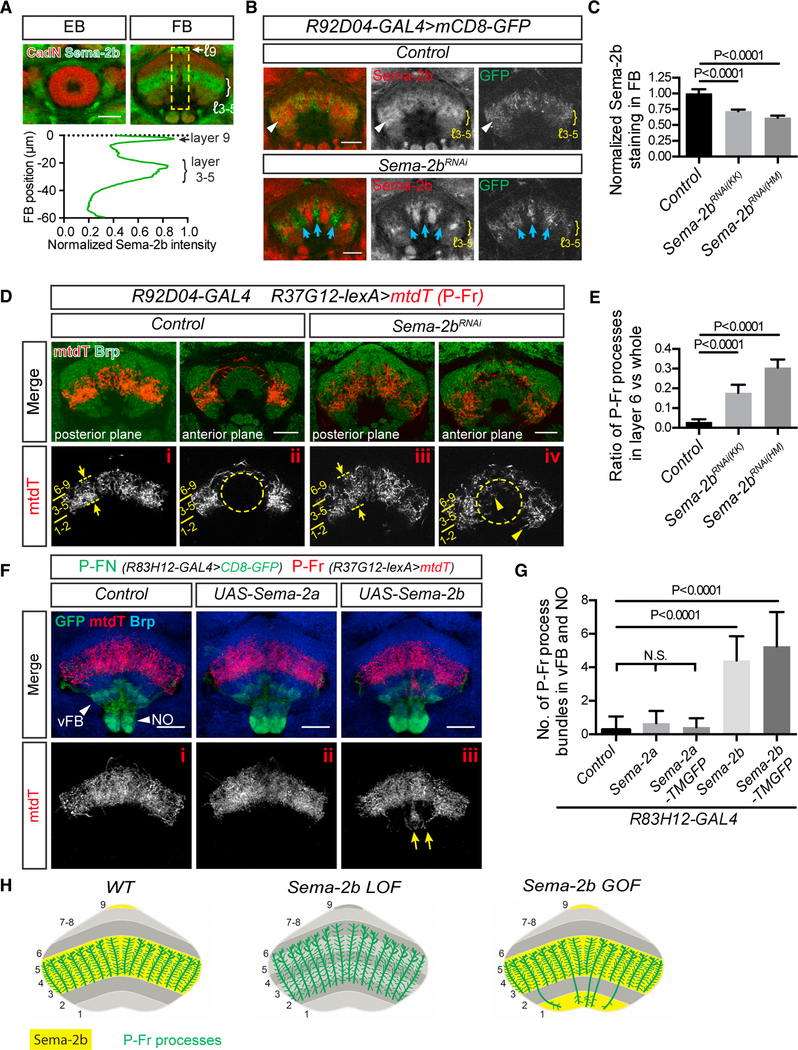
Figure 2. Semaphorin 2b (Sema-2b) Is an Attractive Cue that Regulates Medial FB Neuron Lamination.
(A) sAnti-Sema-2b staining (green) shows enrichment in the medial FB (mFB) (layers 3–5) and to a lesser extent in the dorsal FB (layer 9) during early pupal stages.Sema-2b is not expressed in the ellipsoid body (EB). Anti-N-Cadherin (CadN) staining (red) reveals pupal brain structures at 48 h after pupal formation (APF) (see Figure S2A for additional developmental stages). Quantification of the average Sema-2b immunolabeling intensity along the ventral-dorsal axis (yellow box; bottom panel) (n = 8 brains).
(B) R92D04-GAL4 is expressed in a group of small-field FB neurons (labeled by mCD8-GFP, green) that innervate the mFB (control, upper panels) and that colocalize with Sema-2b (red). When UAS-Sema-2b-RNAi is expressed in R92D04 neurons (lower panels), their processes reorganize and innervate subsets of FB columns that are now devoid of Sema-2b (blue arrows). Sema-2b is still detected in some FB columns and is expressed by other neurons that are not targeted by R92D04-GAL4.
(C) Quantification of Sema-2b immunolabeling across all mFB columns in Control and Sema-2b-RNAi-expressing animals. Two different UAS-Sema-2b-RNAi transgenic lines (KK104842 and HM05143) were used. All data points were normalized to the average value of the control group (n = 8 brains for each group). These expression data are an average of Sema-2b downregulation over a defined FB region. It is important to note that this region includes neuronal processes that extend from neurons in which Sema-2b is not knocked down, owing to the lack of Sema-2b-RNAi expression in all neurons that contribute neuronal processes to FB columns when Sema-2b-RNAi expression is driven by R92D04-GAL4
D) A group of P-Fr neurons, labeled by R37G12-lexA driving mtdT (red), elaborates their processes in mFB layers 3–5 (i) but not in the EB (ii) in control animals. Brp staining (green) reveals EB and FB morphologies and defines FB layers. Layers 2 and 6 are most recognizable because they exhibit stronger Brp staining than do other FB layers. When Sema-2b is knocked down in R92D04 neurons in the mFB, P-Fr neurons expand their projections into the dorsal FB layer 6, seen here in more posterior regions (panel iii, dashed lines and arrows), and mis-project their processes into the EB and also into ventral FB layers 1 and 2 in more anterior regions ([iv], arrowheads).>
(E) Quantification of the P-Fr process dorsal overshooting phenotype shown in (i) and (iii), shown as the ratio of P-Fr process measurement within layer 6 (revealed by higher anit-Brp immunolabeling) to all P-Fr processes across all FB layers (see Star Methods for details) (n = 10 brains for each genotype).
(F) The R83H12-GAL4 fly line was used for expressing Sema-2a or Sema-2b in P-FN neurons (green), which innervate the PB, the ventral FB (layer 1), and the NO (arrowheads). P-Fr neurons were labeled with R37G12-lexA driving mtdT (red), and anti-Brp staining (blue) labels the FB. Note that mtdT-labeled P-Fr neurons ectopically innervate the NO and vFB when Sema-2b, but not Sema2a, is expressed in the R83H12 neurons (yellow arrows).
(G) Quantification of P-Fr process innervation of the ventral FB and NO in control animals and when secreted (or membrane-tethered) Sema-2a or Sema2b were expressed in P-FN neurons using the R83H12-GAL4 driver (n = 15 brains for control; 15 for Sema-2a; 7 for Sema-2a-TMGFP; 15 for Sema-2b; and 16 for Sema-2b-TMGFP). TMGFP = transmembrane-GFP.
(H) Schematics showing co-localization of P-Fr processes with Sema-2b in FB layers 3–5 and how P-Fr processes respond to Sema-2b loss- and gain-of-function in the FB. P-Fr cell bodies and their axons and dendrites outside of the FB are not included in these diagrams. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used for (C), (E), and (G). Bar graphs in this and all subsequent figures are shown as mean ± SD.
Scale bars represent 20 μm.