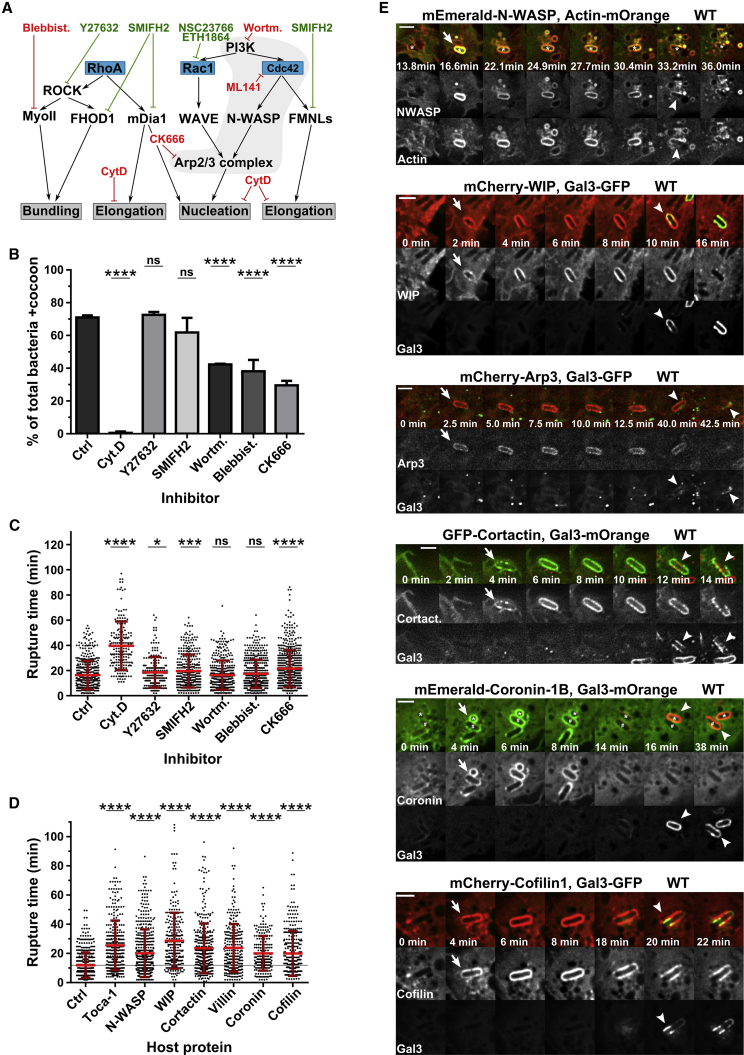
Figure 3.
Host Actin Regulators Are Involved in Actin Cocoon Assembly and Are Recruited to Shigella’s BCV before Vacuolar Escape
(A) Scheme of host proteins inhibited by compounds of the inhibitor screen (B and C; see also Figures 4F, S5F, S6C, and S6D). Blue box, Rho GTPases; black, ABPs and their regulators; gray box, effect on F-actin; red, inhibits cocoon assembly; green, no effect on initial cocoon assembly. CytD, cytochalasin D, an actin polymerization inhibitor; SMIFH2, formin inhibitor; Y27632, ROCK inhibitor; Blebbist, blebbistatin, a myosin II inhibitor; Wortm, wortmannin, a PI3K inhibitor; CK666, Arp2/3 inhibitor; NSC23766, RAC1 GEF inhibitor; ETH1864, RAC1 inhibitor; ML141, CDC42 inhibitor.
(B and C) Quantitative analysis of inhibitor screens identifies host proteins and signaling pathways involved in cocoon assembly (B) and cytosolic access (C) (n = 2,912 total invaders, on average 416 per condition; Ctrl, DMSO control).
(D) Overexpression of seven selected host ABPs that interfere with the timing of vacuolar rupture with galectin-3-mOrange (Ctrl, control; n = 2,641, on average 330 per condition).
(E) Recruitment of host ABPs to Shigella’s BCV before cytosolic escape. Time lapses of HeLa cells expressing fluorescently tagged host proteins and actin or galectin-3 (Gal3; scale bars: 3 μm). Arrow, recruitment to BCV; arrowhead, vacuolar rupture.
Indicated are mean values ± SD of at least 3 independent experiments. Student’s t test with p < 0.05 as significant compared with controls: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ns, not significant.