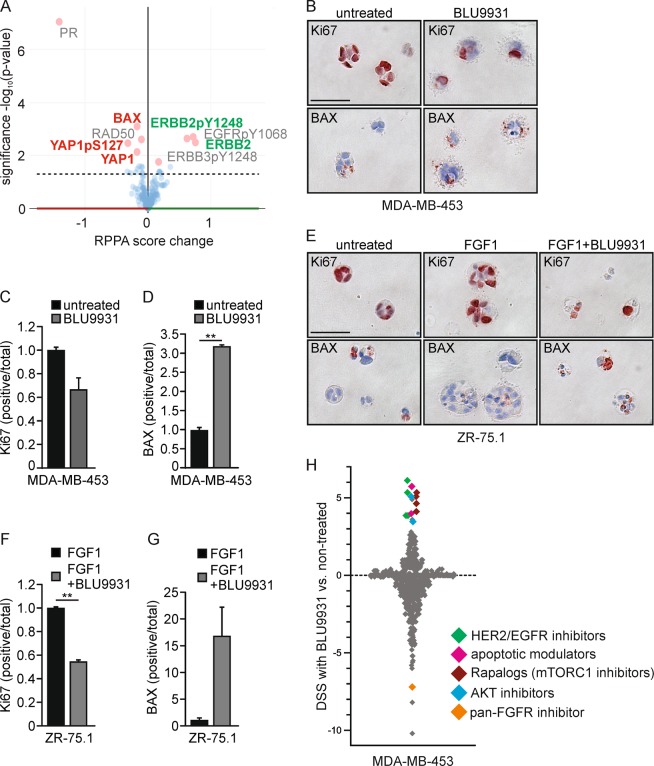
Fig. 7.
FGFR4 confers resistance to apoptotic modulators in comprehensive drug screen. a (Phospho)protein changes in TCGA RPPA data [4] associated with FGFR4 upregulation in breast cancer, visualized using cBioPortal (RPPA score change in breast cancer tumors with and without alterations in FGFR4; (mean FGFR4 altered – mean FGFR4 unaltered) [46, 47]. The most significantly up- and downregulated proteins are highlighted (pink dots); ERBB2, alternative name of HER2; PR, progesterone receptor. b–g Fibrin embedded single-cell suspensions of b–d MDA-MB-453 and e–g ZR-75.1 cells were treated with 100 nm BLU9931 and/or 30 ng/ml FGF1 over a 13–14-day culture, fixed, embedded into paraffin for sectioning, and subjected to immunohistochemistry for Ki67 and BAX expression. Positively stained vs. total number of cells per colony were counted (N = 30, mean ± SD, **P < 0.01). Scale bar 50 µm in b and e. b For comprehensive drug sensitivity testing (N = 1), MDA-MB-453 cells were treated with 527 compounds in five-point dose either alone or in combination with specific FGFR4 inhibitor BLU9931. Dotplot showing the difference in DSS (drug sensitivity score) for cells in treatment combination with BLU9931 (100 nm) versus single agent treatments. Negative values are compounds inducing larger decreases in viability as single agents; positive scores indicate compounds yielding larger decreases in viability in the presence of BLU9931. Colors demarcate compounds with similar class