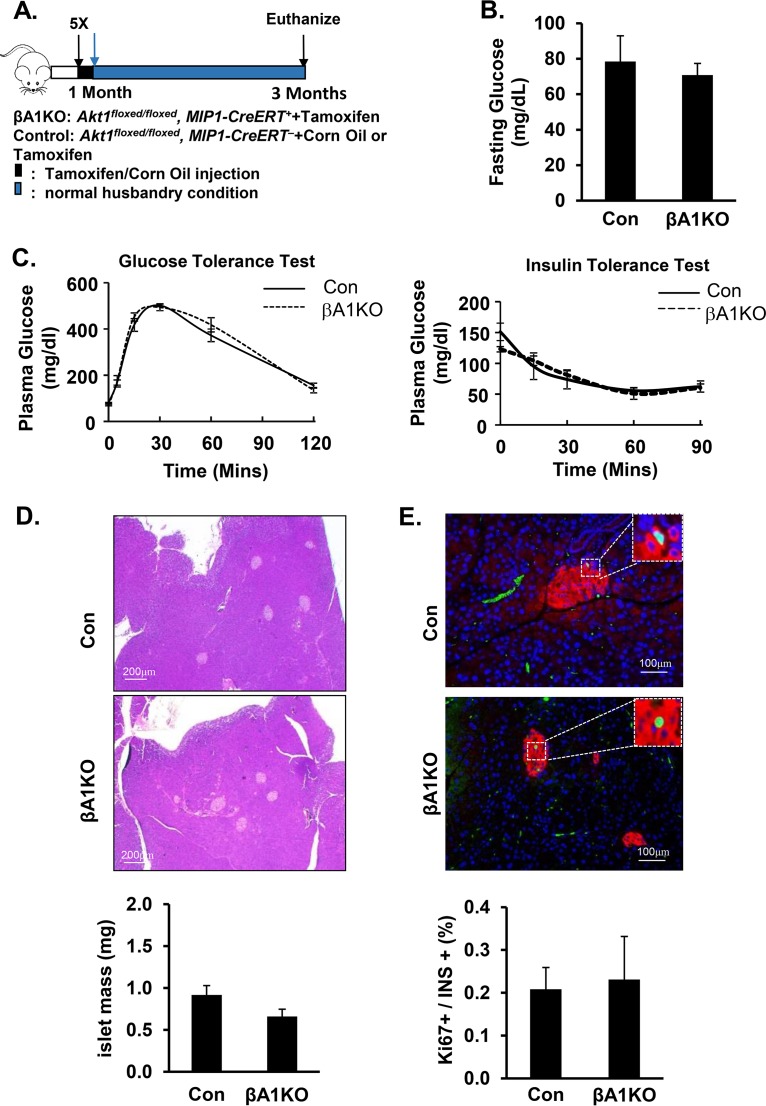
FIG 1.
AKT1 deficiency does not impact the physiological maintenance of pancreatic β cells. (A) Illustration of the protocol for inducing Akt1 deletion with tamoxifen in pancreatic β cells. (B) Plasma glucose determined in control versus βA1KO mice after 16 h of fasting (n = 14 for control; n = 5 for βA1KO). (C, left) Glucose tolerance test (ipGTT) performed with intraperitoneal injection of 2 mg/kg (body weight) glucose after 16 h of fasting. (C, right) Insulin tolerance test (ipITT) performed with 0.5U/g (body weight) insulin intraperitoneal injection after 5 h of fasting (n = 9 for control, n = 4 for βA1KO). (D) The top two panels are representative H&E staining images of control (Con) and βA1KO mouse pancreas. The bottom panel shows islet mass of control (Con) and βA1KO mice (n = 4 to 5/group). (E) The top two panels are representative images of Ki67/insulin/4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-stained pancreas sections from the indicated mouse groups (red, insulin; green, Ki67; blue, DAPI). The bottom panel shows the quantification of the percentage of Ki67-positive β cells versus total insulin-positive β cells in the indicated groups. Three sections (240 μm apart) were analyzed for each mouse (n = 5).