Abstract
Cardiovascular side effects are frequent problems accompanying systemic glucocorticoid therapy, although the underlying mechanisms are not fully resolved. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been shown to promote various cardiovascular diseases although the link between glucocorticoid and ROS signaling has been controversial. As the family of NADPH oxidases has been identified as important source of ROS in the cardiovascular system we investigated the role of NADPH oxidases in response to the synthetic glucocorticoid dexamethasone in the cardiovascular system in vitro and in vivo in mice lacking functional NADPH oxidases due to a mutation in the gene coding for the essential NADPH oxidase subunit p22phox. We show that dexamethasone induced NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS generation, leading to vascular proliferation and angiogenesis due to activation of the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF1). Chronic treatment of mice with low doses of dexamethasone resulted in the development of systemic hypertension, cardiac hypertrophy and left ventricular dysfunction, as well as in pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling. In contrast, mice deficient in p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases were protected against these cardiovascular side effects. Mechanistically, dexamethasone failed to upregulate HIF1α levels in these mice, while vascular HIF1α deficiency prevented pulmonary vascular remodeling. Thus, p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases and activation of the HIF pathway are critical elements in dexamethasone-induced cardiovascular pathologies and might provide interesting targets to limit cardiovascular side effects in patients on chronic glucocorticoid therapy.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase, p22phox, Glucocorticoid, HIF1, Hypertension, Pulmonary vascular remodeling, ROS
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
p22phox‐dependent NADPH oxidases promote superoxide generation in response to dexamethasone.
-
•
p22phox‐dependent NADPH oxidases promote HIF1 activation and vascular proliferation in response to dexamethasone.
-
•
p22phox‐dependent NADPH oxidases promote systemic hypertension and left ventricular dysfunction in response to dexamethasone.
-
•
p22phox‐dependent NADPH oxidases promote pulmonary hypertension in response to dexamethasone.
-
•
p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases promote pulmonary vascular remodeling in response to dexamethasone involving the HIF pathway.
Abbreviations
- l-NAME
N(ω)-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester
- RU486
mifepristone
- TTFA
thenoyltrifluoroacetone
- HIF1
hypoxia-inducible factor-1
- PASMC
pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells
- HMEC-1
human microvascular endothelial cells-1
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- EPR
electron paramagnetic resonance
1. Introduction
The number of patients on systemic glucocorticoid therapy has increased substantially over the last 20 years, primarily due to the rising prevalence of diseases requiring long-term therapy with glucocorticoids as for example asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but also other inflammatory and autoimmune disorders [1,2]. It has been estimated, based on studies in the US and UK, that around 1% of the general population undergoes systemic glucocorticoid therapy, in many cases for months or years [2]. Frequent clinical problems by either the pharmacological administration of glucocorticoids or intrinsic glucocorticoid excess in humans (as for example in Cushing syndrome) are metabolic, but also cardiovascular side effects such as increased blood pressure, coronary artery disease, heart failure, and to a lesser extent stroke [[3], [4], [5], [6]]. Despite the high number of patients suffering from glucocorticoid-induced cardiovascular diseases, the underlying mechanisms are not well understood, thus hampering adequate prevention and/or treatment.
Glucocorticoids act primarily through intracellular glucocorticoid receptors, although some glucocorticoids can also cross-react with mineralocorticoid receptors in varying degrees [7]. Glucocorticoid receptors belong to the nuclear receptor family of ligand-activated transcription factors. They are ubiquitously expressed in most cell types and conserved across species. Ligand-bound glucocorticoid receptors in the nucleus induce or repress the transcription of target genes through different mechanisms including direct binding to glucocorticoid response elements in the DNA of target genes, protein–protein interactions with other transcription factors that affect their transcriptional activity, and composite binding to DNA and protein substrates [1,7]. Rapid non-genomic signaling was also demonstrated since glucocorticoids can act through membrane receptors and activate signal transduction pathways, such as protein kinases, to modulate other transcriptions factors and activate or repress various target genes [8]. By all these different mechanisms, glucocorticoids regulate numerous important functions in a large variety of cells including carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism, endocrine homeostasis, vascular tone, proliferation and apoptosis [7,9].
Physiologically, glucocorticoids are secreted from the adrenal cortex as part of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis and are critical to the stress response at various levels [10]: They can prime the different components of the stress response e.g. by inducing expression and sensitivity of stress hormone receptors, thus preparing the body for various stresses that may occur during the day [11]. Glucocorticoids can also act suppressive thereby preventing stress-activated defense mechanisms from overshooting and damaging the organism, f.e. by controlling inflammatory and immune responses [12]. The anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory role of glucocorticoids and their synthetic analogues and derivatives resulted in their wide use in treatments of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases [1]. However, although glucocorticoids are in general considered anti-inflammatory and protective, this is not a uniform response. In some cases, depending on the dose, chronicity of exposure, and the organ analysed, glucocorticoids can also increase certain parameters of the inflammatory response [13]. Moreover, glucocorticoids prepare the body for periods of low nutritional supply [10], but they also promote liberation of energy substrates such as glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids, to ensure their availability for mitochondrial oxidation in stress conditions [14]. In this regard, glucocorticoids promote whole-body insulin resistance, although in adipose tissue, they enhance insulin signaling and action. These findings demonstrate the complex and tissue-specific mode of action of glucocorticoids which is also observed in the cardiovascular system: In the heart, glucocorticoids likely contribute to normal cardiac activity and the cardiovascular stress response, as glucocorticoid insufficiency induced by adrenalectomy leads to reduced contractile force generation in rat papillary muscle which was reversed by application of the synthetic glucocorticoid dexamethasone [15]. On the other hand, glucocorticoids have negative effects on the cardiovascular system such as increased vascular tone leading to hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy [8,16].
Hypertension in response to glucocorticoids was initially discussed to originate from sodium excess or from an impairment of water reabsorption by the renal mineralocorticoid receptor [3]. However, more recent data using synthetic glucocorticoids such as dexamethasone which act primarily via the glucocorticoid receptor suggest that complex molecular mechanisms independent of the mineralocorticoid receptor result in cardiovascular complications by glucocorticoids [5,17]. Studies in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle specific glucocorticoid receptor knock out animals point to a role for the vasculature in the pathogenesis of glucocorticoid-induced hypertension [18,19]. However, at the molecular level, the role of glucocorticoids in the regulation of the cardiovascular system remains poorly understood.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been shown to act as signaling molecules in the pathogenesis of various cardiovascular diseases including hypertension [[20], [21], [22], [23]]. The family of NADPH oxidases has been identified as a major source of ROS generation in the cardiovascular system contributing to hypertension and various other cardiovascular pathologies [24,25]. Initially, an NADPH oxidase has been characterized in leukocytes to be responsible for the respiratory burst, which generates superoxide anion radicals upon bacterial infections as part of the innate immune system [26]. It contains 2 membrane-bound proteins, p22phox and NOX2, which form the cytochrome b558 as the catalytic core, and in addition several cytosolic proteins and the GTPase Rac, which are required to assemble with the cytochrome for enzyme activation. Subsequently, several homologs of NOX2 have been found in non-phagocytic cells, including the vasculature, which have been termed NOX1, NOX3, NOX4 and NOX5, DUOX1 and DUOX2 [27]. Apart from NOX5, DUOX1 and DUOX2, all NOX proteins require p22phox for function.
Although glucocorticoids and ROS have been both associated with hypertension and other cardiovascular disorders, there are conflicting results reported on the cross-talk between glucocorticoid action and ROS signaling: While glucocorticoids have been initially described to decrease ROS levels in several cell culture models [[28], [29], [30], [31], [32], [33]], there is now mounting evidence that glucocorticoids can also increase ROS levels in different cellular systems including vascular cells [34,35]. Moreover, treatment with antioxidants has been shown to ameliorate glucocorticoid-induced hypertension [[36], [37], [38], [39]]. However, the exact conditions and consequences of glucocorticoid action on ROS generation in the cardiovascular system and the sources of ROS involved are not well understood.
In this study we characterized an essential role of p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases in the vascular response to the synthetic glucocorticoid dexamethasone in vitro as well as in vivo which was mediated by ROS and the transcription factor HIF1. Importantly, as demonstrated in a genetic mouse model, p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases were critically involved not only in the development of systemic but also of pulmonary hypertension and cardiac dysfunction upon chronic treatment with low dose dexamethasone.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Chemicals
All chemicals were from Sigma-Aldrich unless stated differently.
2.2. Cell culture
Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) (ATCC CRL-3243) and pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMC) (Lonza) were cultivated as previously described [40,41]. HMEC-1 is an immortalized cell line established by transfection of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells with a PBR-322-based plasmid containing the coding region for the simian virus 40 A gene product, large T antigen [42]. HMEC-1 were grown in MCDB131 medium (PAA) supplemented with 1 g/l glucose, 10% fetal calf serum (FCS, PAA), 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin (Gibco), 100 μg/ml streptomycin (Gibco), 1 μg/ml hydrocortisone, and 1 μg/ml human epidermal growth factor (hEGF1) (Invitrogen). PASMC were grown in smooth muscle basal medium (SmBM™, Lonza) supplemented by SmGM™-2 SingleQuots™ (Lonza) (containing: FCS, hEGF1, insulin, human fibroblast growth factor B (hFGFB), and gentamicin/amphotericinB). All cells were maintained at 37 °C under the humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2. 16 h prior to stimulation cells were placed in a respective basal medium without additives.
2.3. Isolation of cardiomyocytes
Isolated murine hearts were washed and perfused with EDTA buffer (130 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 0.5 mM NaH2PO4, 10 mM HEPES, 10 mM glucose, 10 mM 2,3-butanedione 2-monoxime, 10 mM taurine, and 5 mM EDTA) and then with perfusion buffer (130 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 0.5 mM NaH2PO4, 10 mM HEPES, 10 mM glucose, 10 mM 2,3-butanedione 2-monoxime, 10 mM taurine, and 1 mM MgCl2). Next, hearts were digested with collagenase buffer (0.5 mg/ml collagenase 2, 0.5 mg/ml collagenase 4, and 0.05 mg/ml protease XIV). Once digestion was completed, perfusion buffer containing 5% FCS was added to the cell-tissue suspension to stop further enzymatic reactions. The suspension containing myocytes was passed through a 100 μm pore-size strainer in order to remove undigested tissue debris. After sequential gravity settlement, myocytes were cultivated in DMEM medium (PAN Biotech) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (PAA), 100 U/ml penicillin (Gibco), 100 μg/ml streptomycin (Gibco) and 2,3-butanedione monoxime to prevent myocyte contractions.
2.4. Transfections and luciferase assay
The expression vector coding for RacT17N and the HIF reporter vector harboring three copies of the hypoxia response element of the 3′UTR of the erythropoietin gene in front of the luciferase gene have been described previously [43,44]. Transfections and luciferase assays were performed as described [40]. Briefly, HMEC-1, grown to 50–70% confluency in 24-well plates, were transiently transfected using Lipofectamine 3000 (Life Technologies GmbH). To assess luciferase activity, cells were harvested and lysed in Reporter Lysis Buffer (Promega) and centrifuged at 500 rcf for 5 min at 4 °C to remove cell debris. Luciferase activities were measured in a luminometer (Berthold) and β-galactosidase activities were determined spectrophotometrically as described in the manufacturer's protocol (Promega). Presented data are normalized to β-galactosidase activities and transfection efficiencies.
2.5. Gene silencing
For gene silencing, HMEC-1 or PASMC were transfected with corresponding short interfering RNAs (siRNA) as has been previously described [40,45]. siRNAs targeting p22phox (SI03078523), NOX1 (SI03043530), NOX2 (SI00008736) and NOX4 (SI05137748) were purchased from Qiagen. siRNA against HIF1A (5′-UCAAGUUGCUGGUCAUCAGdTdT-3′) and negative control siRNA (5′- GACUACUGGUCGUUGAAGUdTdT-3′) were synthesized by Eurogentec.
2.6. Gene silencing by lentiviral transduction
For ex vivo experiments, short hairpin RNA oligonucleotides (shRNA) were used for gene silencing in cultured aortic rings by lentiviral delivery using the BLOCK-iT Inducible H1 Lentiviral RNAi System (Invitrogen) in accordance to the manufacturer's manual. shRNAs against p22phox (sense: 5′- CAC CGG TTA ACC CAA TGC CAG TGA CCG AAG TCA CTG GCA TTG GGT TAA CC-3′, anti-sense: 5′- AAA AGG TTA ACC CAA TGC CAG TGA CTT CGG TCA CTG GCA TTG GGT TAA CC -3′), NOX2 (sense: 5′- CAC CGC TGC CAG TGT GTC GAA ATC TCG AAA GAT TTC GAC ACA CTG GCA GC-3′, anti-sense: 5′- AAA AGC TGC CAG TGT GTC GAA ATC TTT CGA GAT TTC GAC ACA CTG GCA GC -3′) and NOX4 (sense: 5′- CAC CGT TGG CCA GCC AGC TCC TCC ACG AAT GGA GGA GCT GGC TGG CCA A-3′, anti-sense: 5′- AAA ATT GGC CAG CCA GCT CCT CCA TTC GTG GAG GAG CTG GCT GGC CCA AC -3′) were generated and cloned into pLenti4 according to the manufacturer's instructions. shRNA against GFP (sense: 5′- CAC CGC AAG CTG ACC CTG AAG TTC ATC GAA ATG AAC TTC AGG GTC AGC TTG C-3′, anti-sense: 5′- AAA AGC AAG CTG ACC CTG AAG TTC ATT TCG ATG AAC TTC AGG GTC AGC TTG C-3′) were used as controls. The lentivirus was produced in HEK 293FT cells, and the virus-containing media were harvested for infection of mouse aortic rings. For infection, aortic rings were placed in a 96-well plate (1 ring per well) and supplemented with MCDB131 medium with 1 g/l glucose, 10% FCS (PAA), 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin (both Gibco), 1 μg/ml hydrocortisone (Sigma) and 1 μg/ml epidermal growth factor - EGF-1 (Invitrogen). After 24 h, medium was removed and 110 μl MCDB131 medium supplemented with hexadimethrine bromide (8 mg/ml, Invitrogen) was added to each well. Subsequently, 15 μl of the appropriate virus-containing media was added to each well. On the following day, medium was exchanged and dexamethasone was added or not.
2.7. Immunoblot analysis
Proteins were isolated and Western blot analyses were performed as previously described [40,45] using antibodies against: NOX2 (Upstate), NOX4 (Epitomics), HIF1α (BD Transduction), PAI1 (American Diagnostica), V5-tag (Cell Signaling), p22phox and β-actin (Santa Cruz).
