Fig. 4. High dose overexpression of M305L cardiac actin disrupts the IFM in a myosin-dependent fashion.
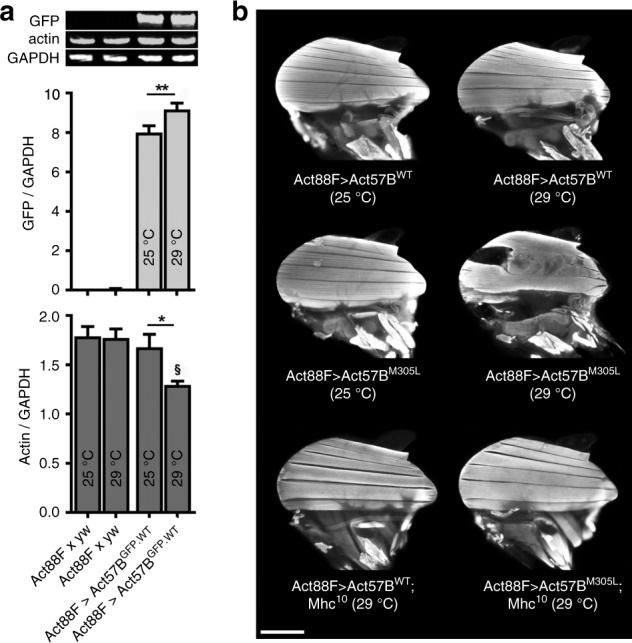
a Quantitative western blot analysis of Act57BGFP.WT and endogenous actin was performed on IFMs from the progeny of Act88F x yw (control) and Act88F > Act57BGFP.WT Drosophila raised at 25 °C and 29 °C, two days after eclosion. Representative western blot, probed with antibodies that targeted GFP, actin, and GAPDH, showing expression of Act57BGFP.WT actin in Act88F > Act57BGFP.WT flies and an absence of GFP-actin in control IFMs. The GFP-actin intensities (normalized to GAPDH) were significantly higher in flies raised at 29 °C. Actin intensities (normalized to GAPDH) revealed that Act88F > Act57BGFP.WT Drosophila raised at 29 °C had a significant reduction in non-tagged, endogenous IFM actin. Quantification was performed on six independent biological replicates with three technical replicates each. Significance was assessed via one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01; §P ≤ 0.01 relative to Act88F x yw at 25 °C or 29 °C. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. b Fluorescent micrographs of dorsal longitudinal IFMs (DLMs) of two-day-old Act88F > Act57BWT and Act88F > Act57BM305L Drosophila. Act88F > Act57BM305L flies raised at 25 °C displayed similar IFM morphology to Act88F > Act57BWT flies. Conversely, Act88F > Act57BM305L flies raised at 29 °C, with elevated mutant actin, showed hypercontracted IFMs, with the middle fibers pulling away from anterior attachment sites. A reduction in IFM myosin content, due to the presence of a single copy of the Mhc10 (IFM-specific MHC null) allele, had no effect on the gross DLM morphology of Act88F > Act57BWT;Mhc10/+ Drosophila (raised at 29 °C). Act88F > Act57BM305L;Mhc10/+ Drosophila (raised at 29 °C) displayed a complete rescue of the hypercontracted phenotype. Scale bar = 250 µm.
