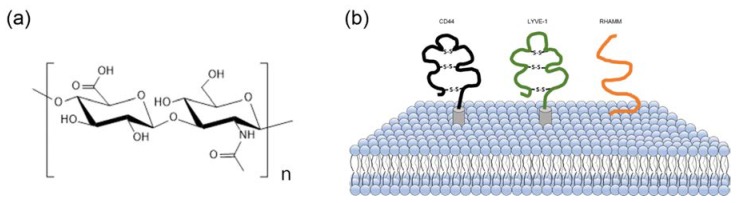
Figure 1.
(a) The structure of hyaluronic acid, composed of alternating units of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, (b) hyaluronic acid receptors in the cell: cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44), lymphatic vessel endocytic receptor (LYVE-1), and the receptor for hyaluronic acid-mediated motility (RHAMM).