2.8. Gene expression analysis
Total RNA was isolated and cDNA was synthesized as previously described [40,45]. Gene expression was assessed by RT-qPCR as described previously [40,45] using the following gene-specific primers: p22phox: 5′-CAC AAA TCA GAC GGC AGC ACT-3′ (sense), 5′-CAT CGG GCG TGG TGA ACT C-3′ (antisense); NOX1: 5′-CAC CCC AAG TCT GTA GTG GGA G-3′ (sense), 5′-CCA GAC TGG AAT ATC GGT GAC A-3′ (anti-sense); NOX2: 5′-GTC ACA CCC TTC GCA TCC ATT CTC AAG TCA GT-3′ (sense), 5′-AAC CAC TCA AAG GCA TGT GTG TC-3′ (anti-sense); NOX4: 5′-CCG GCT GCA TCA GTC TTA ACC-3′ (sense), 5′-TCG GCA CAG TAC AGG CAC AA-3′ (anti-sense); HIF1A: 5′-GAA GAC ATC GCG GGG AC-3′ (sense), 5′-TGG CTG CAT CTC GAG ACT TT-3′ (anti-sense); 18S rRNA 5′-GTA ACC CGT TGA ACC CCA TT-3′ (sense), 5′-CCA TCC AAT CGG TAG TAG CG-3′ (antisense).
2.9. Measurement of superoxide anion production by electron paramagnetic resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) using 1-hydroxy-methoxycarbonyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-pyrrolidine hydrochloride (CMH, 10 μM) as a superoxide detecting spin probe [46] was applied to measure superoxide production rate in cells, aortic rings and pulmonary arteries as previously described [45]. Superoxide specificity of the approach was validated by addition of PEGylated superoxide dismutase.
2.10. Measurement of superoxide anion levels by 2-hydroxyethidium fluorescence
Dihydroethidium (DHE) was used for superoxide detection at a final concentration of 50 μM as previously described [45]. Briefly, aortic samples were macerated in 1 × Krebs Hepes buffer (KHB: 99 mM NaCl, 4.69 mM KCl, 25 mM NaHCO3, 1.03 mM KH2PO4, 5.6 mM d-glucose, 20 mM Na-HEPES, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 1.2 mM MgSO4), incubated with DHE at 37 °C for 1 h, washed twice with 1 × KHB and homogenized. 2-Hydroxy-ethidium was extracted in methanol, separated on a C18 column (Sulpelco C18 column 4.6 × 250 mm, 5 μm) and detected by high pressure liquid chromotagraphy (HPLC) using a fluorescence detector (excitation 480 nm, emission 580 nm).
2.11. Measurement of hydrogen peroxide by amplex red assay
To detect the generation of hydrogen peroxide, a modified amplex red assay (Thermo Fisher) was used. HMEC-1 grown on 96-well plates were washed once with Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS; PAN-Biotech) and incubated with 50 μM amplex red and 0.2 units/ml horseradish peroxidase for 15 min, followed by measurement of the H2O2-dependent oxidation of amplex red by fluorescence (excitation = 550 nm, emission = 590 nm) using a multiplate fluorescence reader (Tecan).
2.12. Proliferation assay
DNA synthesis in HMEC-1 cells was assessed by 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU, Roche) immunoassay as previously described [40]. In brief, cells were seeded in 96-well plates to achieve 50% of confluency. Cells were then incubated with BrdU (10 μM) for 16 h. Thereafter, cells were fixed for 30 min and then incubated for 1 h with the peroxidase-conjugated antibody against BrdU. Immunodetection was performed by adding the colorimetric substrate TMB. When the blue color developed, the reaction was stopped with 1 M H2SO4. Absorbance was measured in an ELISA reader (Tecan) at 450 nm with a reference wavelength at 690 nm.
2.13. In vitro tube formation assay
In vitro tube formation assay was performed with HMEC-1 as previously described [40]. Briefly, HMEC-1 cells (5000 cells per well) were seeded on a micro-slide angiogenesis plate (Ibidi) that was mounted with growth factor-reduced Matrigel (BD Biosciences). Cells were subsequently incubated for 6 h at 37 °C in the presence or absence of 10 nM dexamethasone and counterstained using calcein AM (BD Biosciences). The formation of capillary-like structures was assessed by fluorescence microscopy (Olympus) using the Openlab Modular Software for Scientific Imaging (Improvision) and was quantified for total tube lengths using Image J software (Wright Cell Imaging Facility).
2.14. Animals
The mouse strain B6 Tyr+-Cybanmf333/J (nmf333; Jackson Laboratories) was maintained on a C57BL/6j background as described previously [47]. It carries a point mutation in exon 5 of the Cyba gene (coding for p22phox) leading to the substitution of a tyrosine residue (121) to histidine and loss of p22phox protein while mRNA levels are preserved [48].
Mice with endothelial- or smooth muscle specific inactivation of HIF1α were generated by cross-breeding either Tie2-Cre (B6.Cg-Tg(Tek-cre)12Flv/J; Jackson Laboratories) or Sm22a-Cre (B6.Cg-Tg(Tagln-cre)1Her/J; Jackson Laboratories) transgenic mice with Hif1α+f/+ mice homozygous for the Hif1α allele with exon 2 flanked by loxP sites (B6.129-Hif1atm3Rsjo/J; Jackson Laboratories) [49]. Male mice were orally supplemented with dexamethasone (0.3 mg/kg/day) for 12 weeks. Control litter-mates drunk normal water.
2.15. Ex vivo experimentation
For ex vivo analyses, lungs were dissected and macerated, and aortae and intact pulmonary arteries were isolated. Aortic rings and intact pulmonary arteries were placed in MCDB131 medium and exposed to dexamethasone according to the experimental design.
2.16. Hemodynamic measurements
Hemodynamic measurements were performed as previously described using a transthoracic approach [45]. Mice were anesthetized by isoflurane, weighed, and the left chest was shaved. Hemodynamic measurements were performed using a 24 G needle connected to a pressure amplifier (Isotec) and recorded using HSE-HA HAEMODYN W software for hemodynamic studies. The catheter was inserted into the left ventricle (LV) and then carefully advanced to the right ventricle (RV). The correct position was confirmed by observing the characteristic ventricular waveforms. The pressure profiles were recorded after stabilization for 1 min, and systolic LV and RV pressure values were determined. Mice were euthanized in anesthesia by cervical dislocation.
2.17. Ventricular mass assessment
At the end points, left (LV) and right ventricle (RV) mass as well as body mass (BM) were determined. Ventricular hypertrophy was assessed for each ventricle separately by dividing the mass of the corresponding ventricle by BM.
2.18. Immunohistochemistry and histological analyses
Tissue samples were formalin fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) and immunohistochemistry was performed on FFPE cross-sections at 2.5 μm thickness as previously described [45]. Briefly, heat-induced antigen retrieval was performed at pH 8.0 for 20 min. Sections were blocked in 3% BSA in PBS to block non-specific sites. All sections were incubated with the corresponding primary antibody at a dilution factor of 1:1000 overnight at 4 °C. Mouse α-smooth-muscle actin antibody was from Agilent and mouse 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine (8OHdG) antibody was from Abcam. Secondary goat anti-mouse antibody conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488 (Invitrogen) was applied for 2 h at room temperature in a dark chamber. Sections were counterstained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, 1:10000, Enzo) for 5 min and mounted with anti-fade mounting medium (DAKO), visualized using a fluorescence microscope (OLYMPUS) and analysed with cellSens Dimension imaging software (OLYMPUS). In each lung, α-smooth muscle actin-positive vessels (diameter<30 μm) of four high power fields in 10× magnification were counted. For quantification of 8-OHdG staining, 60 nuclei were randomly analysed in each high power field and absorbance was measured.
2.19. Wheat germ agglutinin assay
To quantify cardiomyocyte size both in left and right ventricle, FFPE heart sections were stained with FITC–Wheat Germ Agglutinin–Alexa Fluor 488 (Invitrogen) to delineate the cell membrane [50] as previously described [47]. For each sample 10 different average cardiomyocyte diameters were determined in longitudinally oriented cardiomyocytes by image analysis software (Image J). Nuclei were visualized with DAPI staining [40]. Criteria for the short axis of the cardiomyocytes were a circular shape and the visibility of the cell nucleus.
2.20. Echocardiography
Echocardiography was performed with a General Electric Vivid S6 Ultrasound System and a 12i linear array transducer (12 MHz) as previously described [51]. In brief, mice were anesthetized with inhaled 1.4–1.6% isoflurane/oxygen mixture and left ventricular end diastolic (LVEDD) and end systolic (LVESD) diameters and wall thicknesses were obtained from M-mode tracings using measurements averaged from 3 separate cardiac cycles. Left ventricular fractional shortening (FS) was derived using the equation FS = [(LVEDD-LVESD)/LVEDD] x 100.
2.21. Statistical analysis
All experimental data have been received from independent experiments. The sample size (number of independent experiments) required to reach an experimental power (1−β) ≥0.8 at a p-value threshold of 0.05 was calculated by power analysis using the power.t.test function in R 2.15 (The R foundation). Independent sample preparations from different cellular batches or animals adjusted to the required sample size were then used. Values are presented as mean ± SD. Results were compared by Student–Newman–Keuls t-test. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Post hoc power analysis to determine (1−β) was performed using Kane SP. Post.ClinCalc: http://clincalc.com/Stats/Power.aspx. Updated November 10, 2018.
2.22. Study approval
All animal procedures were performed in accordance with the European directive 2010/63/EU for animal experiments, and approved by Government of Upper Bavaria, Munich, Germany as the local legislation on protection of animals (55.2.1.54-2532-55-12).
3. Results
3.1. Dexamethasone induces superoxide production in vascular cells and isolated vessels
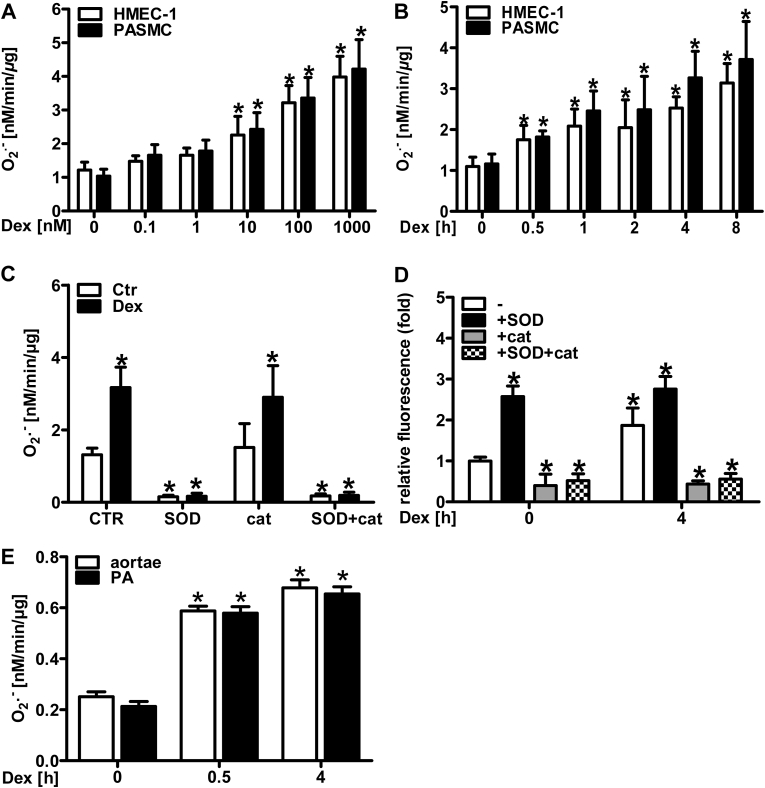
In order to characterize superoxide production in response to glucocorticoids, human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) and human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMC) were stimulated with different concentrations of the synthetic glucocorticoid dexamethasone (0.1–1000 nM) for 4 h. Subsequently, superoxide generation was measured by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) using the spin probe 1-hydroxy-methoxycarbonyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-pyrrolidine hydrochloride (CMH) (Fig. 1A). In both cell types, superoxide production dose-dependently increased starting at 10 nM dexamethasone. Concomitantly, exposure of HMEC-1 and PASMC to 10 nM dexamethasone for increasing time periods resulted in significantly elevated superoxide levels when treated for 0.5–8 h (Fig. 1B). In order to show the specificity of CMH for superoxide detection, HMEC-1 were stimulated with dexamethasone in the presence of either polyethylene glycol-superoxide dismutase (PEG SOD), or PEG catalase or both. Indeed, the EPR signal was inhibited by 97–98% in the presence of PEG SOD (alone or together with PEG catalase), while addition of PEG catalase alone had no effect – thus proving the specificity of the method for superoxide detection (Fig. 1C). Since superoxide can be rapidly transformed to hydrogen peroxide, we also determined H2O2 levels in HMEC-1 by amplex red assay (Fig. 1D). Similar to the results obtained by EPR, dexamethasone increased amplex red mediated fluorescence in HMEC-1 cells (Fig. 1D). Addition of PEG catalase (alone or with PEG SOD) decreased the signal, while addition of PEG SOD alone had little effect (Fig. 1D).
Fig. 1.
Dexamethasone induces superoxide generation in vascular cells and vessels.
(A) Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) and pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMC) were treated with dexamethasone (Dex, 0.1–
1000 nM) for 4 h. The superoxide production rate was measured by EPR using CMH (n = 4–6; *p < 0.05 vs. Dex 0 nM; (1-β) = 1). (B) HMEC-1 and PASMC were treated with 10 nM dexamethasone (Dex) for increasing time periods. Superoxide production rate was measured as above (n = 4–6; *p < 0.05 vs. Dex 0 h; (1-β) = 1). (C) HMEC-1 were treated with 10 nM dexamethasone (Dex) for 4 h and superoxide production rate was measured in the presence of either polyethylene glycol (PEG) superoxide dismutase (SOD) or PEG catalase (cat) or both (SOD + cat) as above (n = 6; *p < 0.05 vs. Dex CTRCtr; (1-β) = 1). (D) HMEC-1 were treated with 10 nM dexamethasone (Dex) for 4 h and hydrogen peroxide levels were measured in the presence of PEG SOD (SOD) or PEG catalase (cat) or both (SOD + cat) by amplex red assay (n = 4; *p < 0.05 vs. Dex 0 h; (1-β) = 1). (E) Murine aortic rings (aortae) or pulmonary arteries (PA) were incubated with 10 nM dexamethasone (Dex) ex vivo. Superoxide production rate was measured as above (n = 4–6; *p < 0.05 vs. Dex 0 h; (1-β) = 1). Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases.
