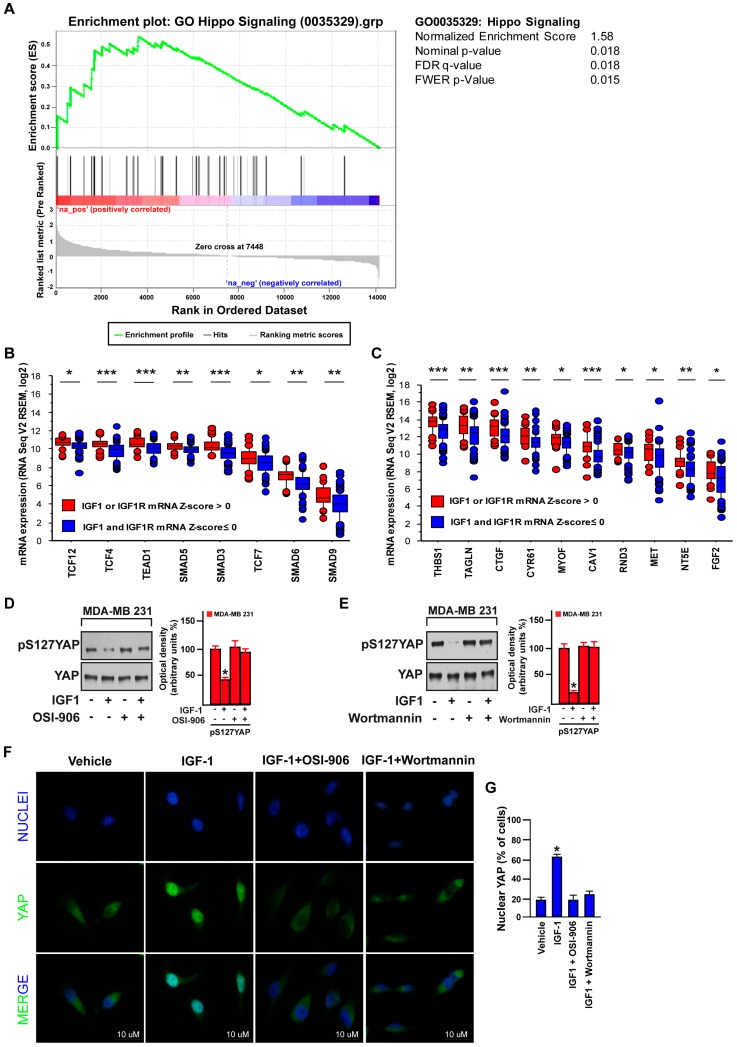
Figure 4.
IGF-1 promotes the nuclear accumulation of yes-associated protein/yes-related protein (YAP). (A) The Gene Set Enrichment analysis (GSEA) for “Hippo signaling” in Gene Ontology (GO) comparing high and low IGF1/IGF1R groups in TNBC. (B) Expression of YAP/TAZ-associated transcriptional factor genes in the TNBC cohort of the TCGA dataset comparing high and low IGF1/IGF1R groups. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. (C) Expression of YAP/TAZ target genes in the TNBC cohort of the TCGA dataset comparing high and low IGF1/IGF1R groups. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Immunoblots showing the phosphorylation of YAP in MDA-MB 231 cells treated for 30 min with IGF-1 (50 ng/mL) alone or in combination with the IGF-1R inhibitor OSI-906 (1 µM). (D) or the PI3K inhibitor Wortmannin (1 µM) (E). Side panels show densitometric analysis of the immunoblots normalized to the loading control. (F) Immunofluorescence staining of YAP (green) and DAPI (blue) in MDA-MB 231 cells treated for 30 min with IGF-1 (50 ng/mL) alone or in combination with the IGF-1R inhibitor OSI-906 (1 µM) or the PI3K inhibitor Wortmannin (1 µM). Scale bars, 10 µm. (G) Percentage of MDA-MB 231 cells with nuclear YAP. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Error bars represent mean ± SD. * indicates p < 0.05 for cells treated with vehicle versus treatments.