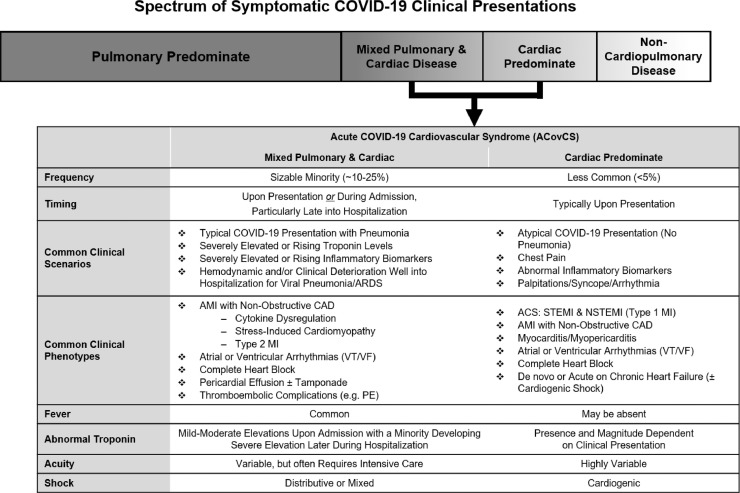
Fig. 1.
Spectrum of symptomatic coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) clinical presentations. Spectrum of pulmonary, cardiac and noncardiopulmonary disease for hospitalized patients with the acute COVID-19 cardiovascular syndrome (ACovCS). Notably asymptomatic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection may represent that greatest prevalence of infected patients; however, the majority of symptomatic patients have respiratory symptoms without cardiac involvement. Predominate cardiac syndromes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 represent a less common clinical phenotype while patients with mixed pulmonary and cardiac disease represent a phenotypic overlap with multiorgan injury that occurs in a sizable minority of hospitalized patients. ACovCS encompasses cardiac manifestations and myocardial injury for both cardiac predominate and mixed disease. Noncardiopulmonary predominate disease represents a variety of other presentations such as altered mental status (neurologic), isolated deep vein thrombosis (hypercoagulable), diarrhea (gastrointestinal), and rash (dermatologic). ACS, acute coronary syndrome; AMI, acute myocardial injury; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; CAD, coronary artery disease; COVID-19, coronavirus disease-2019; MI, myocardial infarction; NSTEMI, non–ST-elevation myocardial infarction; PE, pulmonary embolism; STEMI, ST-elevation myocardial infarction; VF, ventricular fibrillation; VT, ventricular tachycardia.