To test the effects of dexamethasone on intact vessels, murine aortae and pulmonary arteries were explanted and exposed to 10 nM dexamethasone for 0.5 and 4 h. Similar to the situation with cultivated cells, dexamethasone increased the generation of superoxide in both vessel types as determined by EPR (Fig. 1E). Similar results were obtained using dihydroethidium assay in high pressure liquid chromatography (Suppl. Fig. 1).
3.2. Dexamethasone-induced superoxide production is mediated by the glucocorticoid receptor
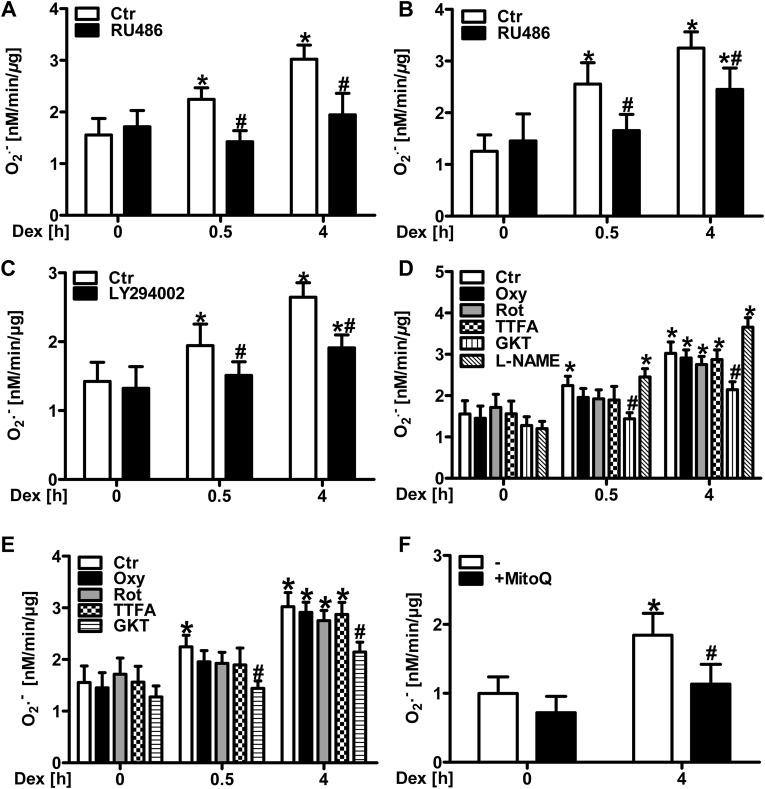
Next, the role of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) in glucocorticoid-stimulated superoxide generation was assessed. Inhibition of the GR by pre-treatment with mifepristone (RU486) prevented superoxide production in HMEC-1 (Fig. 2A) and in PASMC (Fig. 2B) after dexamethasone stimulation. Since the activated glucocorticoid receptor has been reported to signal via binding to the p85α subunit of phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PI-3 kinase) [52], we tested the involvement of this pathway in dexamethasone-induced ROS generation. Pre-treatment with the PI-3 kinase inhibitor LY294002 for 1 h attenuated dexamethasone-induced superoxide production (Fig. 2C).
Fig. 2.
Glucocorticoid receptor signaling mediates superoxide production in vascular cells in response to dexamethasone.
(A/B) Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) (A) and pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMC) (B) were treated with the glucocorticoid receptor inhibitor mifepristone (RU486, 500 μM) for 1 h prior to treatment with 10 nM dexamethasone (Dex), and superoxide production rate was measured by EPR using CMH (n = 4–6; *p < 0.05 vs. CtrDex 0 h; #p < 0.05, vs. CtrDex 0.5 h or CtrDex 4 h; (1-β) = 1). (C) HMEC-1 were treated with the PI3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 (100 μM) for 1 h prior to treatment with 10 nM Dex, and superoxide production rate was measured as above (n = 3; *p < 0.05 vs. CtrDex 0 h; #p < 0.05, vs. either CtrDex 0.5 h or CtrDex 4 h; (1-β) = 1). (D/E) HMEC-1 (D) and PASMC (E) were treated with the xanthine oxidase inhibitor oxypurinol (Oxy, 100 μM), inhibitors of mitochondrial complex II (TTFA, 100 μM) or complex I (rotenone, Rot, 100 μM), the NADPH oxidase inhibitor GKT-137831 (GKT, 50 μM) or the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-(G)-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME, 300 μM) (only D) for 1 h prior to treatment with Dex (10 nM), and superoxide production rate was measured as above (n = 3–4; *p < 0.05 vs. CtrDex 0 h; #p < 0.05 vs. CtrDex 0.5 h or CtrDex 4 h; (1-β) = 1). (F) HMEC-1 were treated with the mitochondria targeted scavenger MitoQ (100 μM), and superoxide production rate was measured as above (n = 4; *p < 0.05 vs. CtrDex 0 h; #p < 0.05 vs. CtrDex 4 h; (1-β)>0.911). Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases.
3.3. Dexamethasone-induced superoxide production is derived from NADPH oxidases in vascular cells
Next, the sources of superoxide generation following dexamethasone stimulation were examined. To this end, HMEC-1 (Fig. 2D) and PASMC (Fig. 2E) were treated with the xanthine oxidase inhibitor oxypurinol as well as with rotenone, an inhibitor of mitochondrial complex I and TTFA, an inhibitor of mitochondrial complex II. However, none of these inhibitors significantly affected basal and dexamethasone-induced superoxide production neither in HMEC-1 nor in PASMC. To assure, that CMH-based EPR is indeed able to detect mitochondrial superoxide production as has been reported previously [46], cells were pre-treated with the mitochondria-targeted ROS scavenger MitoQ (Fig. 2F). Compared to control conditions, application of MitoQ decreased dexamethasone-induced superoxide generation suggesting that dexamethasone increases mitochondrial superoxide generation independently from complex I and complex II (Fig. 2F).
Similarly, treatment with the eNOS inhibitor l-NAME did not affect dexamethasone-induced superoxide generation in HMEC-1 (Fig. 2D), thus ruling out uncoupled eNOS as a source of superoxide in this context. Treatment with the NADPH oxidase inhibitor GKT-137831 [53], however, decreased dexamethasone-induced superoxide production in HMEC-1 (Fig. 2D), as well as in PASMC (Fig. 2E). Similarly, GKT-137831 also reduced the increase in hydrogen peroxide levels induced by dexamethasone in HMEC-1 as was determined by amplex red assay (Suppl. Fig. 2).
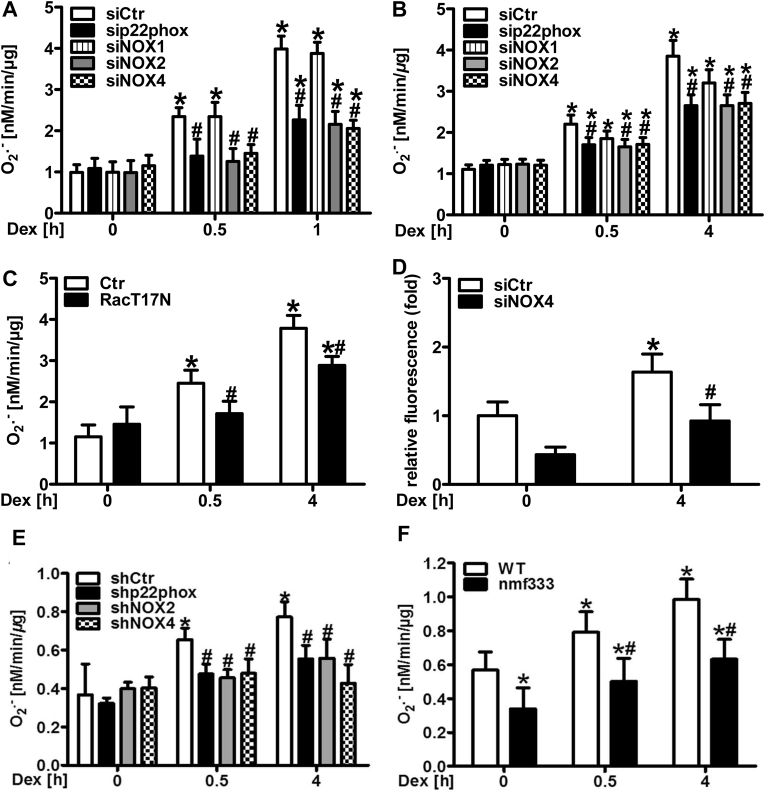
To further dissect the role of NADPH oxidases in the response to dexamethasone, HMEC-1 and PASMC were depleted from p22phox, which is required for the function of the majority of NADPH oxidases, by RNAi (Fig. 3A/B, Suppl. Fig. 3). In both cell types, loss of p22phox decreased superoxide formation in response to 0.5 and 4 h dexamethasone treatment. Since p22phox can interact with NOX1, NOX2 and NOX4 in vascular cells, HMEC-1 and PASMC were silenced for these subunits by RNAi (Fig. 3A/B, Suppl. Fig. 3). While depletion of NOX2 and NOX4 efficiently diminished superoxide production by dexamethasone in both cell types, depletion of NOX1 was less effective in particular in HMEC-1. Furthermore, we tested whether the GTPase Rac1 which is required for activation of NOX2 and NOX1, is involved in dexamethasone-induced superoxide production. Compared to control cells, HMEC-1 expressing dominant-negative RacT17N showed a reduced response towards dexamethasone (Fig. 3C, Suppl. Fig. 4). Since NOX4 has been reported to also generate hydrogen peroxide, we further assessed hydrogen peroxide levels in the context of NOX4 deficiency and dexamethasone treatment (Fig. 3D). Similar to superoxide generation, hydrogen peroxide levels were decreased in dexamethasone-treated HMEC-1 silenced for NOX4.
Fig. 3.
NADPH oxidases generate superoxide in vascular cells and vessels in response to dexamethasone.
(A/B) Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) (A) and pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMC) (B) were silenced for either p22phox, NOX1, NOX2 or NOX4 using RNAi or were transfected with siCtr and exposed to dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM). Superoxide production was measured as above (n = 3–5; *p < 0.05 vs. siCtrDex 0 h; #p < 0.05 vs. siCtrDex 0.5 h or siCtrDex 4 h; (1-β) = 1). (C) HMEC-1 were transfected with a vector coding for dominant-negative Rac1 (RacT17N) or with control vector (Ctr) and treated with dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM). Superoxide production rate was measured as above (n = 3; *p < 0.05 vs. CtrDex 0 h; #p < 0.05 vs. either CtrDex 0.5 h or CtrDex 4 h; (1-β) = 1). (D) HMEC-1 were silenced for NOX4 using RNAi or transfected with siCtr and exposed to Dex (10 nM) for 4 h, and hydrogen peroxide levels were measured by amplex red assay (n = 4; *p < 0.05 vs. siCtrCtr 0 h; #p < 0.05 vs. siCtrDex 4 h; (1-β) = 0.877). (E) Murine aortic rings were transduced by lentiviral delivery of shRNA targeting either p22phox, NOX2 or NOX4, or of scrambled RNA (shCtr) and exposed to dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM). Superoxide production was measured as above (n = 3; *p < 0.05 vs. shCtrDex 0 h; #p < 0.05 vs. shCtrDex 0.5 h or shCtrDex 4 h; (1-β) = 1). (F) Aortic rings from CD57BL6j (WT) mice and mice lacking p22phox due to a point mutation in the Cyba gene (nmf333) were exposed to dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM). Superoxide production was measured as above (n = 3; *p < 0.05 vs. WTDex 0 h; #p < 0.05 vs. WTDex 0.5 h or WTDex 4 h; (1-β) = 1). Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases.
Fig. 4.
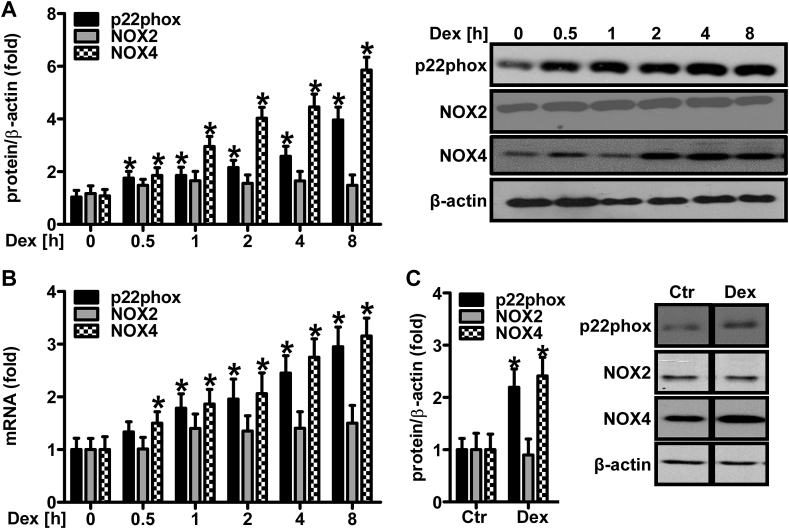
Dexamethasone upregulates NADPH oxidase protein levels in vascular cells and murine lungs.
(A/B) Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) were stimulated with dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM) for increasing time periods as indicated. (A) Western blot analyses were performed using antibodies against p22phox, NOX2 and NOX4. β-Actin served as loading control (n = 3,*p < 0.05 vs. Dex 0 h; (1-β) = 1). Representative blots are shown. (B) RT-qPCR was performed using gene-specific primers for p22phox, NOX2, and NOX4 or for 18S rRNA for normalization (n = 3,*p < 0.05 vs. Dex 0 h; (1-β) = 1). (C) CD57BL6j mice were orally supplemented with dexamethasone (Dex, 0.3 mg/kg/day) in the drinking water for 12 weeks. Litter mates drunk normal water (Ctr). Western blot analyses were performed on murine lung tissues using antibodies against p22phox, NOX2 and NOX4. β-Actin served as loading control (n = 3,*p < 0.05 vs. Ctr; (1-β) = 1). Representative blots are shown. Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases.
To test the involvement of NADPH oxidases in the response to dexamethasone also in isolated vessels, mouse aortic rings were transduced with lentiviral vectors encoding shRNAs against p22phox, NOX2 or NOX4 (Fig. 3E, Suppl. Fig. 5). In line with the data in cultivated cells, downregulation of p22phox, NOX2 and NOX4 decreased superoxide production rate upon treatment with dexamethasone.
Fig. 5.
