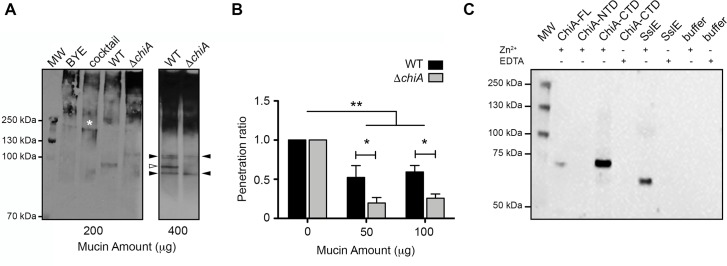
Fig 5. Mucinase activity of ChiA.
(A) Secreted mucinase activity of L. pneumophila wild-type and chiA mutant strains. Left panel: immunoblot of type II porcine stomach mucins (200 μg) incubated with either BYE medium alone (BYE), a cocktail of known mucinase enzymes added to BYE medium (cocktail), or supernatants from BYE cultures of wild-type 130b (WT) or chiA mutant NU318 (ΔchiA). Asterisk highlights a lower-MW (~200 kDa) mucin species generated by the cocktail that is not present in the supernatant samples. Right panel: immunoblot of type II porcine stomach mucins (400 μg) incubated with either supernatants from BYE cultures of wild-type 130b (WT) or chiA mutant NU318 (ΔchiA). White arrow highlights ChiA-dependent mucin fragment (~95 kDa) and black arrows highlight non-ChiA-dependent mucin fragments (~100 and ~90 kDa). The data presented are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Mucin penetration assay of L. pneumophila wild-type (WT) and chiA mutant (ΔchiA) strains applied to the upper chamber of 3.0 μm transwell coated with type II mucin extract. Bacteria that penetrated the transwell were collected from the lower chamber and plated for CFU. Penetration ratio represents CFU in lower chamber 50 or 100 μg mucin / CFU in lower chamber 0 μg mucin. N = 3 experimental replicates. Statistical analysis was done using Two-way ANOVA with Boneferri post-hoc test. Error bars represent standard deviation. *P = <0.05, **P = <0.01. (C) Immunoblot of type II porcine stomach mucin extract incubated with ChiA-FL, subdomains (NTD, CTD), SslE or buffer alone, +/- EDTA, detected with MUC5AC antibody. The bands at ~70 kDa and ~60 kDa correspond to ChiA and SslE processed MUC5AC fragments, respectively.