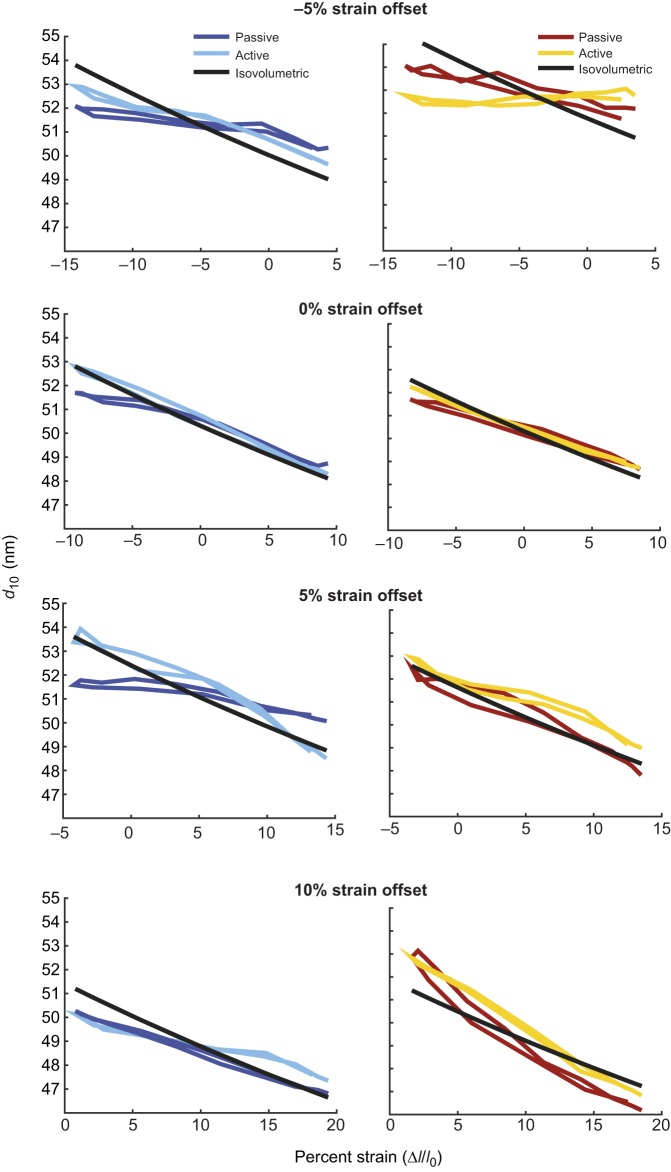
Fig. 6.
Lattice loops (d10 versus strain) during work loops with mean offsets of −5%, +0%, +5%, +10% operating length (OL) (top to bottom) for muscles 178 and 179 (left and right). The lattice spacing change in passive conditions is due to the axial strain of the myofilament lattice during compression and tension. Under activated conditions, the spacing patterns change in part due to the action of active myosin binding and activation of other proteins, such as titin. Sample size, n, for strain conditions (–5,0,5,10) were passive muscle 178, n=5 for all strains; active muscle 178, n=(5,6,5,5); passive and active muscle 179, n=(5,8,8,5). See Fig. 7 for variation in d10.