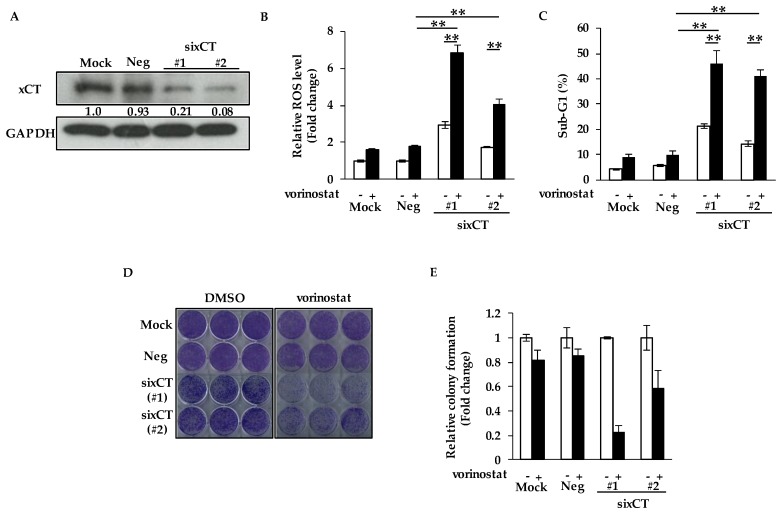
Figure 2.
Genetic ablation of xCT increases sensitivity to vorinostat with reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation. (A) The knockdown efficacies of sixCT were validated by Western blotting in MDA-MB-231 cells. The gray value of bands was assessed by imageJ. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of ROS levels in cells treated with vorinostat after transfection of sixCT or negative control siRNA (siNeg). MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 1.6 μM vorinostat for 48 h following the treatment of each siRNA. The amount of ROS in cells was detected by CM-H2DCFDA using a flow cytometer. The data obtained with DMSO control in siNeg were taken as 1. Columns, means (n = 3); bars, SD. ** p < 0.01. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of cell death after vorinostat treatment with/without transfection of sixCT or siNeg. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 1.6 μM vorinostat for 144 h following the treatment of each siRNA. The percentages of cells in the sub-G1 population were analyzed by flow cytometry. Columns, means (n = 3); bars, SD. ** p < 0.01. (D,E) Colony formation of cells treated with vorinostat after transfection of sixCT or siNeg. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 1.6 μM vorinostat for 144 h following the treatment of each siRNA, and then the media were replaced. After the cells were cultured for 3–7 more days, the colonies were stained with crystal violet. Representative images of colony formation (n = 3) are shown (D). Colony formation was quantified using ImageJ (E). The data obtained with DMSO control for each siRNA were taken as 1. Columns, means (n = 3); bars, SD.