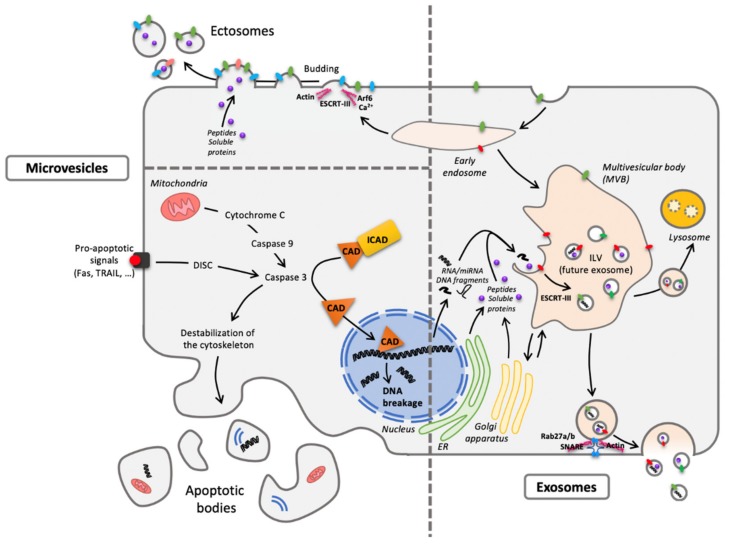
Figure 2.
One cell, different extracellular vesicles (EVs). The two main forms are microvesicles (MVs) and EXOs differing from their origin. Concerning MVs, ectosomes result from membrane budding (left pane, top) and apoptotic bodies from cellular vesiculation following apoptosis (left panel, bottom). As to exosomes (EXOs), they have an endosomal origin, generated by the formation of intraluminal vesicles (ILV) within the multivesicular body (MVB) (right panel) and released through exocytosis routes. Despite a quite homogenous diameter from 30 to 150 nm, EXOs are difficult to distinguish (size exclusion chromatography or differential ultracentrifugation) from the smallest MVs. Abbreviations: CAD: Caspase-Activated DNAse; DISC: Death-Inducing Signaling Complex; ESCRT: Endosomal Sorting Complexes Required for Transport; ER: Endoplasmic Reticulum; ICAD: Inhibitor of Caspase-Activated DNAse; Rab: RAS-related protein; SNARE: Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive-factor Attachment protein REceptor; TRAIL: Tumor-necrosis-factor Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand.