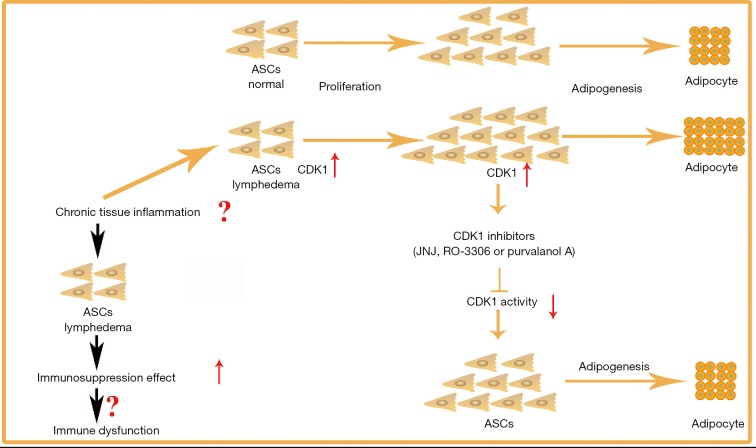
Figure 9.
Schematic difference of lymphedema-associated ASCs and ASCs from normal tissue of the same patients. Lymphedema-associated ASCs had more rapid proliferation and adipogenic differentiation capacity than ASC from normal tissue. CDK1 is a key driver that may prompt these cells toward proliferation and adipogenic differentiation could explain the adipose tissue accumulation widely observed in secondary lymphedema. ASCs from lymphedema adipose tissues showed immunomodulation dysfunction which may play an important role in the pathogenesis of lymphedema. ASCs, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; CDK1, cyclin-dependent kinase 1.