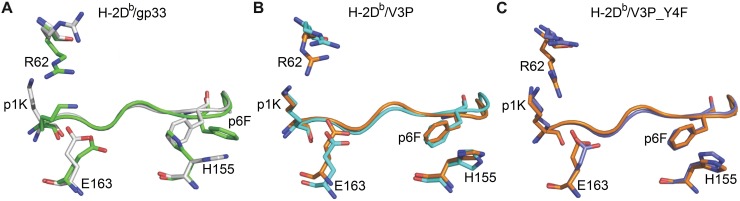
Fig 5. The p3P modification affects the conformations of peptide residues p1K and P6F, as well as H-2Db residues R62, H155 and E163 facilitating TCR recognition.
A. Comparison of H-2Db/gp33 before (in green) and after P14 binding (in white) reveals that the conformation of a very limited amount of pMHC residues is affected (shown as sticks). Following binding to P14, the side chain of peptide residue p1K moves towards the N-terminal part of the peptide binding cleft while the side chain of p6F rotates. As a consequence, conformational changes are observed only for heavy chain residues R62, H155 and E163. B. In contrast to gp33, the introduced p3P modification already positions most peptide and heavy chain residues in optimal conformations, limiting significantly the required movements following binding to P14. pMHC residues before and after binding to P14 are colored orange and cyan. C. Similarly to V3P, the p3P modification in V3P_Y4F results in optimal positioning of all key peptide and heavy chain residues prior to binding to P14. pMHC residues before and after binding to P14 are colored orange and violet.