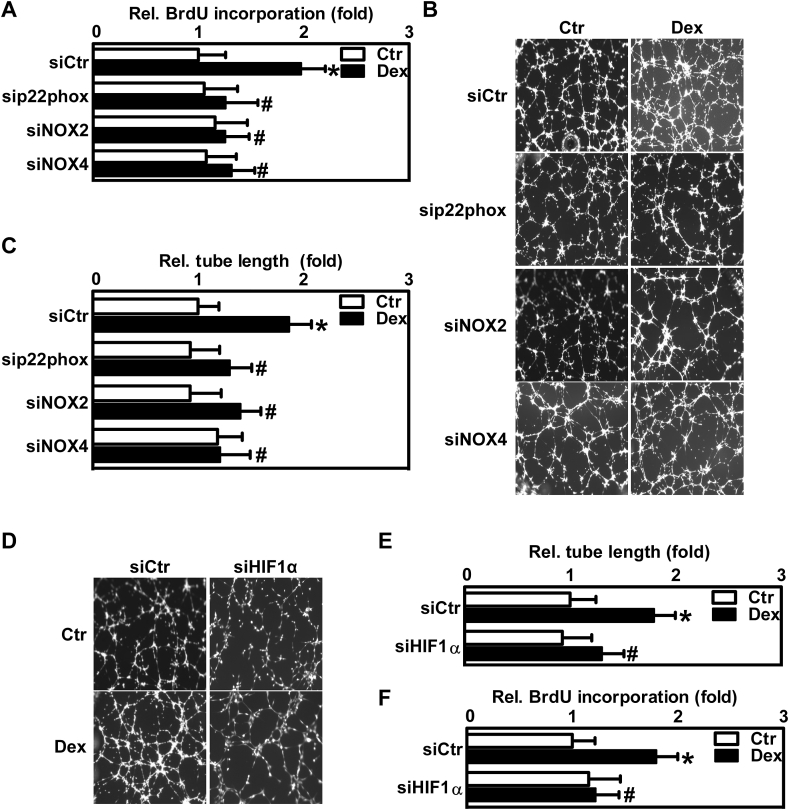
Dexamethasone promotes proliferative responses via NADPH oxidases and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in endothelial cells.
(A–C) Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) were transfected with siRNA against p22phox, NOX2, NOX4 or scrambled RNA (siCtr). (A) Cells were exposed to dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM) for 24 h or remained untreated (Ctr), and a 5-bromo-2′deoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation assay was performed (n = 3,*p < 0.05 vs. siCtrCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. siCtrDex; (1-β) = 1). (B/C) HMEC-1 were seeded on matrigel for an in vitro tube formation assay and exposed to dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM) for 6 h or remained untreated (Ctr). (B) Representative figures are shown. (C) For quantification, total tube lengths were evaluated (n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs. siCtrCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. siCtrDex; (1-β) = 1). (D–F) HMEC-1 were transfected with siRNA against HIF1α (siHIF1α) or with scrambled RNA (siCtr). (D/E) Cells were seeded on matrigel for an in vitro tube formation assay and exposed to dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM) for 6 h. (D) Representative figures are shown. (E) For quantification, total tube lengths were evaluated (n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs. siCtrCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. siCtrDex; (1-β) = 1). (F) For BrdU incorporation assay, cells were exposed to dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM) for 6 h or remained untreated (Ctr) (n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs. siCtrCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. siCtrDex; (1-β) = 1). Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases.
The effect of dexamethasone on vascular superoxide generation was next determined in a model of endogenous deficiency of functional NADPH oxidases: aortae were isolated from nmf333 mice lacking p22phox protein due to a point mutation in the Cyba gene encoding p22phox [48]. Compared to vessels from wild type mice, superoxide production upon dexamethasone treatment was diminished in p22phox-deficient vessels (Fig. 3F, Suppl. Fig. 6).
Fig. 6.
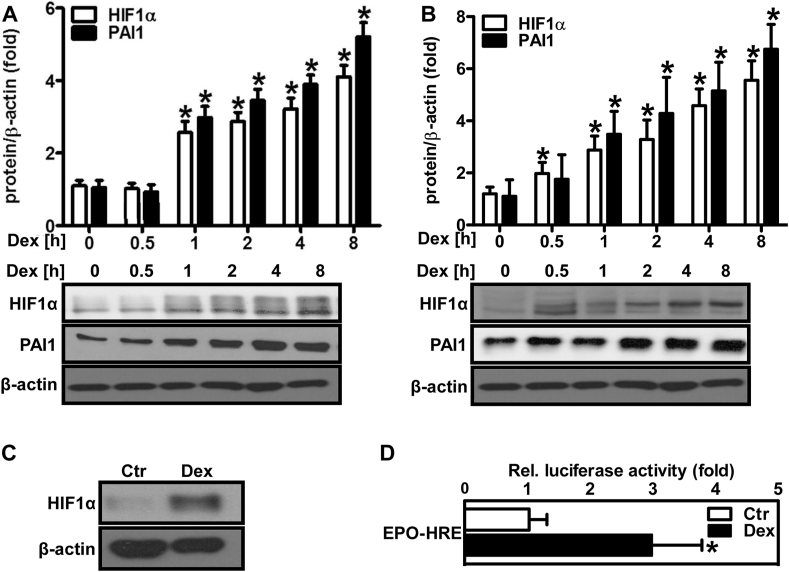
Dexamethasone increases HIF1α protein levels and HIF activity.
(A/B) Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) (A) and human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMC) (B) were exposed to dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM) for different time periods as indicated on the graph. Western blot analyses were performed using antibodies against HIF1α and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI1). β-Actin served as loading control (n = 3,*p < 0.05 vs. Dex 0 h; (1-β)>0.885). Representative blots are shown. (C) Wild type mice were orally supplemented with Dex (0.3 mg/kg/day) in the drinking water for 12 weeks. Litter mates drunk normal water (Ctr). Western blot analyses were performed from lung tissue lysates using an antibody against HIF1α. β-Actin served as loading control. Representative blots are shown. (D) HMEC-1 were transfected with a luciferase construct driven by three hypoxia-response elements from the 3'UTR of the erythropoietin gene (EPO-HRE) and exposed to Dex (10 nM) for 8 h. Luciferase assay was performed (n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs. Ctr; (1-β) = 1). Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases.
3.4. Dexamethasone increases the expression of NADPH oxidases
Since the data suggested that p22phox, NOX2 and NOX4 are important for dexamethasone-induced superoxide generation, we tested, in a next step, whether dexamethasone would also affect the expression levels of these NADPH oxidase subunits. For that purpose, HMEC-1 were stimulated with 10 nM dexamethasone for increasing time periods and Western blot and RT-qPCR analyses were performed (Fig. 4A/B). Exposure to dexamethasone rapidly increased protein and mRNA levels of p22phox and NOX4 in a time-dependent manner starting at 0.5 h and increasing until 8 h of treatment, while NOX2 levels remained unchanged. To test whether treatment with dexamethasone could also increase NADPH oxidase levels in vivo, lung tissue, which is highly vascularized, was extracted from wild type mice orally treated with dexamethasone (0.3 mg/kg/day) for 12 weeks. Western blot analyses revealed increased levels of p22phox and NOX4, but not NOX2, as was observed in cultivated vascular cells (Fig. 4C).
3.5. Dexamethasone enhances endothelial cell proliferation involving NADPH oxidases and HIF1a
ROS derived from NADPH oxidases have been previously shown to promote vascular proliferation and angiogenesis [54]. We, therefore, asked whether induction of ROS generation by NADPH oxidases through dexamethasone treatment would also affect proliferative responses of vascular cells. To this end, HMEC-1 were depleted of p22phox, NOX2 and NOX4 and proliferation was determined by 5-bromo-2′deoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation assay (Fig. 5A). While treatment of control cells with 10 nM dexamethasone for 24 h enhanced BrdU incorporation, this response was abolished in cells deficient of p22phox, NOX2 or NOX4 (Fig. 5A). As endothelial cell proliferation is associated with the formation of new vessels, we next tested whether dexamethasone and induction of NADPH oxidases would also affect the angiogenic response of HMEC-1. To this end, control cells and cells depleted of p22phox, NOX2 or NOX4 were plated on matrigel and exposed to dexamethasone for 6 h. While dexamethasone enhanced tube formation as an indicator of angiogenesis in control cells, this response was not observed in cells depleted of p22phox, NOX2 or NOX4 (Fig. 5B/C).
As the transcription factor HIF1 is known to regulate angiogenesis under hypoxia [55], we tested whether HIF1 would also be involved in dexamethasone-induced tube formation. In contrast to control cells, in HMEC-1 depleted of HIF1α by siRNA, the angiogenic response towards dexamethasone was blunted (Fig. 5D/E, Suppl. Fig. 6). In addition, depletion of HIF1α also decreased dexamethasone-induced proliferation of HMEC-1 (Fig. 5F).
3.6. Dexamethasone upregulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1 involving p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases
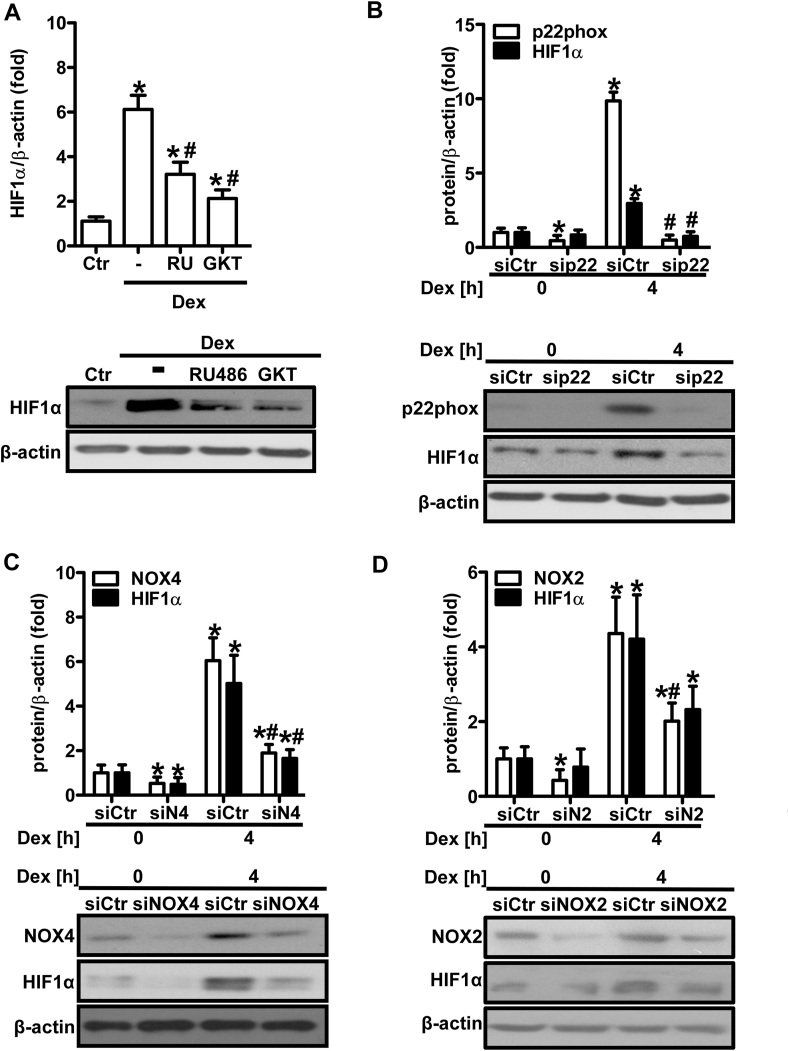
As HIF1α was involved in the angiogenic response towards dexamethasone, we tested whether dexamethasone would be able to induce and activate this transcription factor. Indeed, dexamethasone treatment upregulated protein levels of HIF1α, the inducible subunit of HIF1, in a time-dependent manner in HMEC-1 (Fig. 6A) and PASMC (Fig. 6B). HIF1α protein levels were also elevated in lungs from dexamethasone-treated wild type mice (Fig. 6C). Dexamethasone further increased HIF activity in HMEC-1 as was determined by a reporter gene assay (Fig. 6D). In line, dexamethasone also elevated protein levels of the HIF target gene plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI1), which is known to promote vascular proliferation and angiogenesis [56], in HMEC-1 (Fig. 6A) and PASMC (Fig. 6B). Furthermore, pretreatment with RU486 diminished the induction of HIF1α by dexamethasone (Fig. 7A), indicating the involvement of the glucocorticoid receptor. To test whether ROS and NADPH oxidases are involved in the regulation of HIF1α levels by dexamethasone, HMEC-1 were treated with the NADPH oxidase inhibitor GKT-137831 (Fig. 7A). In fact, HIF1α protein levels were diminished by this inhibitor in dexamethasone-treated HMEC-1. In support, in HMEC-1 cells depletion of p22phox (Fig. 7B) or NOX4 (Fig. 7C) significantly lowered HIF1α protein levels in response to dexamethasone treatment, while this response did not reach significance when NOX2 was depleted (Fig. 7D).
Fig. 7.
NADPH oxidases promote dexamethasone-induced HIF1α protein levels.
(A) HMEC-1 were treated or not (Ctr) with either RU486 (RU, 500 μM) or GKT-137831 (GKT, 50 μM) for 1 h prior to treatment with dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM) for 4 h. Western blot analyses were performed using an antibody against HIF1α. β-Actin served as loading control (n = 3; *p < 0.05 vs. Ctr; #p < 0.05 vs. Dex; (1-β)>0.955). Representative blots are shown. (B) HMEC-1 were transfected with siRNA against p22phox (sip22) or control siRNA (siCtr) and exposed to dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM) for 4 h. Western blot analyses were performed using antibodies against p22phox and HIF1α. β-Actin served as loading control (n = 3; *p < 0.05 vs. siCtrDex 0 h; #p < 0.05 vs. siCtrDex 4 h; (1-β) = 1). Representative blots of are shown. (C/D) HMEC-1 were transfected with siCtr or siRNA against NOX4 (siN4/siNOX4) (C) or NOX2 (siN2/siNOX2) (D) and exposed to Dex (10 nM) for 4 h. Western blot analyses were performed using antibodies against NOX4, NOX2 and HIF1α. β-Actin served as loading control (n = 3; *p < 0.05 vs. siCtrDex 0 h; #p < 0.05 vs. siCtrDex 4 h; (1-β) = 1). Representative blots are shown. Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases.
