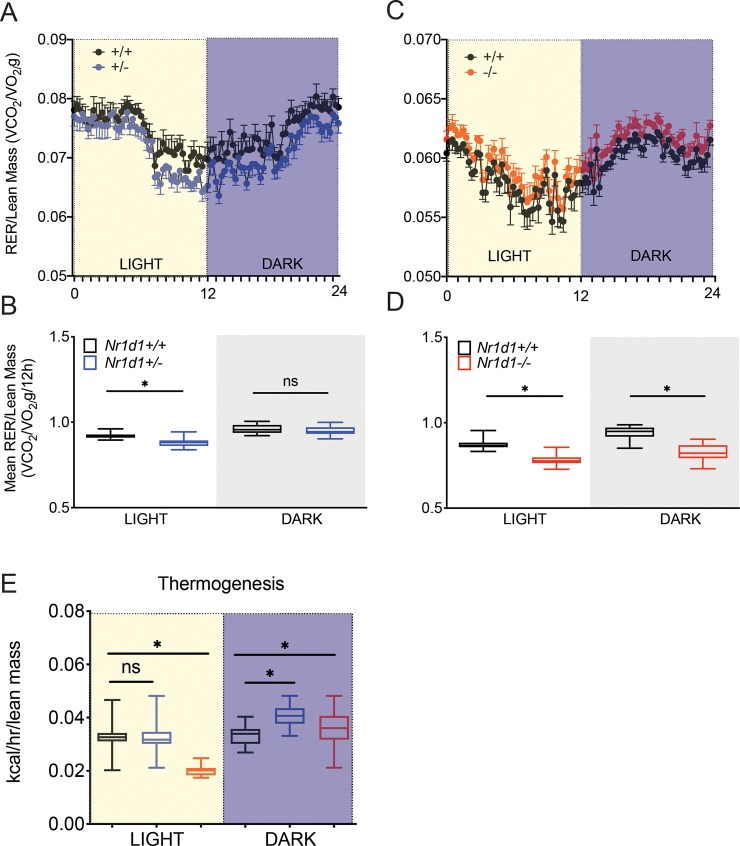
Fig 4. Reduced Nr1d1 expression modulates diurnal fatty acid utilization.
(a) Metabolic trace showing diurnal changes in the Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER:VO2/VCO2 per unit mass in g) in Nr1d1+/+ and Nr1d1+/- mice (b) Mean RER for each genotype over a 12 h light or dark period (a) (c) 24 hr day/night analysis showing diurnal changes in the RER of Nr1d1+/+ and Nr1d1-/- mice (d) Mean RER for each genotype over the time period shown in (b). All mice were kept on a 12:12 light/dark cycle at room temperature (n = 7). Whole body metabolism and thermogenesis was quantified using a Comprehensive Lab Animal Monitoring System (CLAMS). VO2 and VCO2 and RER were normalized to the lean mass of the animals. *p<0.05 was determined by a student’s t-test where relevant or One-Way ANOVA. Data represented as box and whiskers plot error bars +/- stdev.