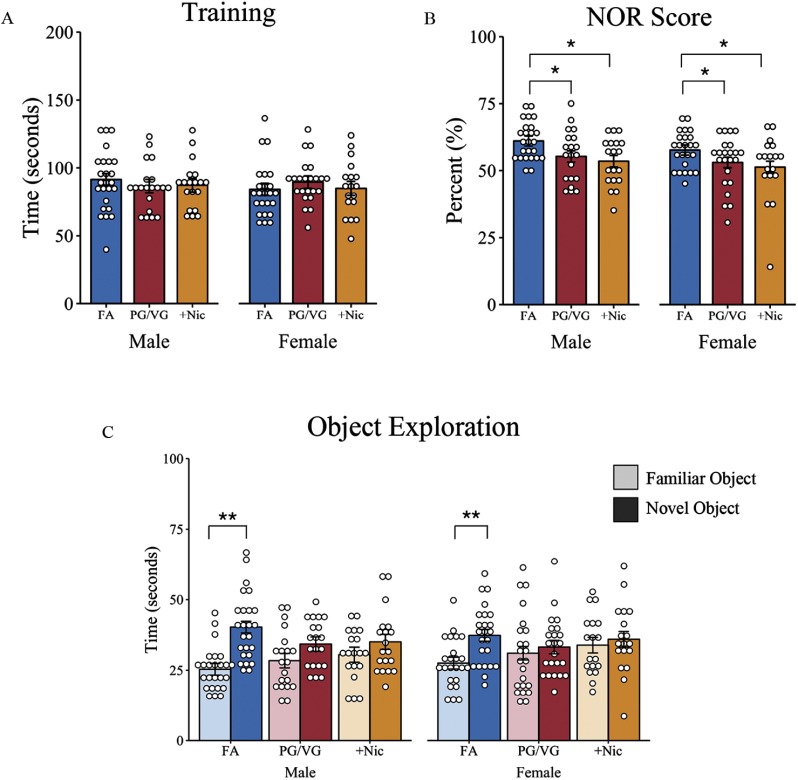
Figure 4.
Measure of short-term memory in offspring of dams exposed to filtered air (FA), e-cigarette aerosol (PG/VG), or e-cigarette aerosol with nicotine (). Offspring were given 10 min to explore two identical objects and then assessed 24 h later for memory performance by replacing one familiar object with a novel object. (A) Total time spent sniffing two objects during the initial learning phase; (B) percentage of novel object recognition determined as the time spent with the novel object over total object exploration time; and (C) time spent sniffing the familiar and novel object 24 h later during the testing phase. *, ** as determined by liner mixed-effects model with treatment and sex as fixed effects (A,B) or as separate models for each treatment group (C) and individual animals nested in litter as random effects. Plots represent individual mice; bars represent marginal means . FA (10 litters) [males (), females ()]; PG/VG (9 litters) [males (), females ()]; (8 litters) [males (), females ()]. Note: NOR, novel object recognition; PG/VG, propylene glycol/vegetable glycerin; SE, standard error; , propylene glycol/vegetable glycerin plus nicotine.