Figure 3.
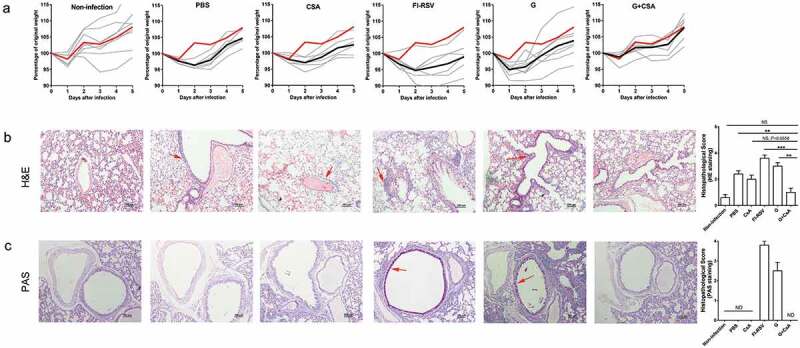
Priming neonates and then boosting infants with the G+ CsA vaccine protects mice from RSV infection without incurring ERD. Neonatal mice (5-day-old) were immunized on days 0 and 14 with vaccines or given control treatments as indicated and then challenged i.n. with RSV on day 28. (A) Body weight changes were recorded daily until day 5 post-infection. Percentage change from the original weight (weight on day 28) is shown (Y axis) plotted against days post-infection (X axis); red solid lines show the means of the non-infected group; black solid lines show the means of the infected groups; gray solid lines show weight changes of individual mice in the groups, n = 6–8). Lung tissues were sectioned and stained with both H&E (B) and PAS (C) at 5 days post-infection. Solid red arrows indicate a typical lymphocyte infiltration seen after H&E staining and typical areas of mucus secretion revealed by PAS staining. Graphs are representative of 5–6 animals per group. The scale bar is 100 μm. Histopathology was scored for severity on a scale of 0 (normal) to 4 (severe). ND, no detection. Data are mean ± SEM, *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001.
