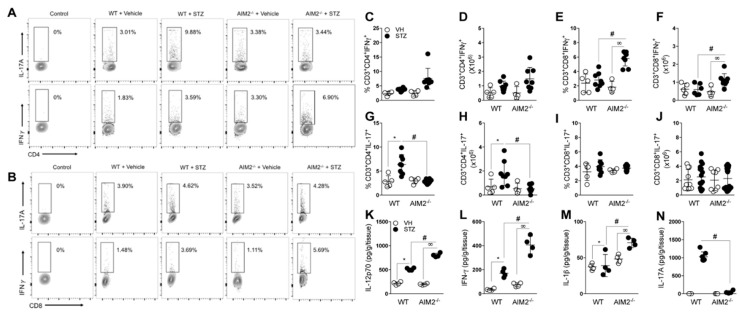
Figure 3.
Deficiency of AIM2 increases Th1 and Tc1 populations in PLNs during T1D. Cells from the PLNs of the WT and AIM2−/− mice were harvested at 15 days after the vehicle (VH) or STZ administration and assessed for extracellular (CD3, CD4 and CD8) and intracellular (IL-17 and IFN-γ) molecules, with a minimum of 2 × 106 cells per sample. (A,B) Representative dot plot of CD4+IL-17+ (Th17), CD8+IL-17+ (Tc17), CD4+ IFN-γ+ (Th1), and CD8+ IFN-γ+ (Tc1) cells in the PLNs of the WT and AIM2−/− mice, after the STZ injections. (C–J) Percentage and absolute numbers of CD4+ IFN-γ+ (Th1), CD4+IL-17+ (Th17), CD8+IL-17+ (Tc17), and CD8+ IFN-γ+ (Tc1) cells in the PLNs of the WT and AIM2−/− mice, after 0, 7 and 15 days of the STZ injections. (K–N) Protein levels of IL-12p70, IFN-γ, IL-1beta and IL-17 cytokines, assessed by ELISA in the pancreatic tissue of the WT and AIM2−/− mice, after 15 days of STZ or vehicle injections. The values are expressed as the mean ± SD. The results were considered statistically significant when p < 0.05 (*; #, ∞). N = 3–6 animals per group. Significant differences between the groups were determined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test.