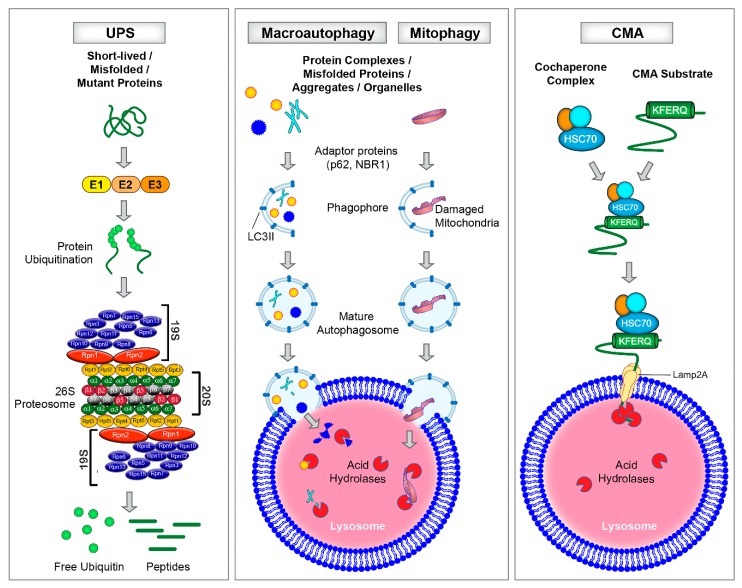
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of different types of protein degradation pathways. Left: Ubiquitin Proteasome System (UPS) employs three different enzymes, E1, E2 and E3 to target and tag proteins with four or more ubiquitin molecules. The 26S proteasome is a large protein complex that is comprised of approximately 33 different subunits which form the 20S proteolytic core particle capped by the 19S regulatory lid particle. The 20S core has six catalytic sites that cleave protein substrates. The ubiquitinated proteins are recognized and degraded by the 20S core particle into smaller peptides and the free ubiquitin is available for recycling. Middle: Macroautophagy and mitophagy require the formation of double-membrane vesicles called autophagosomes to engulf proteins and damaged mitochondria, for eventual fusion with, and degradation by, the lysosome. Right: Chaperone Mediated Autophagy (CMA) functions independently of autophagosomes and employs a co-chaperone complex, Hsc70, and the lysosomal receptor, LAMP2A, for the recognition and degradation of proteins bearing a unique KFERQ-like motif.