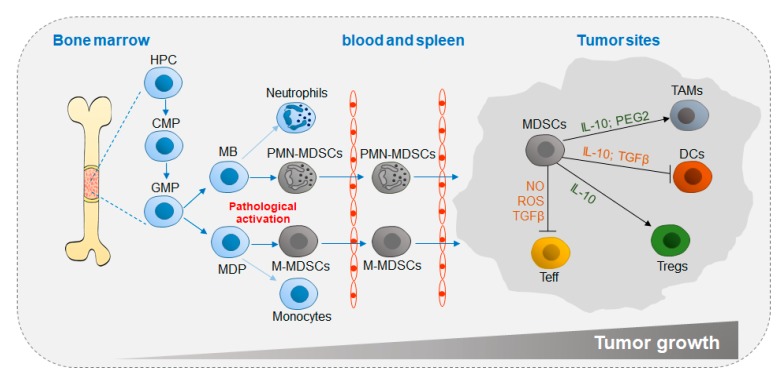
Figure 1.
Differentiation and accumulation of MDSCs in the TME. Chronic inflammatory factors, such as G-CSF and GM-CSF, are secreted to promote myelopoiesis. Instead of neutrophils and monocytes, MDSCs originate from common myeloid progenitor cells under pathological conditions and migrate through the circulatory system to the tumor site, in which MDSCs exert immunosuppressive functions by generating anti-inflammatory cytokines. TME, tumor microenvironment; HPC, hemopoietic progenitor cell; CMP, common myeloid progenitor; GMP, granulocyte-macrophage progenitor; MB, myeloblast; MDP, monocyte/macrophage and dendritic cell precursor; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; DC, dendritic cell; Treg, regulatory T cell; Teff, effector T cell; IL-10, interleukin-10; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; TGFβ, transforming growth factor beta; IFNγ, interferon gamma; NO, nitric oxide; ROS, reactive oxygen species.