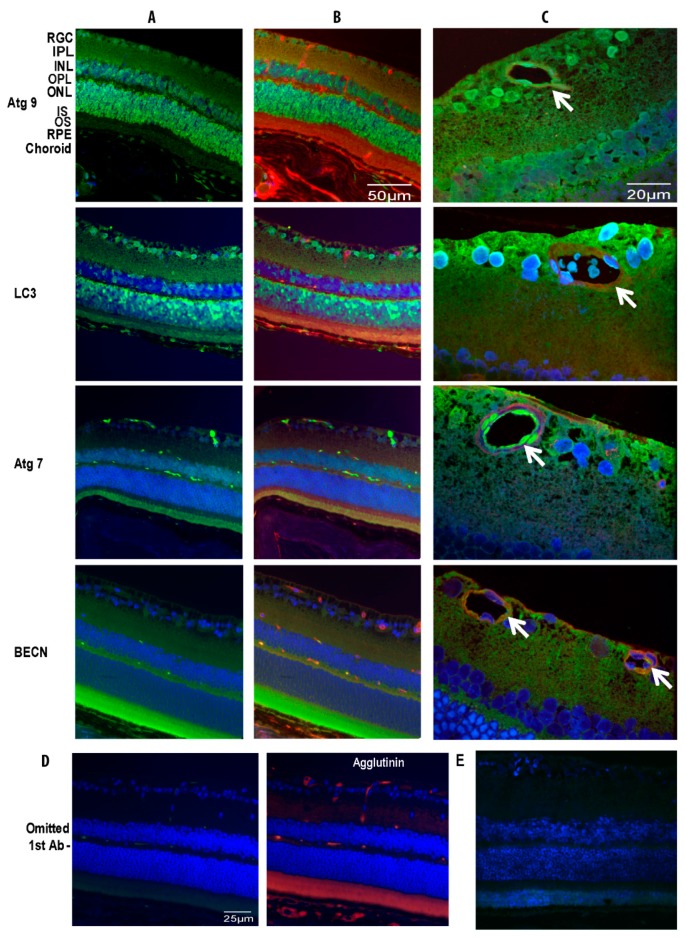
Figure 2.
Localization of autophagy proteins in normal mouse retina and vasculature. Animals were kept in tight 12/12-h light/dark cycle before the experiment. Antibodies for ATG9, LC3, ATG7 and Beclin1 (BECN) were used to detect respective protein expression (green) in the retinas with different staining patterns and DAPI was used to stain nuclei (blue) (A). Agglutinin, an endothelial cell marker, conjugated with TRITC (red) was used to co-localize with antibodies specific to individual autophagy proteins (FITC) in the retinal vasculature (B). High magnification images demonstrated autophagy protein localization to the endothelial cells and pericytes of the retinal vasculature (C). No fluorescence was observed with omission of the primary antibody in the mouse retina. Using agglutinin staining, the section displayed retinal vascular patterns with normal architecture (D). Omitted autophagy primary antibody in rat retina also was negative (E). The arrows indicate autophagy protein localization to retinal vessels. RGC, retina ganglion cell; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; IS, inner segment; OS, outer segment; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.