3.7. p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases promote dexamethasone-induced hypertension and left ventricular dysfunction
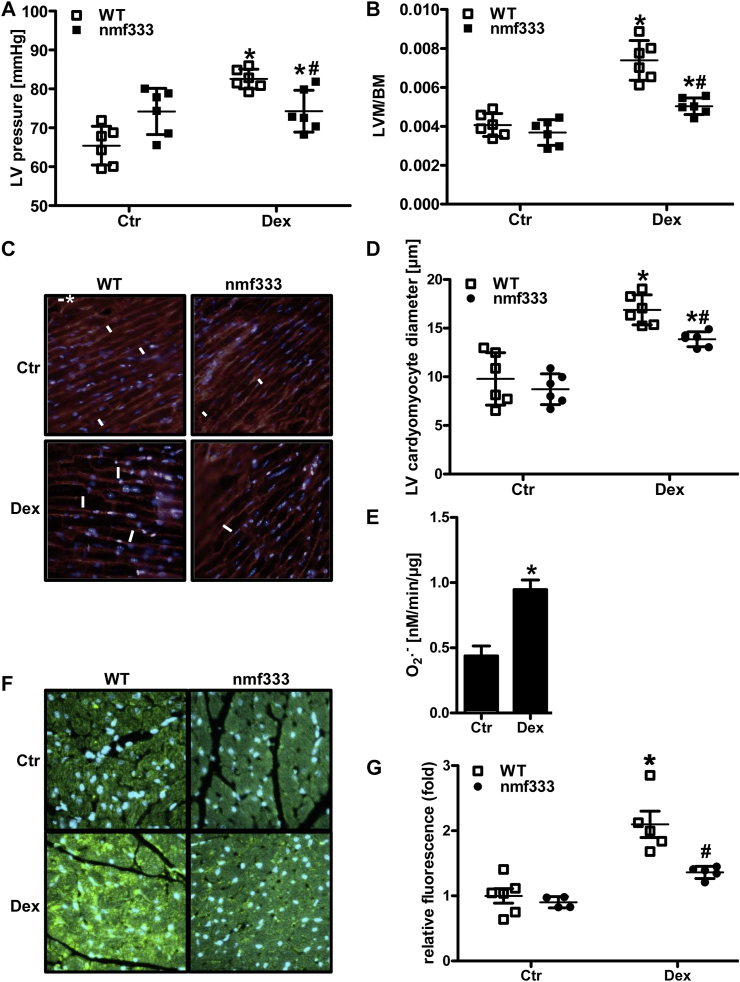
As dexamethasone treatment has been previously reported to lead to hypertension, we tested whether NADPH oxidases would contribute to this response. To this end, wild type mice and mice lacking p22phox protein and thus functional NADPH oxidases due to a mutation in the Cyba gene (nmf333) were chronically treated with low doses of dexamethasone (0.3 mg/kg/day) supplemented in the drinking water for 12 weeks. Indeed, hemodynamic measurements showed that treatment of wild type mice with dexamethasone increased left ventricular systolic pressure indicative of systemic hypertension (Fig. 8A). Consequently, dexamethasone-treated mice showed an increase in left ventricular mass and enlarged cardiomyocytes in the left ventricle pointing to the development of left ventricular hypertrophy (Fig. 8B–D). However, mice lacking p22phox were partially protected against dexamethasone-induced hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy (Fig. 8A–D).
Fig. 8.
Dexamethasone increases left ventricular pressure, remodeling and dysfunction dependent on p22phox.
(A/B) Wild type mice (WT) and mice deficient of p22phox due to a point mutation in the Cyba gene (nmf333) were orally supplemented with dexamethasone (Dex, 0.3 mg/kg/day) in the drinking water for 12 weeks. Litter mates drunk normal water (Ctr). (A) Left ventricular (LV) pressure was determined hemodynamically (n = 6; *p < 0.05 vs. WTCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. WTDex; (1-β) = 1). (B) Body mass (BM) and the mass of the left ventricle and septum (LVM) were evaluated, and LVM/BM ratios were determined ( n = 6; *p < 0.05, vs. WTCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. WTDex; (1-β)>0.837). (C/D) Formalin-fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) sections from the left ventricle were stained with wheat germ agglutinin. Nuclei were visualized with DAPI. (C) Representative stainings are shown. Scale bar with asterisk represents 10 μm. (D) LV cardiomyocyte diameters were determined in four high power fields per LV section (n = 5-6; *p < 0.05, vs. WTCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. WTDex; (1-β)>0.875). (E) Cardiomyocytes isolated from wild type mice were stimulated with dexamethasone (Dex, 10 nM) and superoxide generation was determined by EPR using CMH (n = 8; *p < 0.05, vs. Ctr; (1-β) = 1). (F/G) FFPE heart sections were stained with an antibody against 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine (8OHdG). Nuclei were visualized with DAPI. (F) Representative stainings are shown. (G) Fluorescence intensity of 60 nuclei was measured in four high power fields per heart section (n = 4-6; *p < 0.05, vs. WTCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. WTDex; (1-β) = 1). Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases.
To evaluate whether dexamethasone might be able to also exert a direct effect on cardiomyocyte superoxide production, cardiomyocytes were isolated from wild type mice and stimulated with dexamethasone (10 nM) for 4 h (Fig. 8E). Indeed, treatment with dexamethasone increased superoxide generation measured by EPR using CMH. Moreover, as a surrogate marker for increased ROS in tissues, heart sections were stained for the oxidative DNA damage marker 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine (8OHdG) (Fig. 8F). 8OHdG staining was increased in hearts from dexamethasone-treated wild type mice, while this response was markedly lower in hearts from dexamethasone-treated nmf333 mice (Fig. 8G).
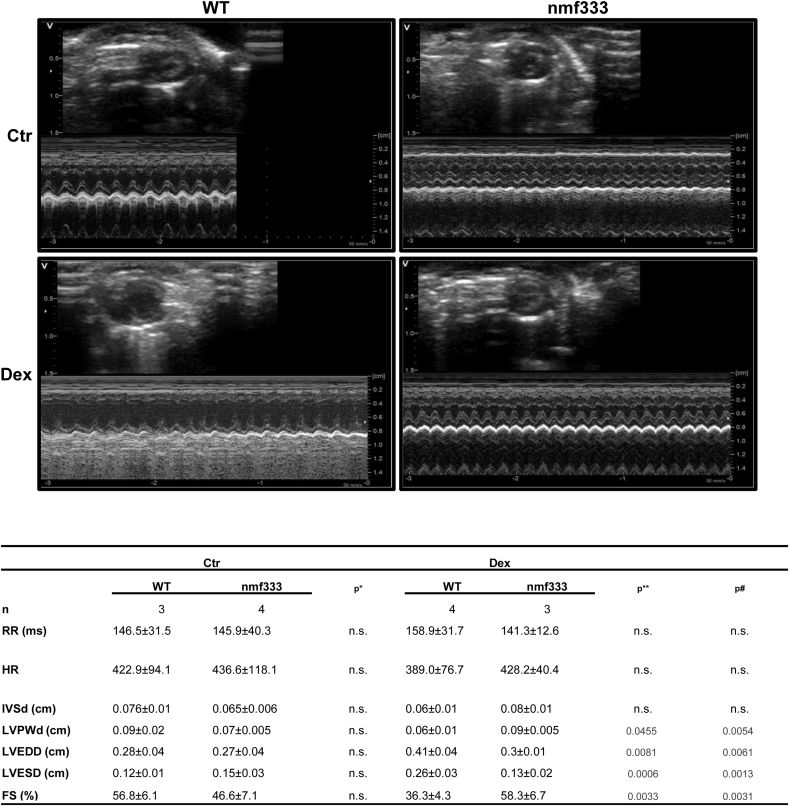
Subsequently, echocardiography showed that dexamethasone treatment of wild type mice leads to an enlarged left ventricle with increased left ventricular end-systolic and end-diastolic diameter, but decreased left ventricular wall thickness and decreased fractional shortening (Fig. 9). Again, p22phox-deficient mice were partially protected against dexamethasone-induced left ventricular dysfunction (Fig. 9).
Fig. 9.
Dexamethasone increases left ventricular dysfunction dependent on p22phox.
Wild type mice (WT) and mice deficient of p22phox due to a point mutation in the Cyba gene (nmf333) were orally supplemented with dexamethasone (Dex, 0.3 mg/kg/day) in the drinking water for 12 weeks. Litter mates drunk normal water (Ctr). Echocardiography of the left ventricle was performed in M-mode. Representative echocardiography figures are shown (n = 3–4, *p < 0.05 WTCtr vs. nmf333Ctr; **p < 0.05 WTCtr vs. WTDex; #p < 0.05 WTDex vs. nmf333Dex; (1-β)>0.999). Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases. n.s. - not significant; n – number of mice; RR – interval duration; HR – heart rate; IVSd - intraventricular septal width (diastole); LVPWd - left ventricular posterior wall (diastole); LVEDD - left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; LVESD - left ventricular end-systolic diameter; FS - fractional shortening.
3.8. NADPH oxidases promote pulmonary hypertension upon dexamethasone treatment
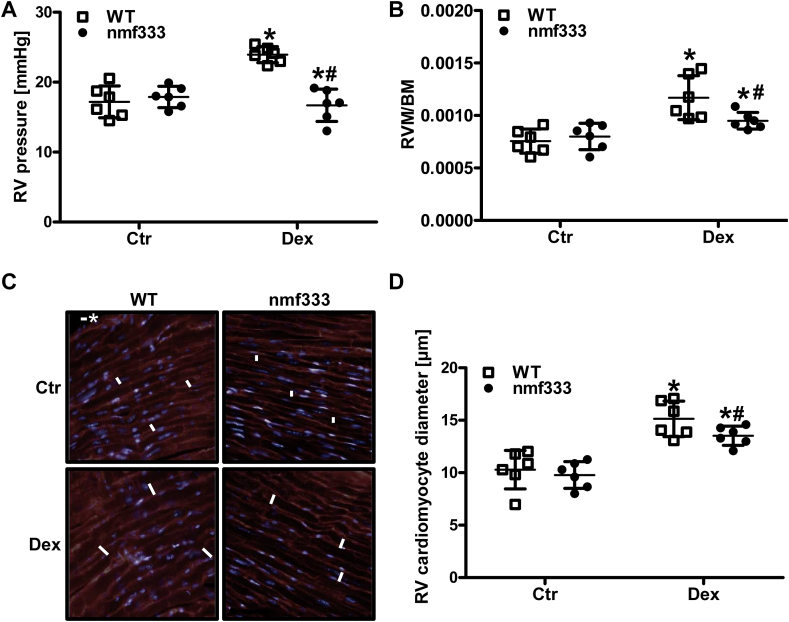
Interestingly, hemodynamic measurements further showed that dexamethasone treatment not only increased the pressure in the left, but also in the right ventricle (Fig. 10A). Moreover, right ventricular mass and the size of right ventricular cardiomyocytes were increased indicative of right ventricular hypertrophy (Fig. 10B/C). However, mice lacking p22phox were partially protected against dexamethasone-induced pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular hypertrophy (Fig. 10A–C).
Fig. 10.
Dexamethasone increases right ventricular pressure and remodeling dependent on p22phox. (A-D) Wild type mice (WT) and mice deficient of p22phox due to a point mutation in the Cyba gene (nmf333) were orally supplemented with dexamethasone (Dex, 0.3 mg/kg/day) in the drinking water for 12 weeks. Litter mates drunk normal water (Ctr). (A) Right ventricular (RV) pressure was determined hemodynamically (n = 6; *p < 0.05 vs. WTCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. WTDex; (1-β)>0.825). (B) Body mass (BM) and the mass of the right ventricle (RVM) were evaluated, and RVM/BM ratios were determined (n = 6; *p < 0.05, vs. WTCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. WTDex; (1-β)>0.856). (C/D) Formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sections from the right ventricle were stained with wheat germ agglutinin. (C) Representative stainings are shown. Scale bar with asterisk represents 10 μm. (D) RV cardiomyocyte diameters were determined in four high power fields per RV section (n = 6; *p < 0.05, vs. WTCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. WTDex; (1-β)>0.832). Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases.
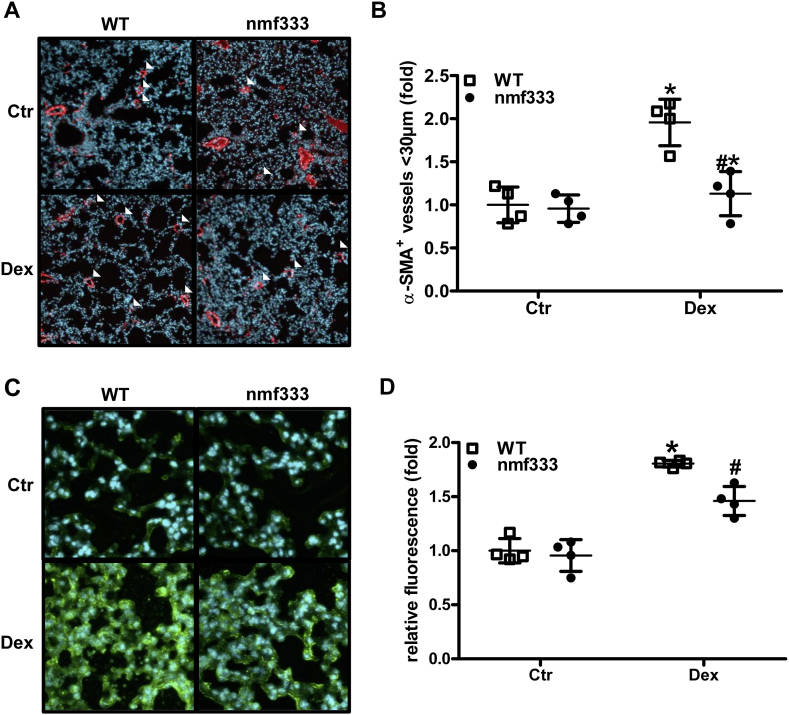
As increased right ventricular pressure and right ventricular hypertrophy are often associated with remodeling of the pulmonary vasculature in pulmonary hypertension, α-smooth muscle actin positive vessels were determined in lung tissue sections. In fact, dexamethasone-treated wild type mice showed an increased number of small muscularized vessels in lungs indicative of pulmonary vascular remodeling (Fig. 11A/B). However, similar to the situation with cardiac remodeling, pulmonary vascular remodeling was decreased in lungs derived from dexamethasone-treated nmf333 mice (Fig. 11A/B). Moreover, similar to the situation in the heart, dexamethasone treatment increased 8OHdG staining in wild type lungs, while this response was reduced in lungs from dexamethasone-treated nmf333 mice (Fig. 11C/D).
Fig. 11.
p22phox promotes dexamethasone-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling and pulmonary ROS.
