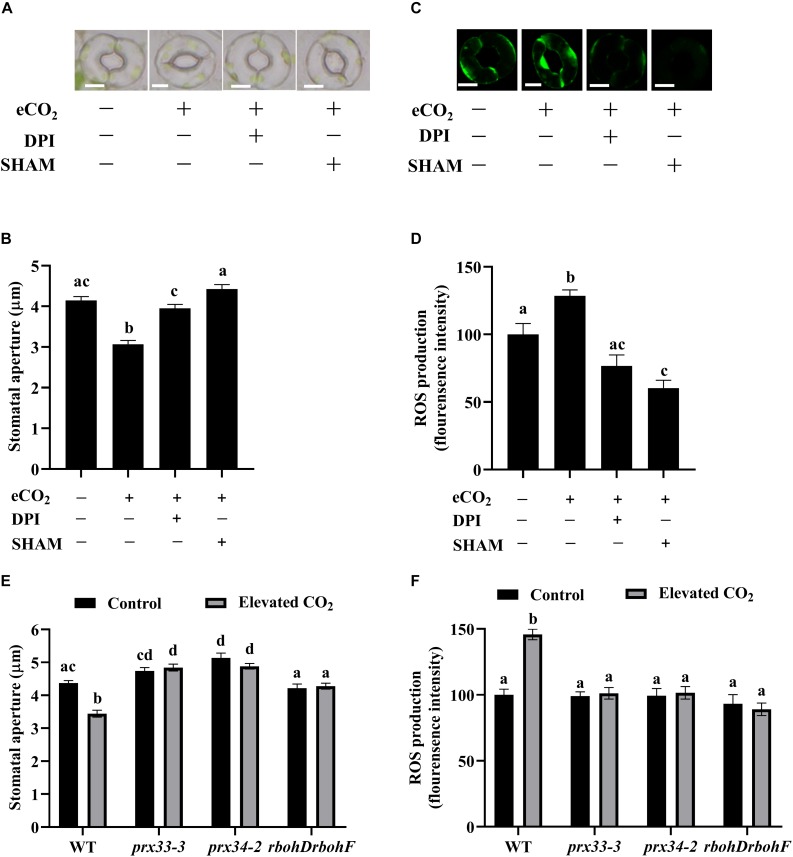
FIGURE 1.
Cell wall peroxidases and NADPH oxidases are required for elevated CO2-induced stomatal closure. (A) eCO2-induced stomatal closure is inhibited by ROS inhibitors DPI and SHAM. Representative images showing guard cells of WT: after 2.5 h light-incubation, epidermal peels of WT plants were treated with 800 ppm CO2 for another 2.5 h before photos taken. 20 μM DPI or 2 mM SHAM added before CO2 treatment for 30 min. Scale bar, 5 μm. (B) Quantitative stomatal aperture from (A). (C) Representative images showing H2DCF-DA fluorescence of WT guard cells under control (CO2-free air) and elevated (800 ppm) CO2 with or without ROS inhibitors DPI or SHAM treatment. Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) Quantitative ROS production from (C). eCO2 stimulates an increase of H2DCF-DA fluorescence in guard cells that is blocked in the presence of DPI/SHAM. (E) eCO2-induced stomatal closure is disrupted in prx33-3, prx34-2, and rbohDrbohF mutants. (F) eCO2-induced ROS production in guard cells is compromised in prx33-3, prx34-2, and rbohDrbohF mutants during stomatal closure. In (B) (n = 120), (D) (n = 50), (E) (n = 80), and (F) (n = 60), values are means ± s.e. All experiments were repeated at least three times. Different letters represent statistically significant differences at P < 0.05 based on a Tukey’s test.