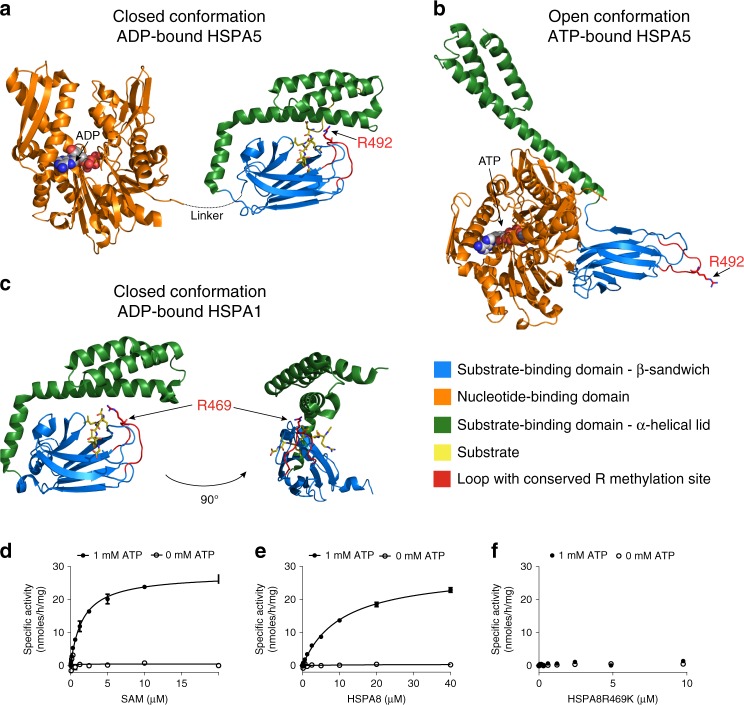
Fig. 4. PRMT7 monomethylation of HSP70 depends on the open (ATP-bound) form of HSP70.
a–c HSP70 structures in closed and open confirmations reveal differential accessibility of the conserved R469-containing sequence (HSPA8) monomethylated by PRMT7. Structures are color coded for domains (orange—ATP binding, blue—substrate binding, and green—lid domains). The HSP70 substrate-binding domain loop containing PRMT7 methylated arginine is colored red. a, b Closely related homolog HSPA5 structures (65% overall sequence identity to HSPA8) were analyzed to investigate the position of the arginine methylation site in the different conformations. In the ADP-bound state, the lid of the substrate-binding domain is closed (PDB 5E85), limiting accessibility of the R492 (analogous to R469 in HSPA8) residue for methylation by PRMT7. In the ATP-bound form (PDB 5E84), the arginine residue is accessible therefore permitting access by the PRMT7 enzyme. c The structure of the more closely HSPA8 related HSPA1A (86% overall sequence identity and 82% sequence identity for aa. 386–646 in the substrate-binding domain, PDB 4PO2) in the closed conformation in which R469 is occluded by the lid subdomain. d–f Kinetic analysis of HSPA8 methylation by PRMT7 in vitro. Kinetic parameters were determined for HSPA8 methylation in the presence and absence of ATP. PRMT7 had no activity in the absence of ATP. d Kinetic analysis at fixed 10 µM HSPA8 (SAM Km = 1.6 ± 0.1 µM). e Kinetic analysis at fixed 20 µM of SAM (HSPA8 Km = 10.6 ± 0.1 µM and kcat of 2.2 ± 0.1 h−1). f HSPA8–R469K mutant is not methylated by PRMT7 in vitro. The results are mean ± SEM of three technical replicates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.