(A–D) Wild type mice (WT) and mice deficient of p22phox due to a point mutation in the Cyba gene (nmf333) were orally supplemented with dexamethasone (Dex, 0.3 mg/kg/day) in the drinking water for 12 weeks. Litter mates drunk normal water (Ctr). Formalin-fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) lung sections were stained with primary antibodies against (A/B) α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) or (C/D) 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine (8OHdG) and visualized with a secondary antibody conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488. Nuclei were visualized with DAPI. (A/C) Representative stainings are shown. (B) α-SMA-positive small- and medium-sized arterioles (<30 μm) were counted and related to the total number of arterioles of the same diameter in four high power fields per lung section (n = 4; *p < 0.05, vs. WTCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. WTDex; (1-β)>0.994). (D) Fluorescence intensity of 60 nuclei was measured in four high power fields per lung section (n = 4; *p < 0.05, vs. WTCtr; #p < 0.05 vs. WTDex; (1-β) = 1). Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases.
3.9. HIF1α contributes to dexamethasone-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling
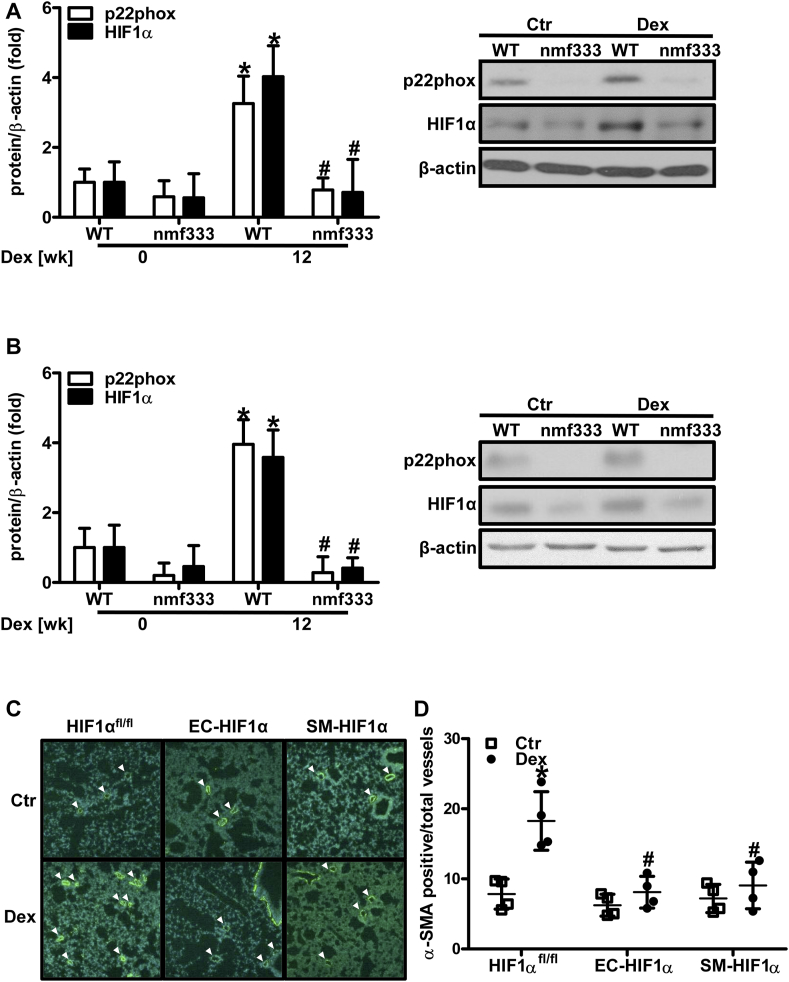
To test whether induction of HIF1α by dexamethasone and NADPH oxidases would also play a role in the in vivo setting, HIF1α levels were determined in lungs and hearts of mice chronically treated with dexamethasone (Fig. 12 A/B). Similar to the situation in vitro, dexamethasone treatment increased the levels of HIF1α in control mice; however, this increase was significantly lower in p22phox-deficient mice indicating that NADPH oxidases are required for the induction of HIF1α also in vivo.
Fig. 12.
Dexamethasone-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling is dependent on p22phox and HIF1α.
(A/B) Wild type mice (WT) and mice deficient of p22phox due to a point mutation in the Cyba gene (nmf333) were orally supplemented with dexamethasone (Dex, 0.3 mg/kg/day) in the drinking water for 12 weeks. Litter mates drunk normal water (Ctr). Western blot analyses were performed from lung (A) and heart (B) tissue lysates using antibodies against HIF1α and p22phox. β-Actin served as loading control (n = 3–4, *p < 0.05 WT DEX 0 wk; #p < 0.05 vs. WT Dex 12 wk; (1-β) = 1). Representative blots are shown. (C/D) Tie2CreHIF1α mice lacking HIF1α in endothelial cells (EC-HIF1α), Sm22CreHIF1α mice lacking HIF1α in smooth muscle cells (SM-HIF1α) and HIF1αfl/fl mice were orally supplemented with Dex (0.3 mg/kg/day) in the drinking water for 12 weeks. Litter mates drunk normal water (Ctr). Formalin-fixed paraffin embedded lung tissue sections were stained with an antibody against α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) to visualize vascular remodeling. (C) Representative stainings are shown. (D) α-SMA-positive small- and medium-sized arterioles (<30 μm) were counted and related to the total number of arterioles of the same diameter in four high power fields per lung section (n = 4; *p < 0.05, vs. HIF1αfl/fl Ctr; #p < 0.05 vs. HIF1αfl/fl Dex; (1-β) = 1). Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in all cases.
Next, we tested whether the NADPH oxidase target HIF1α would also be involved in the chronic response towards dexamethasone in vivo. Since our results showed that dexamethasone treatment increased HIF1α levels in endothelial and smooth muscle cells, which both contribute to pulmonary vascular remodeling, mice lacking HIF1α in the endothelial or smooth muscle cell layer were treated with dexamethasone for 12 weeks (Fig. 12C/D). Compared to control mice, dexamethasone-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling was decreased in mice lacking HIF1α either in the endothelium (Tie2CreHIF1α) or in smooth muscle cells (Sm22CreHIF1α) similar to the situation with nmf333 mice.
4. Discussion
In this study, we demonstrate that chronic glucocorticoid excess induced by treatment with low dose dexamethasone upregulates and activates p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases leading to systemic hypertension, cardiac dysfunction and subsequently pulmonary hypertension in conjunction with pulmonary vascular remodeling. Mechanistically, activation of the HIF pathway following increased vascular superoxide generation contributed to this response.
Although dexamethasone and other glucocorticoids have been reported to decrease the levels of ROS in vascular cells, these studies used dexamethasone in activated or pre-stimulated cells often mimicking an inflammatory condition [[28], [29], [30], [31], [32], [33]]. However, the effects of glucocorticoids on untreated cells or healthy tissues have been overlooked for a long time. Our study showed that in cardiovascular cells and isolated vessels, dexamethasone concentrations between 10 nM and 1 μM robustly increased superoxide production and H2O2 levels. This is in line with more recent studies, demonstrating increased ROS levels upon exposure to dexamethasone in endothelial and smooth muscle cells [35,58], but also in several other cell types [[59], [60], [61], [62], [63]], independent from an inflammatory or otherwise stimulated condition. In support, an increase in blood oxidative stress markers has been reported in patients with hypercortisolism (M. Cushing) [64,65].
Previous reports suggested that glucocorticoids can exert an inhibitory effect on NO synthases which indirectly could contribute to increased superoxide levels [8]. However, NO synthase inhibition had no effects on superoxide levels suggesting that neither a decrease in functional NO synthase nor uncoupling of NO synthase significantly contributed to dexamethasone-stimulated superoxide generation. Furthermore, xanthine oxidase did not appear to mediate the ROS response to dexamethasone in vascular cells whereas the mitochondrial scavenger MitoQ seemed to reduce ROS generation after dexamethasone treatment. While dexamethasone has been linked to mitochondrial dysfunction in some cell types [66], inhibition of complex I and complex II did not affect ROS generation in our study, suggesting the involvement of other mitochondrial ROS sources. Interestingly, recent studies suggest that the p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidase NOX4 could promote mitochondrial ROS production [67]. In line, our data provide strong evidence for a crucial role of p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases promoting superoxide production in response to dexamethasone in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, increased ROS load by dexamethasone was, on the one hand, mediated by upregulation of p22phox and, dependent on the cell type, NOX1 and/or NOX4, at the mRNA and protein level in cultivated cells as well as in the in vivo situation. On the other hand, Rac1 which is required for activation of NOX2 (and NOX1) containing NADPH oxidases also contributed to dexamethasone-induced superoxide production. In line, glucocorticoids have been reported to activate Rac1 dependent on PI-3 kinase [68], and our data show that PI-3 kinase as well as the glucocorticoid receptor promote superoxide formation by dexamethasone. Interestingly, depletion of p22phox as well as of NOX2 or NOX4 in HMEC-1 and PASMC resulted in comparable reductions of superoxide production while depletion of NOX1 only affected superoxide production in PASMC although to a lower extent than depletion of NOX2, NOX4 or p22phox. While one would have expected that loss of p22phox would result in a larger decrease in superoxide production than the loss of a single NOX subunit, findings in triple knock out mice lacking NOX1, NOX2 and NOX4 also showed that there was a substantial, not easily explainable residue in ROS generation [69]. One reason for our observations could be that silencing of p22phox was less effective than silencing of the NOXes, a notion which would also explain that depletion of p22phox was less efficient than the Y121H mutation in reducing superoxide generation. These observations would also be compatible with a role of NOX5, which is independent of p22phox and not expressed in rodents [70]. They also show that the interplay between the different NOX enzymes in one cell is not linear or additive and still lacks further in depth studies.
In contrast to the findings in this study, dexamethasone has been reported to decrease p22phox or NOX2 mRNA levels in activated microglia or stimulated smooth muscle cells [28,31,32]. However, in support of our findings in untreated vascular cells, dexamethasone has been shown to increase levels of NOX1 in smooth muscle cells [35], as well as of p22phox and NOX4 in other cell types [60,61,[71], [72], [73]] independent of inflammatory conditions. Together, these data strongly point to a critical role of p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases in the superoxide response to dexamethasone involving (genomic) upregulation of p22phox, NOX1 and NOX4, as well as (non-genomic) activation of NOX2 by PI-3 kinase and Rac1.
We further identified HIF1 as a target of dexamethasone-induced ROS generation by p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases, in particular NOX4. Although HIF1 is known as the master regulator of the response to hypoxia [74], there is increasing evidence that it is also responsive to non-hypoxic stimuli including growth factors, peptide hormones or hemostatic factors and that ROS derived from NADPH oxidases play an important role in regulating the HIF pathway at various levels [44,[75], [76], [77], [78], [79]]. While several previous studies reported that dexamethasone downregulates HIF1α protein levels or HIF activity in different cellular models under hypoxia [[80], [81], [82], [83]], it has also been shown that dexamethasone promotes HIF signaling under hypoxia [84]. In line with our data under normoxia, recent data indicate that dexamethasone increases HIF activity and HIF1α protein levels in zebrafish and human liver cells involving c-src-dependent degradation of the ubiquitin ligase pVHL, thus allowing HIF1α stabilization under normoxic conditions [85]. As c-src has been shown to be closely linked to ROS and NADPH oxidases [86], such a pathway might also contribute to NADPH oxidase-dependent induction of HIF1α in response to dexamethasone in the cardiovascular system.
As a functional consequence, activation of the NADPH oxidase-HIF1 axis by dexamethasone stimulated vascular proliferation and tube formation of cultivated endothelial cells. While both, NADPH oxidases and HIF1 have been shown to promote vascular proliferation and angiogenesis in response to different stimuli also under normoxic conditions [44,54,57], controversial data exist on the role of dexamethasone and other glucocorticoids in vascular proliferation and angiogenesis. In diseased conditions, such as in wound healing, diabetic retinopathy or in tumors, application of dexamethasone has been reported to decrease vascular proliferation or to even act angiostatic [[87], [88], [89]].
However, this response seems to be crucially dependent on the context and cell type. For example, in mesenchymal derived glioblastomas, but not in proneural glioblastomas, dexamethasone elevated cell proliferation and angiogenesis in vivo [90,91]. Moreover, dexamethasone not only stimulated endothelial proliferation, but also angiogenesis in the chicken allantois model [92] and in an osteogenesis model [93] independent of an inflammatory context. In addition to context and cell type, also the concentrations of glucocorticoids seem to determine the proliferative outcome: while high concentrations of dexamethasone and other glucocorticoids more frequently decreased proliferation or even induced apoptosis in vascular cells [94,95], low doses of dexamethasone as applied in our study promoted proliferation of endothelial [92,96] and smooth muscle cells [97]. Since endothelial proliferation promoting an angiogenic response has been observed in early stages of cardiac hypertrophy [98] such a response might also take place in dexamethasone-induced cardiac hypertrophy.
Our study further indicated that NADPH oxidases contribute to the development of hypertension upon chronic treatment with dexamethasone in vivo: whereas wild type mice developed an increase in left ventricular pressure indicative of systemic hypertension, p22phox-deficient mice were protected from this complication. In support of our findings, antioxidant treatment has been shown to prevent the development of hypertension in response to dexamethasone treatment in mice [36,37,39] and to reduce endothelial dysfunction in glucocorticoid-treated patients [34], pointing to a role of ROS derived from NADPH oxidases in the pathogenesis of glucocorticoid-induced hypertension. In line, NADPH oxidases have been shown to contribute to the pathogenesis of hypertension in several animal models including angiotensin–II–induced hypertension by promoting ROS-induced vasoconstriction [99]. In addition, patients lacking functional NADPH oxidases seem to be protected against the development of endothelial dysfunction [100]. Interestingly, it has been suggested that glucocorticoids can increase blood pressure by inducing the generation of angiotensin-II [101]. Thus, the hypertensive response by glucocorticoids might not only be mediated by direct upregulation/activation of NADPH oxidases in the vascular wall, but also secondary due to increased angiotensin-II levels with subsequent activation of NADPH oxidases. Further studies, which are beyond the scope of this study, will be required to dissect this particular point.
