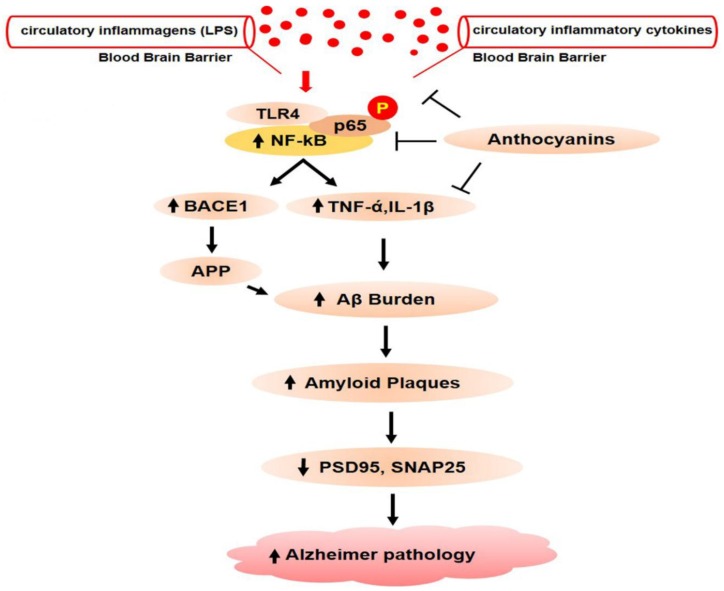
Figure 7.
Anthocyanins prevent inflammatory and amyloid genic pathways in the central nervous system. When circulatory lipopolysaccharides and inflammatory cytokines gain entry to the brain, toll-like receptor 4 on microglia is activated, which subsequently leads to the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB). After NF-κB phosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus, it goes on to bind with proinflammatory cytokine genes, that results in the production and release of proinflammatory cytokines. NF-κB also binds with the promoter region of BACE1 that produces β-secretase enzymes. Increased BACE1 activities later result in abnormal APP cleavage. Chronic deposition of amyloid beta proteins in the brain causes amyloid beta plaque formation and neuronal cell death. Amyloid beta plaques also deregulate pre- and postsynaptic proteins, which results in dementia and memory impairment.