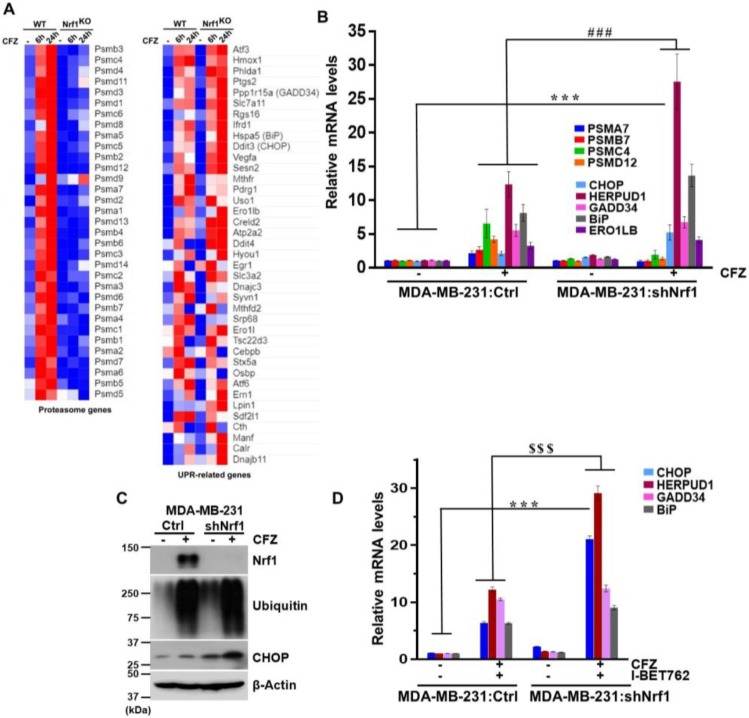
Figure 4.
Depletion of Nrf1 leads to exacerbation of UPR under proteotoxic stress conditions. (A) Wild-type (WT) and Nrf1 knock-out (KO) NIH-3T3 cells were treated or not with 200 nM CFZ for 6 or 24 h and the samples from 3 biological replicates were analyzed by RNA-seq. Heat maps for changes in proteasome and UPR-related genes are shown and were generated using the Morpheus software (https://software.broadinstitute.org/morpheus/). A relative color scheme is employed where the minimum and maximum values in each row were used to convert values to color. The relative levels are indicated by varying color intensities of blue (low) and red (high); (B) MDA-MB-231 cells expressing a vector (Ctrl) or shNrf1 were treated with CFZ (200 nM) for 8 h and RNA was extracted and analyzed for indicated proteasome and UPR-related mRNA levels using quantitative RT-PCR with gene specific primers. The levels of 18s rRNA were used for normalization. Error bars denote SD (n = 3); (C) From cells treated as above, whole cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for Nrf1, ubiquitin, and CHOP levels. β-Actin was used as loading control; (D) The MDA-MB-231:Ctrl and MDA-MB-231:shNrf1 cells were cotreated with CFZ (200 nM) and I-BET762 (10 µM) for 8 h and total RNA was isolated and analyzed for mRNA levels of UPR target genes using quantitative RT-PCR. The 18s rRNA levels were used for normalization. Error bars denote SD (n = 3). ***, p < 0.0005 as compared with the controls; ###, p < 0.0005 as compared with the CFZ-treated group. $$$, p < 0.0005 as compared with the CFZ + I-BET762 treated group.