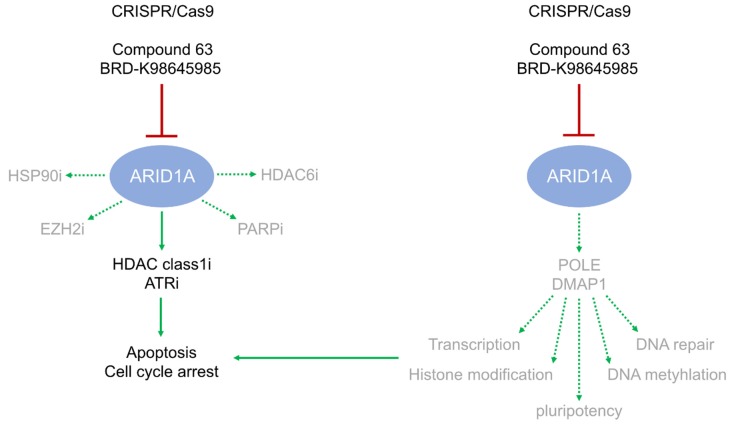
Figure 4.
Illustration of the effects of ARID1A inhibition and molecular functions of ARID1A. Deficiency or pharmacological inhibition of ARID1A sensitizes GCTs cells slightly to HDAC class 1 inhibitor romidepsin and more prominently to ATR inhibition, causing a reduction in viability, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest (left side). On a molecular level, ARID1A normally regulates transcription, DNA repair, DNA methylation, histone modifications and the pluripotency program at least in parts via POLE and DMAP1 (right side). These regulatory cascades diminish upon inhibition of ARID1A, subsequently contributing to the induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Arrow: sensitization/activation; dotted arrow: no sensitization/diminished activation; T-shaped arrow: inhibition/inactivation.