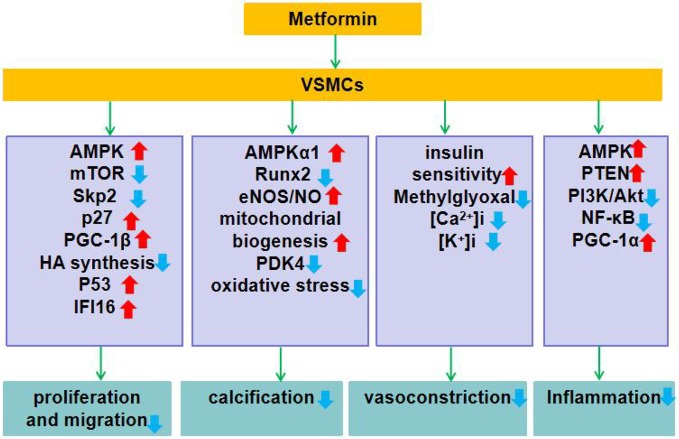
Figure 1.
Role of metformin in VSMCs dysfunction. Metformin exerts its function of improving the function of VSMCs by regulating the expression and function of genes or proteins closely related to VSMCs proliferation and migration, calcification, contraction, and inflammation. ↑indicates increase or activation, and ↓indicates decrease or suppression. Metformin inhibits VSMCs proliferation: 1. Activates AMPK, inhibits mTOR, down-regulates Skp2 while up-regulates p27. 2. Up-regulates expression of PGC-1β. 3. Activates AMPK, reduces HA synthesis. 4. Activates AMPK, up-regulates P53 and IFI16. Metformin inhibits vascular calcification: 1. Activates AMPKα1 and inhibits Runx2 expression. 2. Activates the AMPK-eNOS-NO pathway. 3. Enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and inhibits PDK4/oxidative stress-mediated apoptotic pathway. Metformin inhibits smooth muscle contraction: 1. Enhances insulin sensitivity and inhibits methylglyoxal activation of renin angiotensin system. 2. Inhibits the rise of [Ca2+]i and [K+]i in VSMCs. Metformin inhibits inflammation: 1. Activates AMPK and up-regulates PTEN expression. 2. Inhibits PI3K-Akt and NF-κB activation. 3. Up-regulates the expression of PGC-1α.