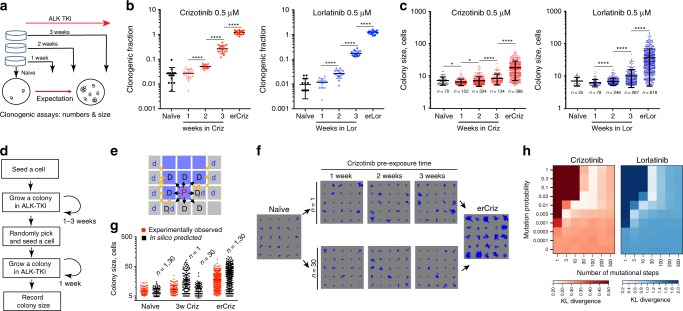
Fig. 3. Graduality of evolution of ALK-TKI resistance.
a Experiment schemata. Therapy-naive cells were pre-cultured in the presence of crizotinib or lorlatinib for 0–3 weeks, then seeded at clonogenic densities in the presence of ALK-TKIs or DMSO control. After 7 days, numbers and sizes of colonies are determined. b Clonogenic survival in the presence of the indicated ALK-TKIs after pre-incubation for indicated times; data are normalized to clonogenic survival in DMSO control. Mean ± SD of 15 replicates (separate wells) is shown. c Distributions of colony sizes in the indicated ALK-TKI. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.0001 of a Mann–Whitney test. Mean ± SD of individual colonies are shown. d Logical flow diagram for the agent-based model, simulating growth during both pre-incubation and the clonogenic assay. e Proliferation space check scheme. Cells are seeded into a 2d lattice that simulates the surface of a culture dish. If space is available (no more than one cell separating the cell from an empty space), a cell can proliferate with a given probability inferred from the experimental data. Blue and gray cells denote occupied and empty spaces respectively. “P” stands for the parent cell, “D” for daughter cell, “d” for displaced cell. Black arrows indicate options for placement of daughter cells, yellow arrows indicate options for displaced cells. Proliferation can occur if a nearby space is either immediately available or separated by a single cell, in which case this cell is pushed into an empty space, with an extra copy of the proliferating cell displacing it. f Example of colony growth simulations, initiated from cells pre-incubated in crizotinib for the indicated time, during the clonogenic growth phase off the assay, contrasting n = 1 vs. n = 30. g Comparing divergence between in silico and experimental data, with n = 1 and n = 30 (epi)mutational steps. Mean ± SD of individual experimental and simulated colonies are shown. h Kullback–Leibler divergence-based comparison of the experimental data with the outcomes of simulations, covering parameter space for the indicated mutation probabilities and numbers of mutational steps.