Moreover, dexamethasone-treated wild type mice developed an enlarged left ventricle with signs of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and left ventricular dysfunction possibly as a result of the hypertensive state, although direct hypertrophic effects of dexamethasone on cardiomyocytes have been reported and cannot be ruled out [102]. In line with our findings, rats treated with dexamethasone developed hypertension and left ventricular dysfunction [103], and cardiac dysfunction has also been described in patients with Cushing syndrome [104,105] or in preterm infants treated with dexamethasone [104,105]. In line, dexamethasone increased superoxide generation in isolated cardiomyocytes as well as in the heart as emphasized by increased oxidative DNA damage staining. Importantly, however, mice deficient in p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases were completely protected from these cardiac side effects of dexamethasone treatment further emphasizing the critical role these enzymes play in the in vivo response of the cardiovascular system towards dexamethasone. In support, an increase in lipid peroxidation indicative of ROS generation, and elevated levels of HIF1α have been found in hearts from mice suffering from dexamethasone-induced cardiac remodeling and left ventricular dysfunction [103], while NADPH oxidases have been reported to mediate cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction in response to angiotensin-II or adrenergic stimulation [106].
While the development of systemic hypertension is a well perceived side effect of dexamethasone treatment, our study provides further evidence that this treatment also affects the pulmonary vasculature and the right ventricle, since dexamethasone-treated wild type mice showed signs of pulmonary hypertension with increased right ventricular pressure, right ventricular hypertrophy and pulmonary vascular remodeling. In line with our study, right ventricular dysfunction has been reported in patients with Cushing syndrome [105]. In addition, dexamethasone treatment of rats increased pulmonary vascular collagen deposition, frequently observed in pulmonary vascular remodeling [107]. While it is not completely clear whether pulmonary hypertension developed as a consequence of left ventricular dysfunction [108], and/or whether dexamethasone has also direct effects on right ventricular cardiomyocytes and the pulmonary vasculature, our data clearly show that p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases are critically involved in dexamethasone-induced pulmonary hypertension. This is underlined by our findings that dexamethasone and p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases not only contribute to increased superoxide generation in vitro in HMEC-1 cells, PASMC and cardiomyocytes, but also in vivo as evidenced by increased oxidative DNA damage as a surrogate marker of ROS. Similarly, dexamethasone and p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases not only increased HIF1α levels in cultivated cells but also in the in vivo situation in heart and lung tissues. In strong support, HIF1α deficiency in endothelial and smooth muscle cells protected against the development of pulmonary vascular remodeling upon dexamethasone treatment. In line, both p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases and HIF1α have been shown to contribute to the development of pulmonary hypertension in response to hypoxia [[109], [110], [111], [112], [113]] and have been suggested to also play a role in non-hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and vascular remodeling induced by monocrotaline [112,114,115]. In support, dexamethasone induced endothelial proliferative activity dependent on p22phox and HIF1α as was shown by tube formation assays, suggesting that this pathway might be linked to the dysfunctional angiogenesis observed in pulmonary vascular remodeling eventually leading to plexiform lesions in human pulmonary hypertension [116].
On the contrary, dexamethasone has been shown to protect against the development of proinflammatory pulmonary hypertension induced by monocrotaline [95,117] and of pulmonary artery endothelial dysfunction in response to hypoxia [118]. While the role of ROS has not been investigated in these studies, they further emphasize the distinct roles glucocorticoids play in inflammatory or diseased conditions as opposed to the healthy situation.
While the reasons for the divergent effects of dexamethasone on ROS levels under basal and inflammatory conditions are not well understood, they might at least in part relate to the different roles of glucocorticoids during the stress response [10,11]: in the context of stress or disease, glucocorticoids act repressive. Thus, reduced ROS levels in activated or diseased cells or tissues in the presence of glucocorticoids might prevent further tissue damage. Furthermore, during an inflammatory state, stress-induced (or pharmacological) concentrations of glucocorticoids might restrain the immune response, by blunting the propagation of innate immune response signaling not only at the level of cytokines [1], but possibly also by restricting ROS generation by NADPH oxidases in the diseased tissues, thereby shortening the duration of the immune response.
On the other hand, in non-diseased conditions or organs, glucocorticoids can exert stimulatory actions. Thus, increased generation of signaling molecules such as ROS by dexamethasone might contribute to activate cells, e.g. to prepare for a stress response. In this regard, it might well be that in the absence of inflammation, glucocorticoid exposure at low doses and/or before challenge will sensitize the innate immune system not only by upregulating pattern recognition receptors, cytokine receptors and complement factors, thus allowing for rapid responses to danger signals [1], but also by inducing NADPH oxidases which might help to activate a rapid inflammatory response upon tissue insult. Whether increased ROS generation might also be related to the proposed pro-inflammatory role of glucocorticoids remains to be determined [13].
In conclusion, this study provides strong evidence that dexamethasone increases NADPH oxidase-dependent superoxide generation in a non-inflammatory cardiovascular context, leading to activation of the HIF pathway, and that this signaling cascade promotes cardiovascular side effects of chronic dexamethasone therapy. Thus, targeting NADPH oxidases and the HIF pathway might be interesting novel strategies to prevent cardiovascular complications of glucocorticoid therapy or other conditions of glucocorticoid excess.
Funding
The study has been supported by German Research Foundation, DFG grant GO709/4-5, EU FP7 project Metoxia, Förderverein Deutsches Herzzentrum München eV, Bavarian-Czech Academic Agency, Bavarian Research Alliance, and Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF, Epiros/Acidox, projects). Anna Knirsch and Mathieu Klop hold a scholarship of the Translational Medicine Program of the Medical School, Technical University Munich.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. Karim Sabrane for generating Tie2CreHIF1α and Sm22CreHIF1α mice, and Dr. Zuwen Zhang for breeding all genetically modified mouse lines.
Footnotes
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101536.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following are the Supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.Cain D.W., Cidlowski J.A. Immune regulation by glucocorticoids. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017;17(4):233–247. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fardet L., Feve B. Systemic glucocorticoid therapy: a review of its metabolic and cardiovascular adverse events. Drugs. 2014;74(15):1731–1745. doi: 10.1007/s40265-014-0282-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baid S., Nieman L.K. Glucocorticoid excess and hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2004;6(6):493–499. doi: 10.1007/s11906-004-0046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Peppa M., Krania M., Raptis S.A. Hypertension and other morbidities with Cushing's syndrome associated with corticosteroids: a review. Integrated Blood Pres. Contr. 2011;4:7–16. doi: 10.2147/IBPC.S9486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pimenta E., Wolley M., Stowasser M. Adverse cardiovascular outcomes of corticosteroid excess. Endocrinology. 2012;153(11):5137–5142. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wei L., MacDonald T.M., Walker B.R. Taking glucocorticoids by prescription is associated with subsequent cardiovascular disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004;141(10):764–770. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-141-10-200411160-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kadmiel M., Cidlowski J.A. Glucocorticoid receptor signaling in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013;34(9):518–530. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.07.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lee S.R., Kim H.K., Youm J.B., Dizon L.A., Song I.S., Jeong S.H. Non-genomic effect of glucocorticoids on cardiovascular system. Pflueg. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2012;464(6):549–559. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Girod J.P., Brotman D.J. Does altered glucocorticoid homeostasis increase cardiovascular risk? Cardiovasc. Res. 2004;64(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sapolsky R.M., Romero L.M., Munck A.U. How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr. Rev. 2000;21(1):55–89. doi: 10.1210/edrv.21.1.0389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Munck A., Naray-Fejes-Toth A. Glucocorticoids and stress: permissive and suppressive actions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994;746:115–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb39221.x. discussion 31-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Duque Ede A., Munhoz C.D. The pro-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids in the brain. Front. Endocrinol. 2016;7:78. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Geer E.B., Islam J., Buettner C. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance: focus on adipose tissue function and lipid metabolism. Endocrinol Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2014;43(1):75–102. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2013.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lefer A.M. Influence of corticosteroids on mechanical performance of isolated rat papillary muscles. Am. J. Physiol. 1968;214(3):518–524. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.3.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Oakley R.H., Cidlowski J.A. Glucocorticoid signaling in the heart: a cardiomyocyte perspective. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015;153:27–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.03.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Goodwin J.E., Geller D.S. Glucocorticoid-induced hypertension. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2012;27(7):1059–1066. doi: 10.1007/s00467-011-1928-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Goodwin J.E., Zhang J., Geller D.S. A critical role for vascular smooth muscle in acute glucocorticoid-induced hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. : JASN (J. Am. Soc. Nephrol.) 2008;19(7):1291–1299. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2007080911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Goodwin J.E., Zhang J., Gonzalez D., Albinsson S., Geller D.S. Knockout of the vascular endothelial glucocorticoid receptor abrogates dexamethasone-induced hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2011;29(7):1347–1356. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328347da54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sugamura K., Keaney J.F., Jr. Reactive oxygen species in cardiovascular disease. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2011;51(5):978–992. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kietzmann T., Petry A., Shvetsova A., Gerhold J.M., Gorlach A. The epigenetic landscape related to reactive oxygen species formation in the cardiovascular system. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017;174(12):1533–1554. doi: 10.1111/bph.13792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Brown D.I., Griendling K.K. Regulation of signal transduction by reactive oxygen species in the cardiovascular system. Circ. Res. 2015;116(3):531–549. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Madamanchi N.R., Runge M.S. Redox signaling in cardiovascular health and disease. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2013;61:473–501. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sirker A., Zhang M., Shah A.M. NADPH oxidases in cardiovascular disease: insights from in vivo models and clinical studies. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2011;106(5):735–747. doi: 10.1007/s00395-011-0190-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lassegue B., San Martin A., Griendling K.K. Biochemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology of NADPH oxidases in the cardiovascular system. Circ. Res. 2012;110(10):1364–1390. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.243972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Babior B.M. NADPH oxidase: an update. Blood. 1999;93(5):1464–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bedard K., Krause K.H. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007;87(1):245–313. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00044.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Marumo T., Schini-Kerth V.B., Brandes R.P., Busse R. Glucocorticoids inhibit superoxide anion production and p22 phox mRNA expression in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Hypertension. 1998;32(6):1083–1088. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.32.6.1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gero D., Szabo C. Glucocorticoids suppress mitochondrial oxidant production via upregulation of uncoupling protein 2 in hyperglycemic endothelial cells. PloS One. 2016;11(4) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Colton C.A., Chernyshev O.N. Inhibition of microglial superoxide anion production by isoproterenol and dexamethasone. Neurochem. Int. 1996;29(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(95)00139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Huo Y., Rangarajan P., Ling E.A., Dheen S.T. Dexamethasone inhibits the Nox-dependent ROS production via suppression of MKP-1-dependent MAPK pathways in activated microglia. BMC Neurosci. 2011;12:49. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Condino-Neto A., Whitney C., Newburger P.E. Dexamethasone but not indomethacin inhibits human phagocyte nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activity by down-regulating expression of genes encoding oxidase components. J. Immunol. 1998;161(9):4960–4967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Roshol H., Skrede K.K., Ce A.E., Wiik P. Dexamethasone and methylprednisolone affect rat peritoneal phagocyte chemiluminescence after administration in vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995;286(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00430-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Iuchi T., Akaike M., Mitsui T., Ohshima Y., Shintani Y., Azuma H. Glucocorticoid excess induces superoxide production in vascular endothelial cells and elicits vascular endothelial dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2003;92(1):81–87. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000050588.35034.3c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Siuda D., Tobias S., Rus A., Xia N., Forstermann U., Li H. Dexamethasone upregulates Nox1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Pharmacology. 2014;94(1–2):13–20. doi: 10.1159/000365932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhang Y., Croft K.D., Mori T.A., Schyvens C.G., McKenzie K.U., Whitworth J.A. The antioxidant tempol prevents and partially reverses dexamethasone-induced hypertension in the rat. Am. J. Hypertens. 2004;17(3):260–265. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2003.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Safaeian L., Zabolian H. Antioxidant effects of bovine lactoferrin on dexamethasone-induced hypertension in rat. ISRN Pharmacol. 2014;2014:943523. doi: 10.1155/2014/943523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chaumais M.C., Ranchoux B., Montani D., Dorfmuller P., Tu L., Lecerf F. N-acetylcysteine improves established monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Respir. Res. 2014;15:65. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-15-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hu L., Zhang Y., Lim P.S., Miao Y., Tan C., McKenzie K.U. Apocynin but not L-arginine prevents and reverses dexamethasone-induced hypertension in the rat. Am. J. Hypertens. 2006;19(4):413–418. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2005.09.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kracun D., Riess F., Kanchev I., Gawaz M., Gorlach A. The beta3-integrin binding protein beta3-endonexin is a novel negative regulator of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2014;20(13):1964–1976. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Djordjevic T., Hess J., Herkert O., Gorlach A., BelAiba R.S. Rac regulates thrombin-induced tissue factor expression in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells involving the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2004;6(4):713–720. doi: 10.1089/1523086041361703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ades E.W., Candal F.J., Swerlick R.A., George V.G., Summers S., Bosse D.C. HMEC-1: establishment of an immortalized human microvascular endothelial cell line. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1992;99(6):683–690. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12613748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kietzmann T., Cornesse Y., Brechtel K., Modaressi S., Jungermann K. Perivenous expression of the mRNA of the three hypoxia-inducible factor alpha-subunits, HIF1alpha, HIF2alpha and HIF3alpha, in rat liver. Biochem. J. 2001;354(Pt 3):531–537. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3540531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gorlach A., Diebold I., Schini-Kerth V.B., Berchner-Pfannschmidt U., Roth U., Brandes R.P. Thrombin activates the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells: role of the p22(phox)-containing NADPH oxidase. Circ. Res. 2001;89(1):47–54. doi: 10.1161/hh1301.092678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chalupsky K., Kracun D., Kanchev I., Bertram K., Gorlach A. Folic acid promotes recycling of tetrahydrobiopterin and protects against hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension by recoupling endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2015;23(14):1076–1091. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Dikalov S.I., Kirilyuk I.A., Voinov M., Grigor'ev I.A. EPR detection of cellular and mitochondrial superoxide using cyclic hydroxylamines. Free Radic. Res. 2011;45(4):417–430. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2010.540242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhang Z., Trautz B., Kracun D., Vogel F., Weitnauer M., Hochkogler K. Stabilization of p22phox by hypoxia promotes pulmonary hypertension. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2019;30(1):56–73. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Nakano Y., Longo-Guess C.M., Bergstrom D.E., Nauseef W.M., Jones S.M., Banfi B. Mutation of the Cyba gene encoding p22phox causes vestibular and immune defects in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2008;118(3):1176–1185. doi: 10.1172/JCI33835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ryan H.E., Poloni M., McNulty W., Elson D., Gassmann M., Arbeit J.M. