FIGURE 6.
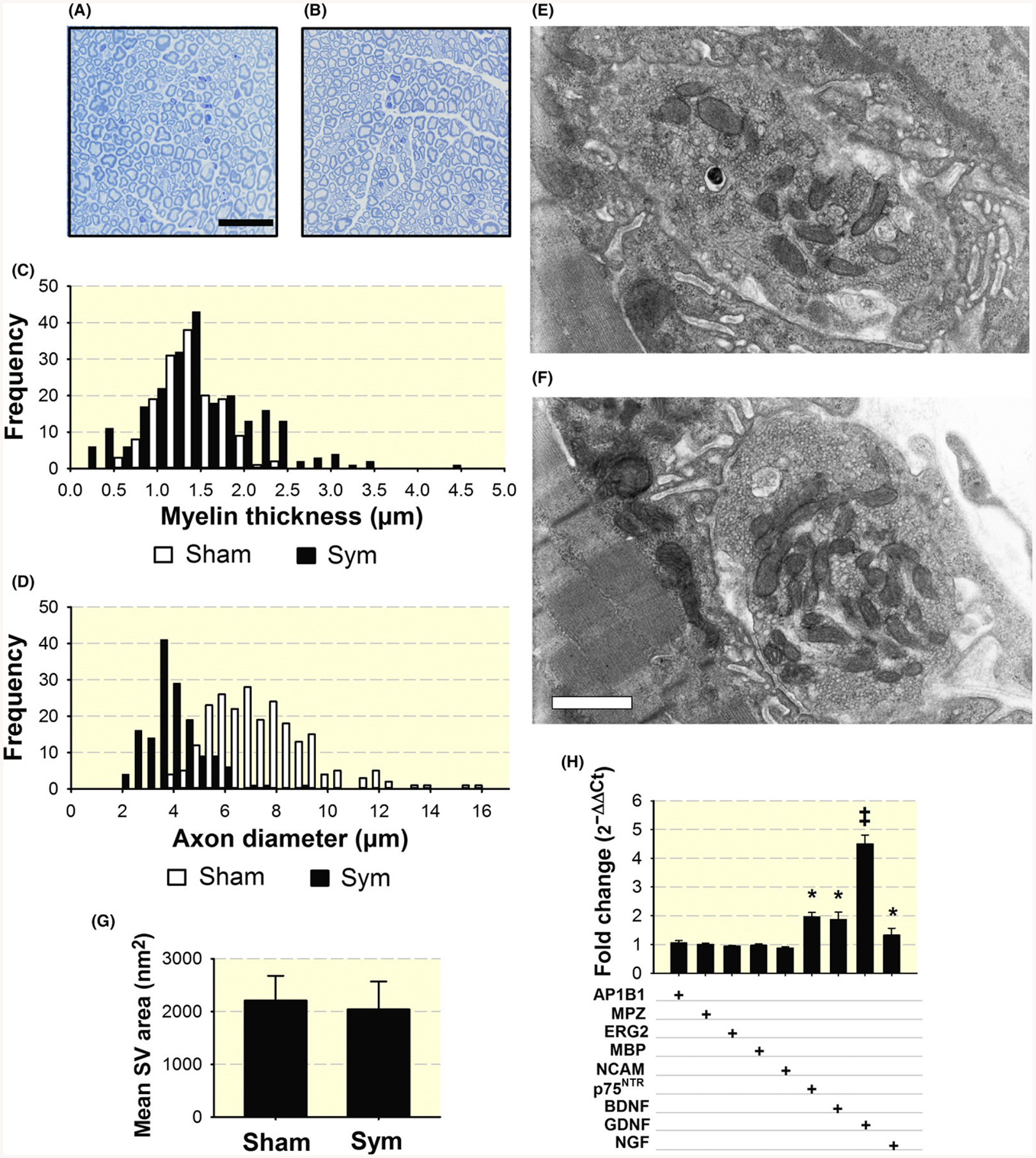
Increased variability in myelin thickness and decrease axonal diameter with SNS ablation and increased expression of nerve neurotrophin and trophic factor genes in the sciatic-tibio-peroneal nerve after sympathectomy. Representative toluidine-blue staining of myelin in the peroneal nerve from sham- (A) and sympathetic-denervated mice (B). Calibration bar = 25 μm. Quantification of myelin thickness (n = 251 and 233 axons) (C) and axon diameter (n = 301 and 466 axons) (D) in four nerves from four sham and four symptectomized mice, one nerve per mouse was analysed. Electron microscopy of synaptic vesicles (SV) in axon buttons from three sham (1053 SV in five terminals) (E), and three sympathectomized (1042 SV in five terminals) mice (F). Calibration bar = 500 nm. Quantification of mean synaptic vesicle (SV) area (G). qPCR analysis of neurotrophins and trophic factor p75NTR receptor, BDNF, and GDNF mRNAs and Schwann cell reprogramming transcripts, adaptor related protein complex 1 beta 1subunit (AP1B1), Myelin protein zero (MPZ), ERG2/Krox20, myelin basic protein (MBP), and neural-cell adhesion molecule, (NCAM). Values, expressed as fold change of sympathectomized compared to sham mice, are means of three nerves from either sham or sympathectomized mice, each studied in triplicate (H). *P < 0.05 and ‡P < 0.001
