. (A) Timeline of the experimental procedure. At –60 min time point, the venous catheter as well as the blood pressure and heart rate monitor were placed. Before (–5 min) and after (5, 15, 60, 90, and 120 min) the TSST, different immunological and physiological parameters where assessed. (B) Area under the curve with respect to ground (AUC) analysis indicates that urban participants growing up with no animal contact at all (n = 5) vs. urban subjects growing up with “occasional” animal contact until the 15th birthday (n = 15), respectively showed significantly higher counts of plasma peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) between time point 1 and 3. This effect was also by trend visible in plasma interleukin (IL)-6 levels between time point 5 and 6 (E). There were no significant differences between both groups in the AUC between time point 1 and 3 of plasma cortisol levels (C) and the mean arterial pressure (MAP; D), respectively. Normally distributed data are presented as bars (mean + SEM). Non-normally distributed data are presented as box plots (Median, min, max, 25th and 75th percentile) ***p < 0.001.