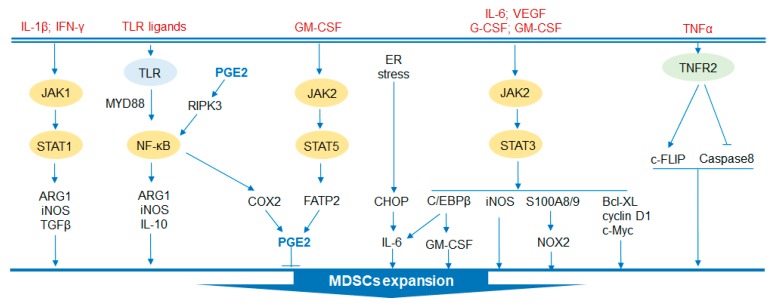
Figure 2.
Regulatory signaling pathways in MDSC development and functions. Several signaling pathways are involved in the expansion of MDSCs. JAK2/STAT3 signaling enhances the immunosuppressive function of MDSCs by activating S100A8/9/NOX2 and iNOS to promote the generation of ROS. The pathway also protects MDSCs from apoptosis by expressing Bcl-XL, cyclin D1 and c-Myc. Moreover, this pathway promotes the activation of C/EBPβ. In addition, JAK1/STAT1 signaling accelerates the expansion of MDSCs by inducing the expression of ARG1, iNOS and TGFβ. Similarly, the proliferation of MDSCs can be accelerated by increased production of PGE2 through JAK2/STAT5 signaling. Furthermore, the TLR family also regulates the activation of MDSCs by activating NK-κB to generate protumor cytokines. CHOP is activated by ER stress and is involved in the activation of MDSCs. Additionally, TNFα-TNFR2 signaling is crucial to MDSC expansion by c-FLIP upregulation and caspase 8 reduction. JAK, Janus activated kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; ARG1, arginase 1; TLR, toll-like receptor; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; RIPK3, receptor-interacting protein kinase 3; COX2, cyclooxygenase-2; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor; G-CSF, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; NOX2, NADPH oxidase 2; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; FATP2, fatty acid transport protein 2; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; Bcl-XL, B-cell lymphoma-XL; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; TNFR2, tumor necrosis factor receptor 2; c-FLIP, cellular FLICE (FADD-like IL1β-converting enzyme)-inhibitory protein.