Fig. 1. AGP released dissolved oxygen through the intact skin.
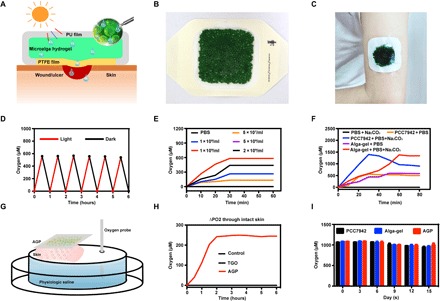
(A) Schematic illustration of microalga-hydrogel patch (AGP) preparation through polyurethane film and polytetrafluoroethylene membrane to perform the light response dissolved oxygen release for chronic wound. (B) Images of the AGP. (C) Photograph of the AGP sticking on the arm. (D) Comparison of releasing dissolved oxygen of alga-gel under light or dark conditions. (E) Comparison of releasing dissolved oxygen of PCC7942 with different concentrations. (F) Comparison of releasing dissolved oxygen between the PCC7942 solution and alga-gel (1 × 109 cells/ml) supplement with or without 500 μM Na2CO3. (G) Diagram of apparatus for measuring delivery of dissolved oxygen. (H) Transfer of dissolved oxygen through mice intact skin into saline at 37°C. (I) Comparison of releasing dissolved oxygen during the storage of PCC7942 solution, alga-gel beads, and AGP (1 × 109 cells/ml) at days 0, 5, 10, and 15. Photo credit (B and C): Huanhuan Chen (Medical School and School of Life Sciences, Nanjing University).
