FIGURE 4.
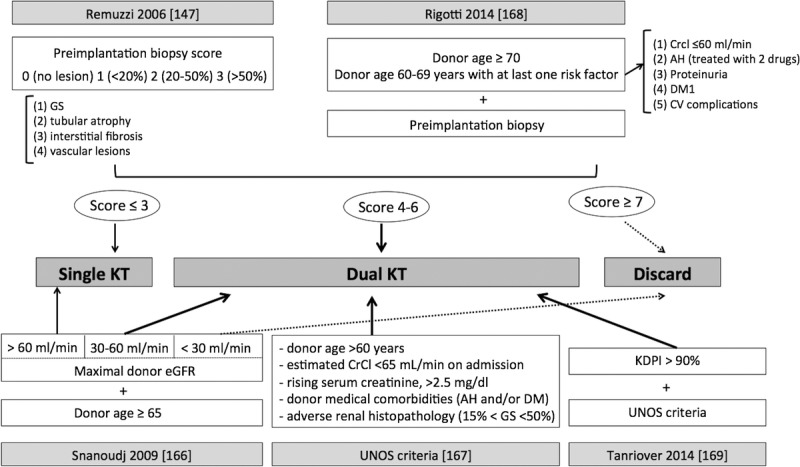
Different criteria for allocating kidneys to dual KT. According to Remuzzi et al,132 the allocation of a dual KT may be based in histopathological criteria in preimplantation donor biopsy with the assessment of 4 compartments (glomerulosclerosis, tubular atrophy, interstitial fibrosis and vascular lesions). The score ascribes 0 to 3 points to each compartment according to the degree of lesions. If the overall score is 3 points or less, a single KT is carried out, between 4 and 6 points, a dual KT, and 7 points or more lead to kidney discard. Rigotti et al, in addition to the histological score, takes into account donor age and donor comorbidities.152 If the donor is 70 years or older, or is 60 to 69 years old with at least 1 comorbid condition such as creatinine clearance below 61 mL/min, AH controlled with 2 drugs or more, proteinuria, diabetes or any cardiovascular complication, the recipient receives 2 kidneys in a dual KT. Snanoudj et al150 proposal is based in donor kidney function and donor age: a donor 65 years or older and eGFR between 30 and 60 mL/min is allocated to dual KT, if >60 ml/min to a single KT and if <30 ml/min discarded.150 UNOS criteria to allocate kidneys for dual KT are based in donor age (>60 years old), creatinine clearance (lower to 65 ml/min at admission), creeping creatinine after admission (to 2.5 mg/dl or higher) and comorbidities such as AH or DM, with glomerulosclerosis between 15-50%.151 Tanriover proposal for dual KT is based in UNOS criteria for kidneys with a KDPI higher than 90%.153 HTA, arterial hypertension; DM, diabetes mellitus; GS, glomerulosclerosis; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; CV, cardiovascular; CrCl, creatinine clearance.
