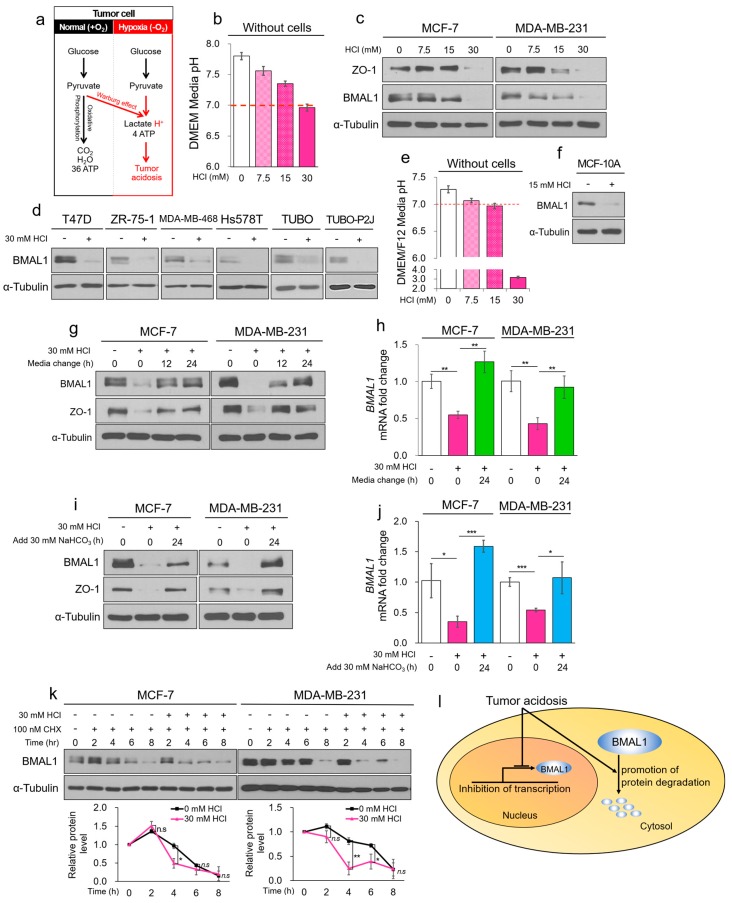
Figure 3.
Tumor acidosis reduces BMAL1 via inhibition of transcriptional activity and protein stability in breast cancer cells. (a) The summarization of the glycolysis pathway in normoxia and hypoxia. (b) HCl-mediated acidic DMEM media were incubated for 24 h without cells, and media pH was immediately measured using a pH meter. (c,d) Breast cancer cell lines were treated with HCl-mediated acidic media for 24 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. (e) HCl-mediated acidic DMEM/F12 media were incubated for 24 h without cells. pH of the cultured media was immediately measured using a pH meter. (f) MCF-10A was treated with HCl-mediated acidic media for 24 h. Cell lysate was analyzed by immunoblotting. (g,h) MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 were treated with HCl-mediated acidic media for 24 h. The acidic cultured media were exchanged to fresh media and then incubated for 12 and 24 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting (g) and RT-qPCR (h). (i,j) MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 were treated with HCl-mediated acidic media for 24 h. The acidic cultured media were added to NaHCO3 and then incubated for 24 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting (i) and RT-qPCR (j). (k) MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 were treated with CHX in acidic condition for the indicated periods. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. The blots of BMAL1 were quantified using ImageJ (bottom panel). (l) Graphical summarization of the dual pathways that reduce BMAL1. Data represent the mean ± SD, n = 3. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. the control group or between two groups by a Student’s t-test.