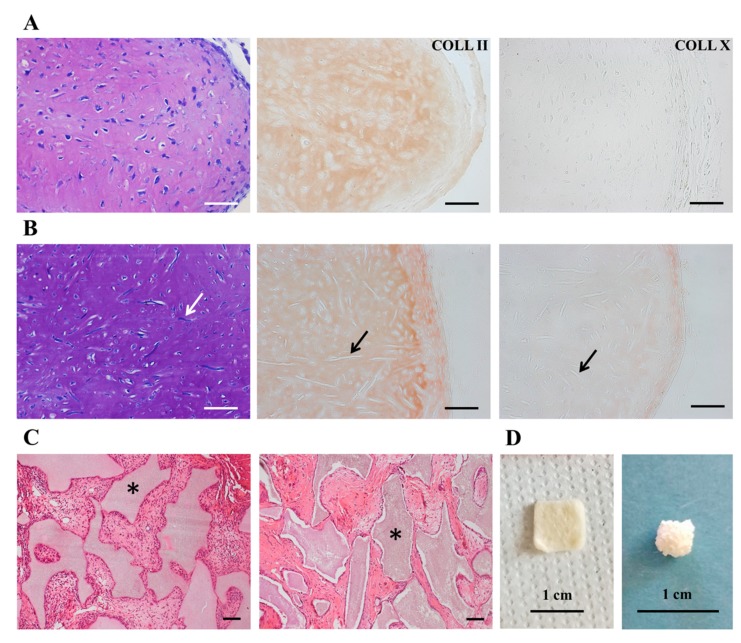
Figure 6.
In vivo ectopic chondrogenesis and osteogenesis assay of CPCs. (A,B) Histological analysis of ectopic cartilage formed in vivo after subcutaneous implantation of CPC-pellets (A) and CPCs-seeded biomaterials (B) in nude mice; from left to right: toluidine blue staining, type II and type X collagen stainings. Arrows point out the remnants of polyglycolic-acid (PGA)-scaffold fibers. (C) Histological analysis by hematoxylin/eosin staining of ectopic tissue formed in vivo after subcutaneous implantation of ACs-FBS (left) or CPCs (right)-seeded osteoinductive scaffolds in nude mice. Asterisks point out the biomaterial. (D) Representative view of selected scaffolds, polyglycolic-acid–hyaluronan (PGA-HA) mat (left) and hydroxyapatite/β-tricalcium phosphate (HA/β-TCP) assembled granules (right). Scale bars correspond to 50 µm (upper panel), 100 µm (middle and bottom panels) and 1 cm.