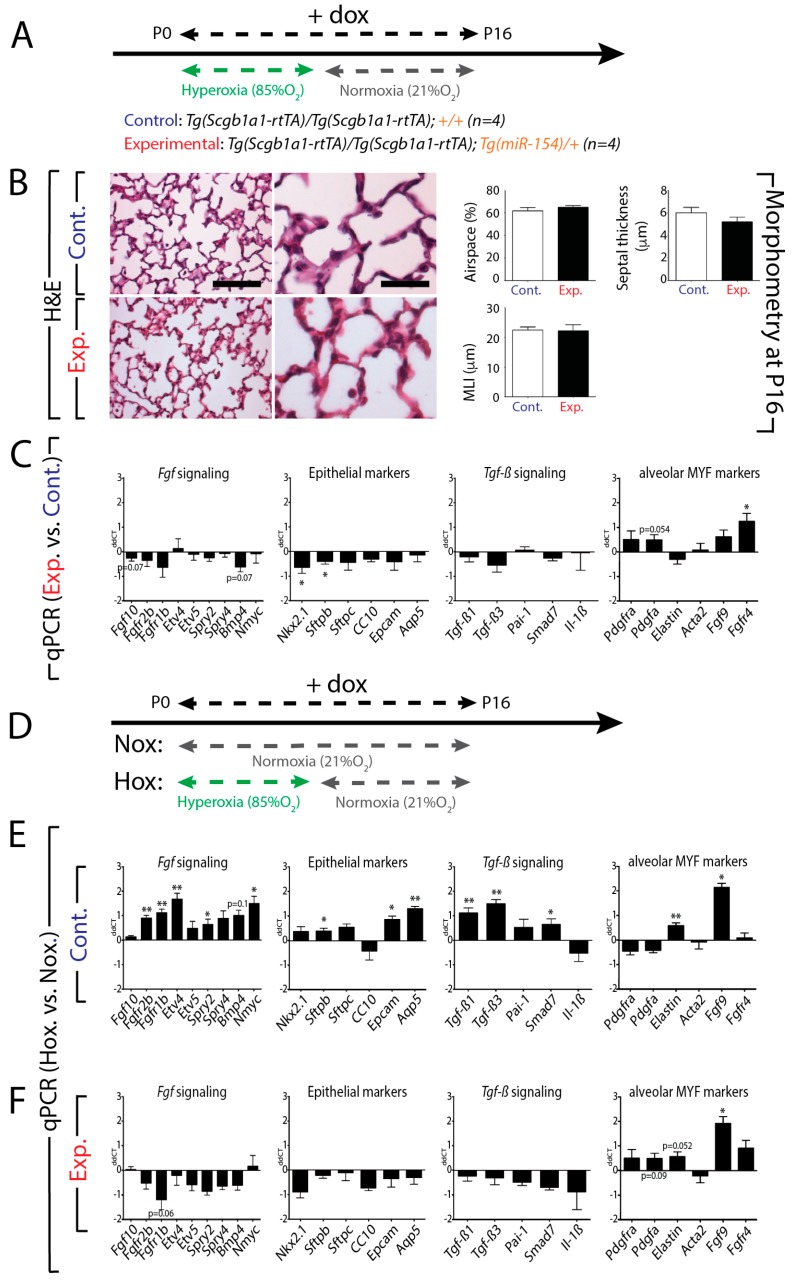
Figure 6.
Hyperoxic lung injury on top of overexpression of miR-154 (double injury) compared to miRNA overexpression only (single injury): A. Model of hyperoxic treatment and doxycycline (Dox) administration in order to activate miR-154 overexpression. B. Alveolar Morphometry reveals no further effect of double injury (hyperoxia and miRNA overexpression) on alveolar parameters compared to single injury (miRNA overexpression only). C. RT-qPCR data show no obvious effect of additional hyperoxic injury on top of miR-154 overexpression for Fgf signaling, Tgf-β signaling and epithelial cell markers. Merely genes connected to alveolar myofibroblast formation and function seem to be affected by additional hyperoxic exposure. (HOX and NOX each n = 4). D. Model of either normoxia or hyperoxia treatment in control and experimental mice. E. RT-qPCR analysis in the control mice reveals a global increase in Fgf signaling as well as the associated alveolar epithelial markers (Sftpb, Epcam and Aqp5), Tgf-β signaling was also increased (Tg-fβ1, Tgf-β3, Smad7). F. The data from experimental mice suggest no significant changes for Fgf signaling, the epithelial markers and Tgf-β signaling. Scale bar in B: low magnification: 125 μm; high magnification: 50 μm. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001.