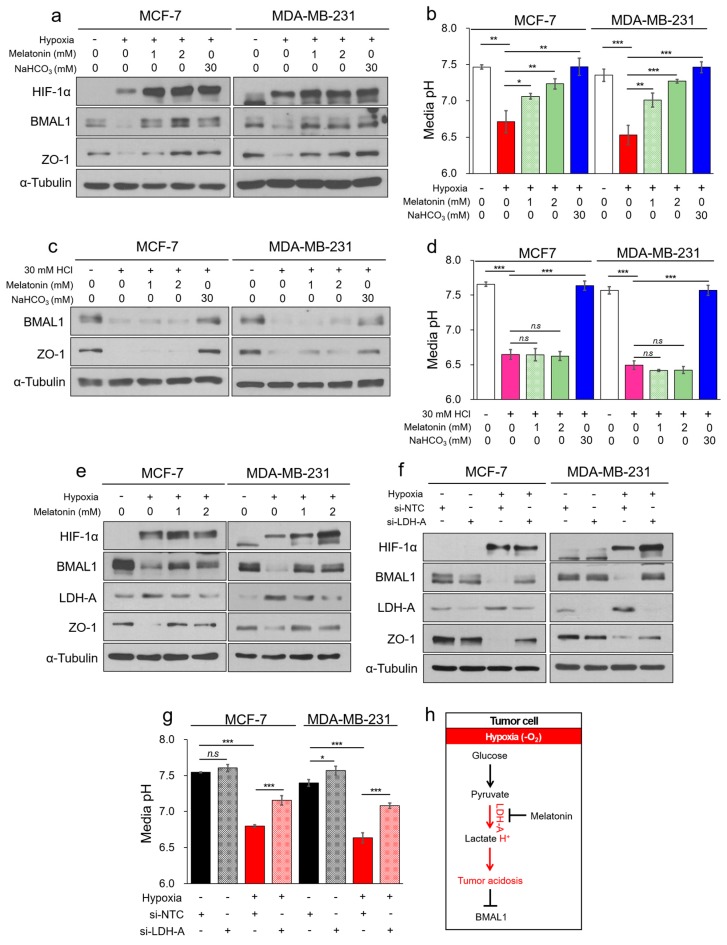
Figure 5.
Melatonin attenuates decrease of BMAL1 expression by inhibiting hypoxia-mediated LDH-A in breast cancer cells. (a,b) MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 were incubated in normoxia or 2% O2 hypoxia with melatonin or NaHCO3 for 48 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting (a) and pH of the cultured media was immediately measured using a pH meter (b). (c,d) MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 were incubated in acidic condition with melatonin or NaHCO3 for 24 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting (c) and pH of the cultured media was immediately measured using a pH meter (d). (e) MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 were incubated in normoxia or 2% O2 hypoxia with melatonin for 48 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. (f,g) MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 were transfected with si-NTC or si-LDH-A, and cells were incubated in normoxia or 2% O2 hypoxia for 48 h. Cell lysates were determined by immunoblotting (f) and pH of the cultured media was immediately measured using a pH meter (g). (h) The summarization of pathway that melatonin attenuates acidosis-mediated decrease of BMAL1 by inhibiting LDH-A in hypoxia. Data represent the mean ± SD, n = 3. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 vs. the control group or between two groups by a Student’s t-test.