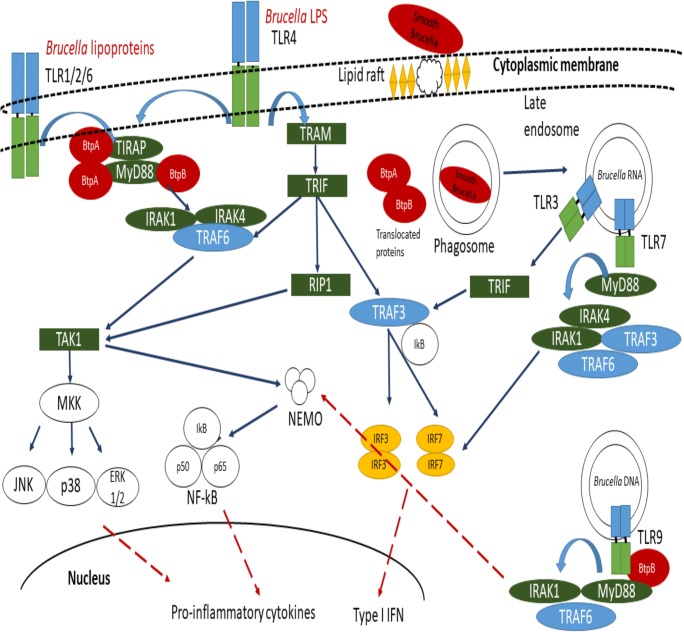
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of Brucella-DC interaction. Lipid rafts-mediated interaction between Brucella and DCs has been reported. TLR2, TLR4, TLR6, TLR3, TLR7, and TLR9 have been involved in Brucella recognition. However, Brucella phagocytosis involved recruitment of TLR2 but not TLR4 at the cytoplasmic membrane, and almost 90% of the ingested Brucella are eliminated by professional phagocytes; the fusion of late endosomes with intracellular receptors such as TLR9 allows type I IFN induction. Once inside, Brucella survive inside phagocytic vacuole and evade late endosomal traffic to reach intracellular niche. Brucella TIR proteins are translocated into cytoplasmic compartment. BtpA impairs DC activation/maturation through MyD88 and TIRAP interaction (Chaudhary et al. 2012; Radhakrishnan et al. 2009; Sengupta et al. 2010), and BtpB binds to various eukaryotic TIR-proteins (TLR2, TLR4, TLR9 MyD88, TIRAP, etc.) (Salcedo et al. 2013). Moreover, Brucella impairs type I Interferon family expression. Blue solid arrows indicate intracellular pathways activated via Brucella recognition by TLRs. Red dashed arrows indicate impaired cytokine pathways by Brucella TIR proteins and subsequent DCs maturation