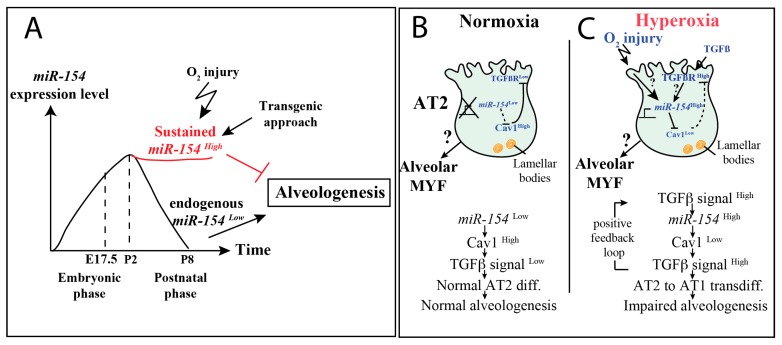
Figure 8.
Hypothetical Model of Action describing miR-154 function in lung development. A. miR-154 expression level alterations during embryonic and postnatal phases. Postnatal miR-154 decrease allows proper alveologenesis, whereas hyperoxia-induced sustained miR-154 levels lead to the disturbance of alveologenesis. B. Under normoxic conditions postnatal miR-154 repression occurs to enable Cav1 to inhibit Tgf-β signaling by Tgf-βr1 internalization leading to proper alveologenesis in postnatal development. C. Hyperoxia leads to miR-154 induction and subsequent repression of Cav1-mediated Tgf-βr1 internalization. Tgf-β signaling is unleashed disturbing alveologenesis.