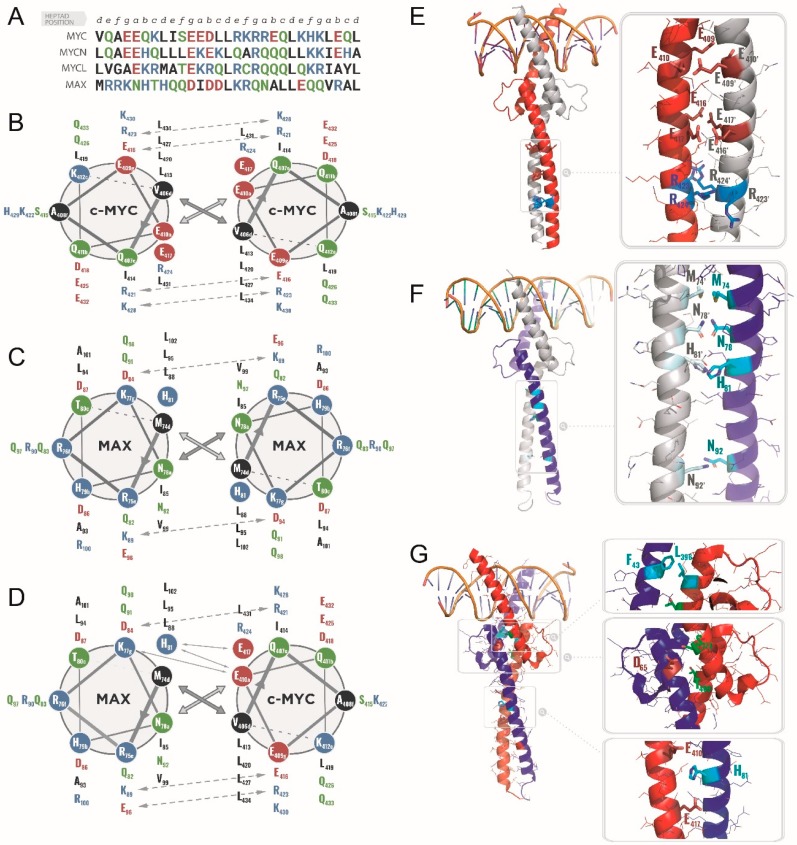
Figure 4.
(A). Sequence alignment of the LZ of MYC, MYCL, MYCN, and MAX with heptad-repeat numbering. (B–D). Helical-wheel representation for the interfacial interactions in the LZ domains from MYC and MAX putative dimeric complexes: The MAX/MAX homodimer is shown in panel (B), the putative MYC/MYC homodimer in panel (C) and the MYC/MAX heterodimer in panel (D). The favorable and unfavorable inter-molecular contacts are displayed as arrows. The amino acids are colored blue for positively charge residues, red for negatively charged residues, green for polar residues and black for the remainder apolar residues. Adapted from Lavigne et al. 1995 [40]. (E,F) Molecular models of the tridimensional structure of a putative DNA-bound MYC homodimer (E), of the crystal structure of the MAX homodimer (PDB 1AN2, F) and of the MYC/MAX heterodimer (PDB 1NKP, G). (E). Homology model of a putative MYC/MYC homodimer (the sequence of MYC was superimposed on the MAX structure from 1NKP.pdb) with one monomer shown in red and the other in grey. The inset highlights the highly unfavorable electrostatic repulsions between the clusters of negatively charged interfacial residues Glu409-Glu410, Glu416-Glu417, and Arg423-Arg424 and their respective counterpart on the other monomer are shown with stick representation. Negatively charged residues are shown in red, positively charged residues in blue. F. Crystal structure of the MAX homodimer; the inset evidences the polar residues at interfacial a and d positions, namely Met74, Asn78, His81, Asn92 (shown in cyan stick representation). (G). Crystal structure of the MYC/MAX heterodimer with close up views on the MYC-Leu396/MAX-Phe43 interaction within the HLH (top inset); the Ser373 and Thr400 phosphorylation sites are shown in green (note: Asp65 from MAX, directly facing MYC-Ser373, is shown in red—middle inset); the interfacial, buried interaction between MAX-His81 (cyan) and MYC-Glu410 and Glu417 (in red) is shown (bottom inset).