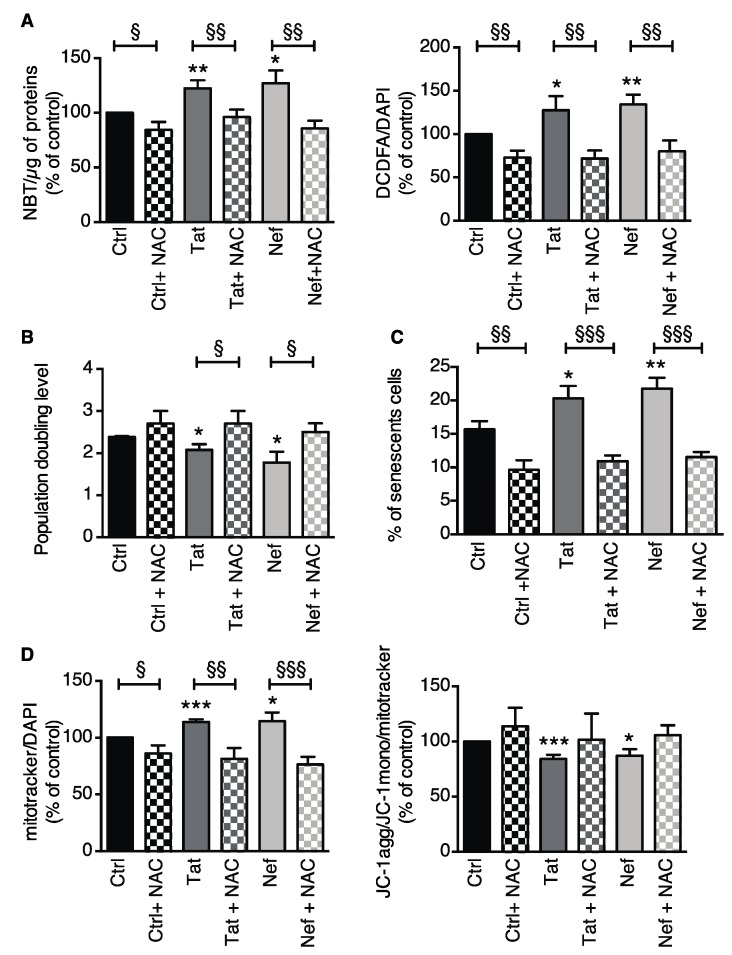
Figure 5.
The suppression of oxidative stress using NAC prevented Tat- or Nef-induced senescence in ASCs. ASCs were treated with the HIV proteins Tat or Nef for 15 days. After these 15 days of treatment, we started a concomitant NAC treatment for 10 days. Experiments were performed on day 25 in ASCs, isolated from different abdominal SCAT healthy donors. (A) ROS production was assessed spectroscopically by measuring the NBT absorbance (normalized against protein content) and the CM-H2DCFDA fluorescence (normalized against DAPI) (n = 5, in duplicate). (B) The population doubling level (PDL) was calculated as described previously (n = 5, in duplicate). (C) Senescence was evaluated in terms of SA-β-galactosidase activity at pH 6 and expressed as the proportion (in %) of SA-β-galactosidase-positive cells (n = 5, in duplicate). (D) Mitochondrial mass was evaluated using MitoTracker dye. The cationic dye JC-1 was used to evaluate the mitochondrial membrane potential. The fluorescence results are expressed as the mean ± SEM % JC-1 aggregate/monomer ratio. The results were normalized against DAPI fluorescence, and expressed as the mean ± SEM % of control cells (n = 5, in duplicate). * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001 vs. control cells. § P < 0.05, §§ P < 0.01, and §§§ P < 0.001 NAC-treated vs. nontreated cells.