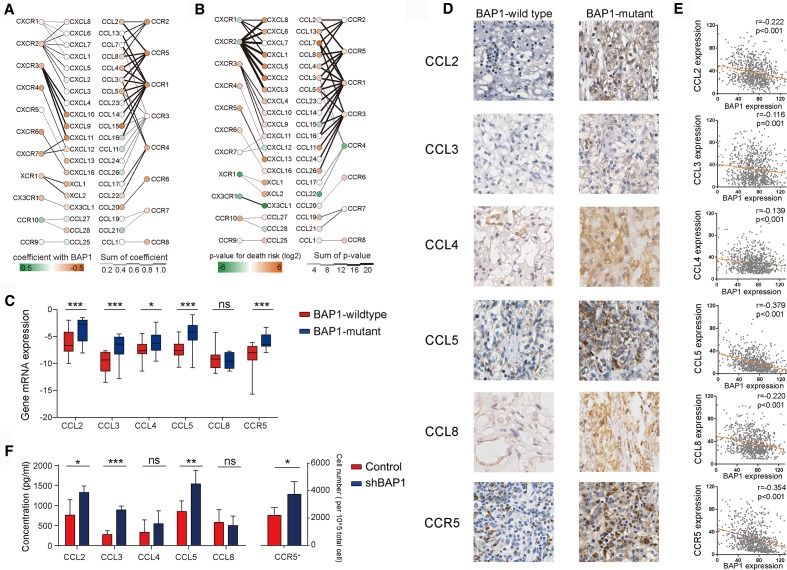
Figure 1.
The expression of C-C chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) and its ligands increases in BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1)-mutant clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). (A) Association between BAP1 RNA expression vs various chemokines and their receptors RNA expression in patients with ccRCC from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) cohort. ‘Coefficient with BAP1’ means the Spearman's rank correlation coefficients between chemokines or their receptors and BAP1, or ‘Spearman's Rho’. Death risk is the HRs of the overall survival (OS) calculated with Cox model by inputting continuous variables. (B) Association between chemokines and their receptors RNA expression vs risk of death in patients with ccRCC from the TCGA cohort. (C) CCL2-5, CCL8 and CCR5 mRNA expression levels in fresh BAP1-mutant and BAP1-wildtype ccRCC tumor specimens measured by real-time PCR (n=8 per group). Box-and-whisker diagrams were used (median, lower and upper quartiles; horizontal lines define min and max). (D) Representative images showing CCL2-5, CCL8 and CCR5 expression in BAP1-wildtype and BAP1-mutant ccRCC tumor specimens via immunohistochemistry. (E) Correlation between chemokines RNA expression and BAP1 RNA expression from the Shanghai cohort. (F) Left: CCL2-5, CCL8 expression levels in BAP1 knockdown tumor-bearing mice measured by ELISA; right: proportion of CCR5+ cells determined by flow cytometry (n=10 per group).