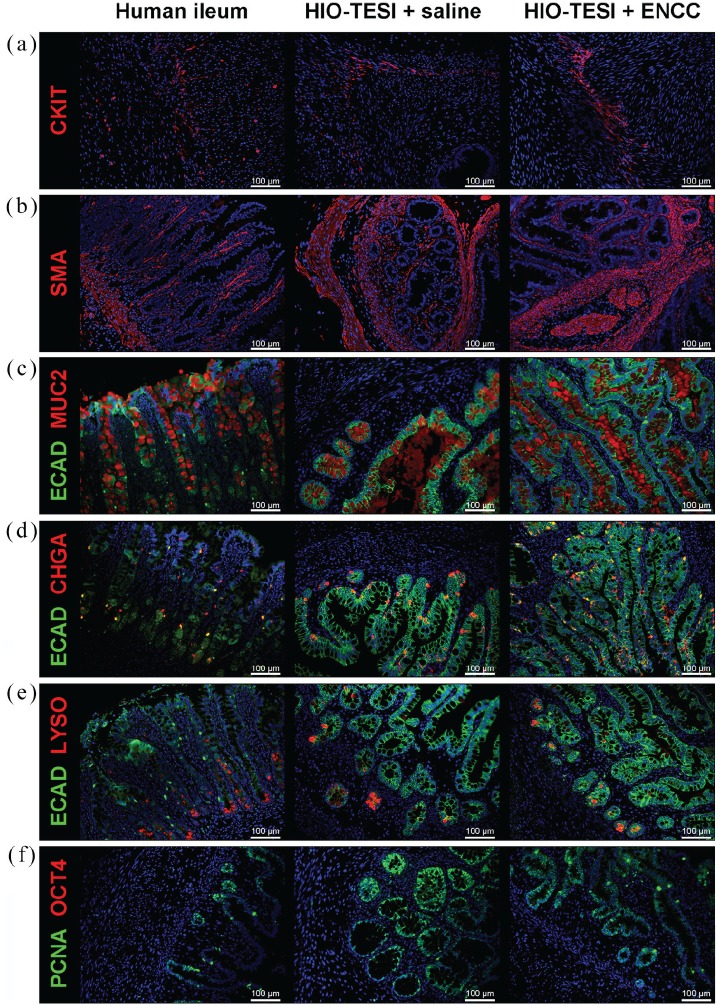
Figure 5.
Human intestinal organoid–derived aganglionic tissue-engineered small intestine. Intestinal pacemaker cells ICC (CKIT+, a) and smooth muscle cells (SMA+, b) are identified in HIO-TESI with or without ENCC injection. Different cell types of epithelial lineage (ECAD+), including goblet cells (MUC2+, c), enteroendocrine cells (CHGA+, d), and Paneth cells (LYSO+, e), are present in HIO-TESI + saline and HIO-TESI + ENCC cysts. PCNA+ proliferating cells are located in the crypts and villus regions in the TESI (f). No OCT4 teratoma marker is observed (f). DAPI stained cell nuclei in all images. CKIT: ICC-selective receptor tyrosine kinase; SMA: alpha-smooth muscle actin; ECAD: E-cadherin; MUC2: mucin 2; CHGA: chromagranin A; LYSO: lysozyme; CALB: calbindin; CHAT: choline acetyltransferase; NOS1: neuronal nitric oxide synthase; 5-HT: serotonin/5-hydroxytryptamine; PGP9.5: protein gene product 9.5; PCNA: proliferating cell nuclear antigen; OCT4: octamer-binding transcription factor 4; hPSC: human pluripotent stem cell; ICC: interstitial cells of Cajal; HIO-TESI: tissue-engineered small intestine derived from human intestinal organoids.