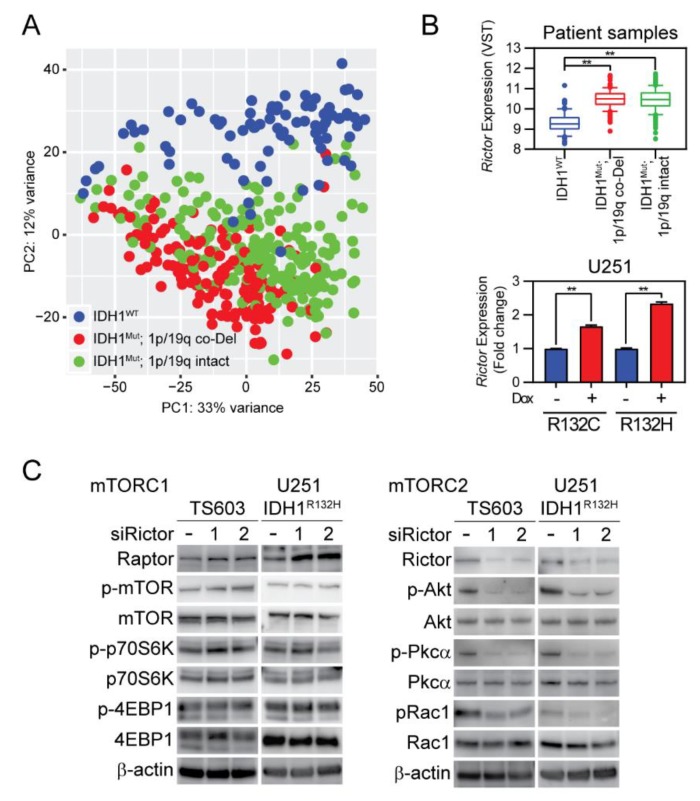
Figure 4.
Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mammalian target of rapamycin (Rictor)/Rac1 enhanced mTORC2 pathway in IDH1-mutated cells. (A) The principal component analysis showed a distinct transcriptomic pattern of expression in IDH-mutant gliomas. Whole transcriptomic profiling data from 367 IDH-mutant and 85 IDH-WT patient samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) were used in the analysis. Diffusive astrocytoma (1p/19q intact) and oligodendroglioma (1p/19q co-deleted) were specified in green and red, respectively. (B) Enhanced Rictor expression in IDH1-mutated tumors and cells. Rictor expression from TCGA data (upper panel), IDH1WT: 9.30 ± 0.06, n = 85; IDH1mut 1p/19q intact: 10.5 ± 0.04, n = 215; IDH1mut 1p/19q Co-deletion (CoDel): 10.5 ± 0.04, n = 151. VST: variance-stabilizing transformation; Rictor expression as measured by quantitative PCR analysis in U251 cells (lower panel). R132C: without doxycycline (-DOX), 1.00 ± 0.002, n = 3; +DOX, 1.66 ± 0.03, n = 3. R132H: -DOX, 1.00 ± 0.02; +DOX, 2.34 ± 0.03, n = 3. t-test, ** p < 0.01. Diffusive astrocytoma (1p/19q intact) and oligodendroglioma (1p/19q co-deleted) were specified in green and red, respectively. (C) Western blot analysis showed the effect of RNA interference targeting Rictor. Suppressing Rictor expression minimally influenced mTORC1 downstream p70S6K or 4EBP1, whereas mTORC2 downstream Akt, Pkcα, and Rac1 phosphorylation were reduced. This experiment was repeated three times.