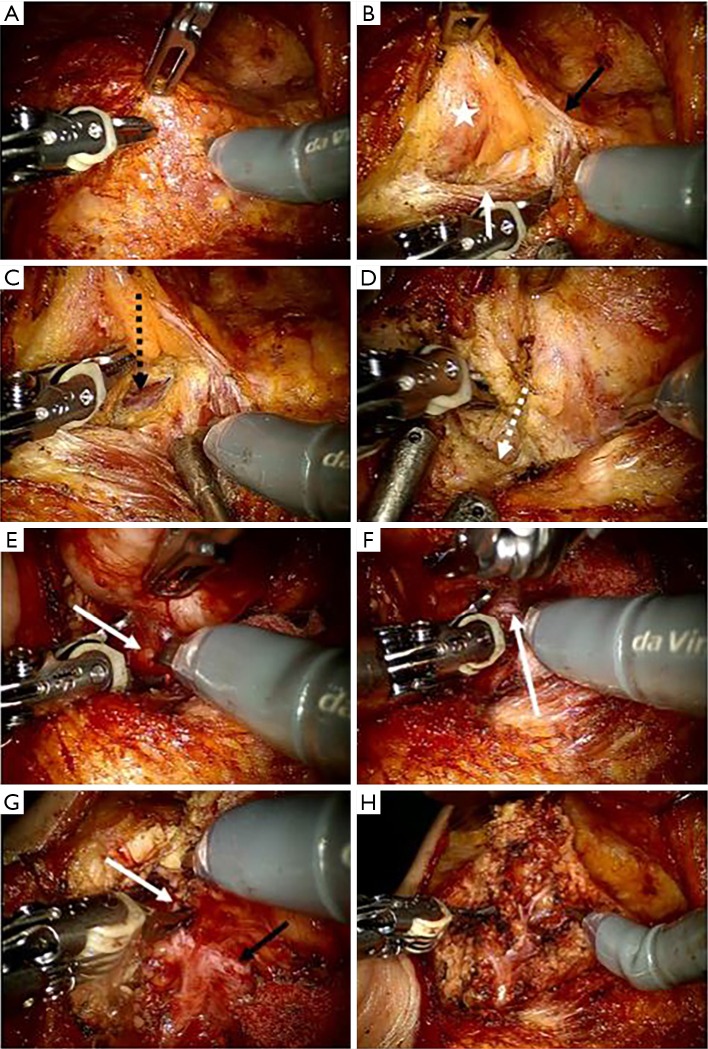
Figure 2.
Surgical procedure of robotic parotidectomy on the right side in patients with parotid tumor. (A) Maryland dissector was equipped on left robotic arm and scissor was equipped on right robotic arm. And prograsper forcep was installed on the third robotic arm; (B) the dissection of parotid gland (asterix) was started from the anterior border (white arrow) of sternocleidomastoid muscle (black arrow: greater auricular nerve); (C) posterior belly (black dotted arrow) of the digastric muscle (black arrow) was identified below the inferior part of the parotid gland; (D) a preauricular incision was dissected along the auricular cartilage (white dotted arrow) to find the tragal pointer; (E) the facial nerve main truck (white arrow) was identified at 1 cm below the tragal pointer and at 1cm superior the posterior belly of digastric muscle; (F) dissection was performed along the facial nerve using tunnel technique (white arrow: facial nerve); (G) the superior pole of the parotid gland was dissected along the upper branch (white arrow) of the facial nerve (black arrow: lower branch); (H) after completing the parotidectomy, all branches of the facial nerve were preserved.