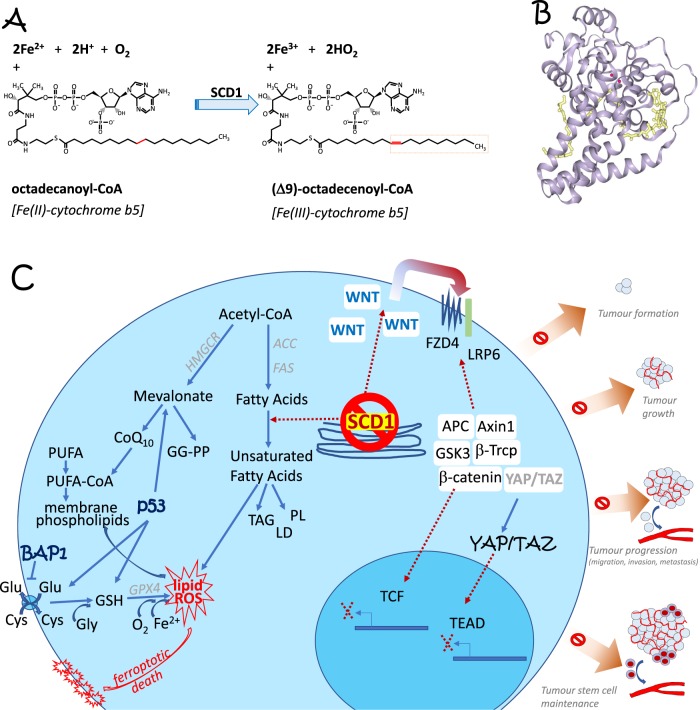
Fig. 1.
a Chemical reactions triggered by Δ9-fatty acyl-CoA desaturase, EC:1.14.19.1, also known as Stearoyl-CoA-desaturases (SCD), introducing a double bond and thus affecting lipid metabolism. b Crystal structure of SCD1. PDB file 4YMK. c Inhibition of SCD1 induces cell death via ferroptosis by impinging on lipid metabolism. Indeed, ferroptosis and SCD1 enzymatic action share a number of lipid mediators, linking the two phenomena. At the same time it acts on cancer stem cells by regulating the autocrine Wnt pathway and the hippo pathway, shown on the intracellular right side, as well as by regulating apoptotic programmed cell death, not shown. Both actions contribute to the regulation of different stages of cancer progression, as highlighted on the far right. See main text for details. ACC acetyl-CoA carboxylase, FAS fatty acids synthase, GGPP geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate, GG-transferase geranylgeranyl transferase, HMGCR HMG CoA-reductase, PL phospholipids, TAG triacylglycerols, YAP Yes associated protein, TAZ transcriptional co-activator with PDZ binding motif (tafazzin), TEAD TEA domain transcription factor 1, GSH glutathione, PE phosphatidylethanolamine, PUFA polyunsaturated fatty acyl chains, GPX4 glutathione peroxidase 4, ROS reactive oxygen species, SCD1 steroyl CoA desaturase 1