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is a positive factor in solid tumor growth. Canc. Res. 2000;60(15):4010–4015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Coelho-Filho O.R., Shah R.V., Mitchell R., Neilan T.G., Moreno H., Jr., Simonson B. Quantification of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by cardiac magnetic resonance: implications for early cardiac remodeling. Circulation. 2013;128(11):1225–1233. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.000438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wolf C.M., Moskowitz I.P., Arno S., Branco D.M., Semsarian C., Bernstein S.A. Somatic events modify hypertrophic cardiomyopathy pathology and link hypertrophy to arrhythmia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005;102(50):18123–18128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509145102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Limbourg F.P., Liao J.K. Nontranscriptional actions of the glucocorticoid receptor. J. Mol. Med. 2003;81(3):168–174. doi: 10.1007/s00109-003-0418-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Aoyama T., Paik Y.H., Watanabe S., Laleu B., Gaggini F., Fioraso-Cartier L. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase in experimental liver fibrosis: GKT137831 as a novel potential therapeutic agent. Hepatology. 2012;56(6):2316–2327. doi: 10.1002/hep.25938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ushio-Fukai M. Redox signaling in angiogenesis: role of NADPH oxidase. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006;71(2):226–235. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Pugh C.W., Ratcliffe P.J. Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: role of the HIF system. Nat. Med. 2003;9(6):677–684. doi: 10.1038/nm0603-677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Agirbasli M. Pivotal role of plasminogen-activator inhibitor 1 in vascular disease. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2005;59(1):102–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2005.00379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rey S., Semenza G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent mechanisms of vascularization and vascular remodelling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010;86(2):236–242. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Furst R., Zahler S., Vollmar A.M. Dexamethasone-induced expression of endothelial mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 involves activation of the transcription factors activator protein-1 and 3',5'-cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate response element-binding protein and the generation of reactive oxygen species. Endocrinology. 2008;149(7):3635–3642. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhu F.B., Wang J.Y., Zhang Y.L., Quan R.F., Yue Z.S., Zeng L.R. Curculigoside regulates proliferation, differentiation, and pro-inflammatory cytokines levels in dexamethasone-induced rat calvarial osteoblasts. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015;8(8):12337–12346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Li J., He C., Tong W., Zou Y., Li D., Zhang C. Tanshinone IIA blocks dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in osteoblasts through inhibiting Nox4-derived ROS production. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015;8(10):13695–13706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Guo B., Zhang W., Xu S., Lou J., Wang S., Men X. GSK-3beta mediates dexamethasone-induced pancreatic beta cell apoptosis. Life Sci. 2016;144:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.11.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kraaij M.D., van der Kooij S.W., Reinders M.E., Koekkoek K., Rabelink T.J., van Kooten C. Dexamethasone increases ROS production and T cell suppressive capacity by anti-inflammatory macrophages. Mol. Immunol. 2011;49(3):549–557. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2011.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Park G.B., Choi Y., Kim Y.S., Lee H.K., Kim D., Hur D.Y. ROS and ERK1/2-mediated caspase-9 activation increases XAF1 expression in dexamethasone-induced apoptosis of EBV-transformed B cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013;43(1):29–38. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Karamouzis I., Berardelli R., D'Angelo V., Fussotto B., Zichi C., Giordano R. Enhanced oxidative stress and platelet activation in patients with Cushing's syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015;82(4):517–524. doi: 10.1111/cen.12524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Prazny M., Jezkova J., Horova E., Lazarova V., Hana V., Kvasnicka J. Impaired microvascular reactivity and endothelial function in patients with Cushing's syndrome: influence of arterial hypertension. Physiol. Res. 2008;57(1):13–22. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.931126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Luan G., Li G., Ma X., Jin Y., Hu N., Li J. Dexamethasone-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance-study in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and mitochondria isolated from mouse liver. Molecules. 2019;24(10) doi: 10.3390/molecules24101982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Koziel R., Pircher H., Kratochwil M., Lener B., Hermann M., Dencher N.A. Mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I is inactivated by NADPH oxidase Nox4. Biochem. J. 2013;452(2):231–239. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Pan J., Kao Y.L., Joshi S., Jeetendran S., Dipette D., Singh U.S. Activation of Rac1 by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in vivo: role in activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways and retinoic acid-induced neuronal differentiation of SH-SY5Y cells. J. Neurochem. 2005;93(3):571–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Rezende F., Lowe O., Helfinger V., Prior K.K., Walter M., Zukunft S. Unchanged NADPH oxidase activity in nox1-nox2-nox4 triple knockout mice: what do NADPH-stimulated chemiluminescence assays really detect? Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2016;24(7):392–399. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.BelAiba R.S., Djordjevic T., Petry A., Diemer K., Bonello S., Banfi B. NOX5 variants are functionally active in endothelial cells. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2007;42(4):446–459. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.10.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Huang Y., Cai G.Q., Peng J.P., Shen C. Glucocorticoids induce apoptosis and matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in chondrocytes through the NOX4/ROS/p38 MAPK pathway. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018;181:52–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Sun L., Chen Y., Shen X., Xu T., Yin Y., Zhang H. Inhibition of NOX2-NLRP1 signaling pathway protects against chronic glucocorticoids exposure-induced hippocampal neuronal damage. Int. Immunopharm. 2019;74:105721. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Bai S.C., Xu Q., Li H., Qin Y.F., Song L.C., Wang C.G. NADPH oxidase isoforms are involved in glucocorticoid-induced preosteoblast apoptosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019;2019:9192413. doi: 10.1155/2019/9192413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Semenza G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine. Cell. 2012;148(3):399–408. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Pouyssegur J., Mechta-Grigoriou F. Redox regulation of the hypoxia-inducible factor. Biol. Chem. 2006;387(10–11):1337–1346. doi: 10.1515/BC.2006.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Gorlach A., Kietzmann T. Superoxide and derived reactive oxygen species in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factors. Methods Enzymol. 2007;435:421–446. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)35022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Agani F., Jiang B.H. Oxygen-independent regulation of HIF-1: novel involvement of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 2013;13(3):245–251. doi: 10.2174/1568009611313030003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Gorlach A., Dimova E.Y., Petry A., Martinez-Ruiz A., Hernansanz-Agustin P., Rolo A.P. Reactive oxygen species, nutrition, hypoxia and diseases: problems solved? Redox Biol. 2015;6:372–385. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Dery M.A., Michaud M.D., Richard D.E. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: regulation by hypoxic and non-hypoxic activators. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005;37(3):535–540. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Wagner A.E., Huck G., Stiehl D.P., Jelkmann W., Hellwig-Burgel T. Dexamethasone impairs hypoxia-inducible factor-1 function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008;372(2):336–340. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.05.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Lim W., Park C., Shim M.K., Lee Y.H., Lee Y.M., Lee Y. Glucocorticoids suppress hypoxia-induced COX-2 and hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha expression through the induction of glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014;171(3):735–745. doi: 10.1111/bph.12491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Gaber T., Schellmann S., Erekul K.B., Fangradt M., Tykwinska K., Hahne M. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor counterregulates dexamethasone-mediated suppression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha function and differentially influences human CD4+ T cell proliferation under hypoxia. J. Immunol. 2011;186(2):764–774. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Simko V., Takacova M., Debreova M., Laposova K., Ondriskova-Panisova E., Pastorekova S. Dexamethasone downregulates expression of carbonic anhydrase IX via HIF-1alpha and NF-kappaB-dependent mechanisms. Int. J. Oncol. 2016;49(4):1277–1288. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Kodama T., Shimizu N., Yoshikawa N., Makino Y., Ouchida R., Okamoto K. Role of the glucocorticoid receptor for regulation of hypoxia-dependent gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278(35):33384–33391. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302581200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Vettori A., Greenald D., Wilson G.K., Peron M., Facchinello N., Markham E. Glucocorticoids promote Von Hippel Lindau degradation and hif-1alpha stabilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2017;114(37):9948–9953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1705338114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Giannoni E., Chiarugi P. Redox circuitries driving Src regulation. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2014;20(13):2011–2025. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Martens B., Drebert Z. Glucocorticoid-mediated effects on angiogenesis in solid tumors. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019;188:147–155. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Whitehead M., Wickremasinghe S., Osborne A., Van Wijngaarden P., Martin K.R. Diabetic retinopathy: a complex pathophysiology requiring novel therapeutic strategies. Expet Opin. Biol. Ther. 2018;18(12):1257–1270. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2018.1545836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Luo J.C., Shin V.Y., Liu E.S., Ye Y.N., Wu W.K., So W.H. Dexamethasone delays ulcer healing by inhibition of angiogenesis in rat stomachs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004;485(1–3):275–281. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2003.11.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Luedi M.M., Singh S.K., Mosley J.C., Hassan I.S.A., Hatami M., Gumin J. Dexamethasone-mediated oncogenicity in vitro and in an animal model of glioblastoma. J. Neurosurg. 2018:1–10. doi: 10.3171/2017.7.JNS17668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Badruddoja M.A., Krouwer H.G., Rand S.D., Rebro K.J., Pathak A.P., Schmainda K.M. Antiangiogenic effects of dexamethasone in 9L gliosarcoma assessed by MRI cerebral blood volume maps. Neuro Oncol. 2003;5(4):235–243. doi: 10.1215/S1152851703000073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Cheng X., Yan Y., Chen J.L., Ma Z.L., Yang R.H., Wang G. Dexamethasone exposure accelerates endochondral ossification of chick embryos via angiogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. : Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2016;149(1):167–177. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Chen Y., Chen S., Kawazoe N., Chen G. Promoted angiogenesis and osteogenesis by dexamethasone-loaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles/collagen composite scaffolds with microgroove networks. Sci. Rep. 2018;8(1):14143. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32495-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Chen W.L., Lin C.T., Yao C.C., Huang Y.H., Chou Y.B., Yin H.S. In-vitro effects of dexamethasone on cellular proliferation, apoptosis, and Na+-K+-ATPase activity of bovine corneal endothelial cells. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2006;14(4):215–223. doi: 10.1080/09273940600732380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Price L.C., Shao D., Meng C., Perros F., Garfield B.E., Zhu J. Dexamethasone induces apoptosis in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Respir. Res. 2015;16:114. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0262-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Hettmannsperger U., Tenorio S., Orfanos C.E., Detmar M. Corticosteroids induce proliferation but do not influence TNF- or IL-1 beta-induced ICAM-1 expression of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1993;285(6):347–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00371835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Volk K.A., Roghair R.D., Jung F., Scholz T.D., Lamb F.S., Segar J.L. Coronary endothelial function and vascular smooth muscle proliferation are programmed by early-gestation dexamethasone exposure in sheep. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010;298(6):R1607–R1614. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00824.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Gogiraju R., Bochenek M.L., Schafer K. Angiogenic endothelial cell signaling in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019;6:20. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2019.00020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Montezano A.C., Touyz R.M. Reactive oxygen species, vascular Noxs, and hypertension: focus on translational and clinical research. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2014;20(1):164–182. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Liu S.F., Kuo H.C., Tseng C.W., Huang H.T., Chen Y.C., Tseng C.C. Leukocyte mitochondrial DNA copy number is associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PloS One. 2015;10(9) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Pandey V.G., Jain S., Rana A., Puri N., Arudra S.K., Mopidevi B. Dexamethasone promotes hypertension by allele-specific regulation of the human angiotensinogen gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2015;290(9):5749–5758. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.601922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Sangeetha K.N., Lakshmi B.S., Niranjali Devaraj S. Dexamethasone promotes hypertrophy of H9C2 cardiomyocytes through calcineurin B pathway, independent of NFAT activation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016;411(1–2):241–252. doi: 10.1007/s11010-015-2586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Roy S.G., De P., Mukherjee D., Chander V., Konar A., Bandyopadhyay D. Excess of glucocorticoid induces cardiac dysfunction via activating angiotensin II pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. : Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009;24(1–2):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000227803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Halliday H.L. Update on postnatal steroids. Neonatology. 2017;111(4):415–422. doi: 10.1159/000458460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Kamenicky P., Redheuil A., Roux C., Salenave S., Kachenoura N., Raissouni Z. Cardiac structure and function in Cushing's syndrome: a cardiac magnetic resonance imaging study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2014;99(11):E2144–E2153. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Burgoyne J.R., Mongue-Din H., Eaton P., Shah A.M. Redox signaling in cardiac physiology and pathology. Circ. Res. 2012;111(8):1091–1106. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.255216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Poiani G.J., Tozzi C.A., Thakker-Varia S., Choe J.K., Riley D.J. Effect of glucocorticoids on collagen accumulation in pulmonary vascular remodeling in the rat. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994;149(4 Pt 1):994–999. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.4.8143066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Rosenkranz S., Gibbs J.S., Wachter R., De Marco T., Vonk-Noordegraaf A., Vachiery J.L. Left ventricular heart failure and pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2016;37(12):942–954. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Semenza G.L. Involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in pulmonary pathophysiology. Chest. 2005;128(6 Suppl) doi: 10.1378/chest.128.6_suppl.592S. 592S-4S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Diebold I., Petry A., Djordjevic T., Belaiba R.S., Fineman J., Black S. Reciprocal regulation of Rac1 and PAK-1 by HIF-1alpha: a positive-feedback loop promoting pulmonary vascular remodeling. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2010;13(4):399–412. doi: 10.1089/ars.2009.3013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Liu J.Q., Zelko I.N., Erbynn E.M., Sham J.S., Folz R.J. Hypoxic pulmonary hypertension: role of superoxide and NADPH oxidase (gp91phox) Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2006;290(1):L2–L10. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00135.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Shimoda L.A., Laurie S.S. HIF and pulmonary vascular responses to hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014;116(7):867–874. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00643.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Zhang Z., Trautz B., Kracun D., Vogel F., Weitnauer M., Hochkogler K. Stabilization of p22phox by hypoxia promotes pulmonary hypertension. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2019;30(1):56–73. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Veit F., Pak O., Egemnazarov B., Roth M., Kosanovic D., Seimetz M. Function of NADPH oxidase 1 in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells after monocrotaline-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2013;19(18):2213–2231. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Barman S.A., Chen F., Su Y., Dimitropoulou C., Wang Y., Catravas J.D. NADPH oxidase 4 is expressed in pulmonary artery adventitia and contributes to hypertensive vascular remodeling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014;34(8):1704–1715. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Voelkel N.F., Gomez-Arroyo J. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in pulmonary arterial hypertension. The angiogenesis paradox. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014;51(4):474–484. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0045TR. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Price L.C., Montani D., Tcherakian C., Dorfmuller P., Souza R., Gambaryan N. Dexamethasone reverses monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats. Eur. Respir. J. 2011;37(4):813–822. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00028310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Murata T., Hori M., Sakamoto K., Karaki H., Ozaki H. Dexamethasone blocks hypoxia-induced endothelial dysfunction in organ-cultured pulmonary arteries. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004;170(6):647–655. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200309-1311OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.