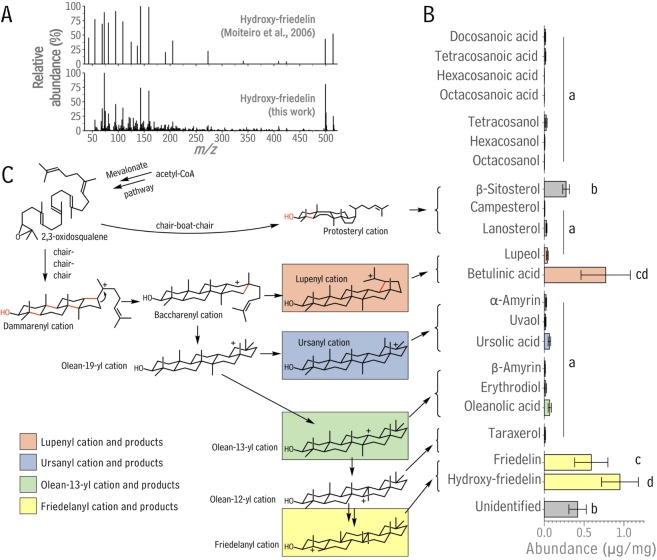
Figure 1.
Non-polar extractable compounds from Quercus suber cork tissue. (A) Comparison of a published mass spectrum of hydroxy-friedelin (Moiteiro et al. 2006) and the mass spectrum of the major non-polar extractable compound in cork tissue, identified as hydroxy-friedelin. (B) Abundance of each wax component detected in cork in μg per mg dry tissue. Wax compounds are grouped according to their biosynthetic relationships. Bar heights and error bars represent the average and standard deviation of n = 4 biologically independent measurements. Significant differences (p < 0.01) were determined using a one-way ANOVA and subsequent Tukey Honest Significant Difference tests. (C) Biosynthetic routes to the triterpenoid wax compounds found in cork wax, predicted in analogy to other species (Xu et al., 2004). 2,3-Oxidosqualene, the precursor to triterpenoid compounds, is synthesized from six acetyl-CoA-derived isopentenyl diphosphate units supplied by the cytosolic mevalonate pathway. This compound can then be cyclized by oxidosqualene cylases to form diverse tetra- and pentacyclic structures.