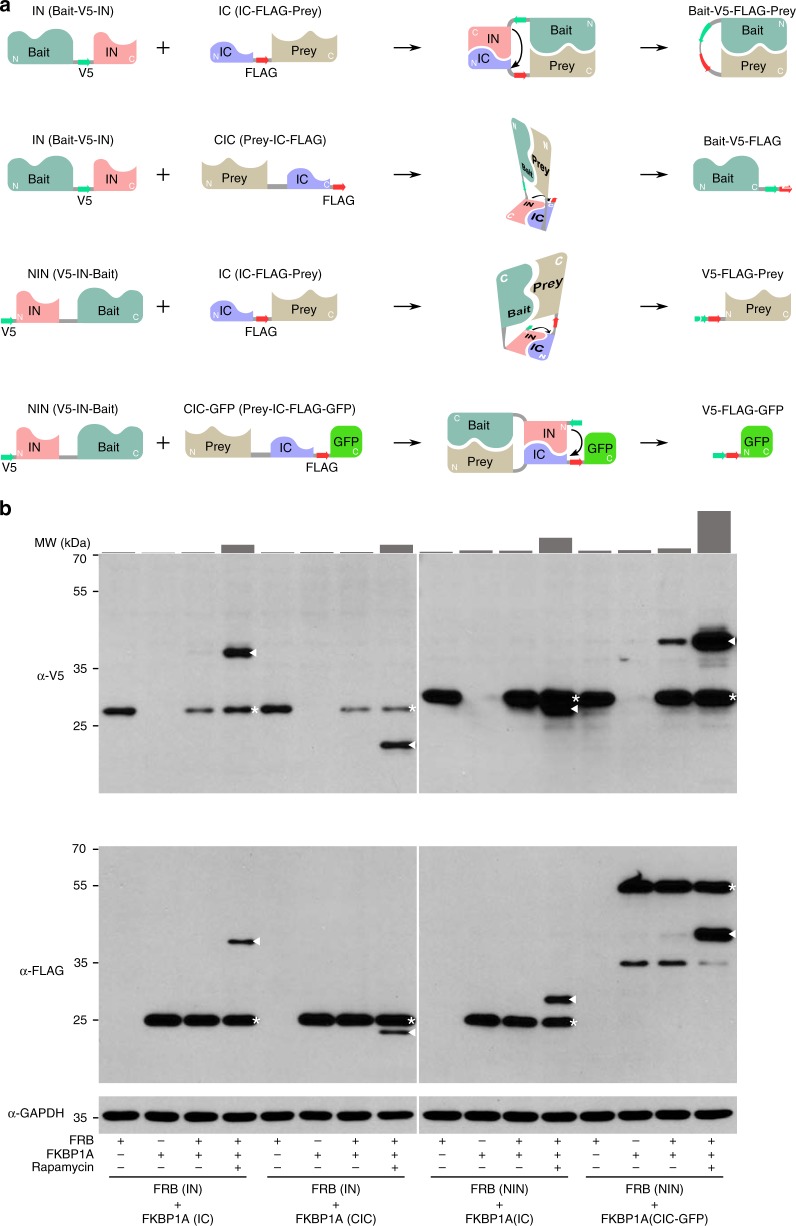
Fig. 2. Design of alternative formats of SIMPL to expand its capability.
a The IN/IC formats allow splicing between bait and prey. In the CIC orientation, IC-FLAG is fused to the C-terminus of a prey protein (Prey-IC-FLAG). Its combination with IN bait (Bait-V5-IN) leads to the transfer of FLAG tag to the bait generating Bait-V5-FLAG. In the NIN orientation, V5-IN is fused to the N-terminus of a bait (V5-IN-Bait). Its use with IC prey (IC-FLAG-Prey) causes the transfer of V5 tag to the prey thus generating V5-FLAG-Prey. The CIC-GFP construct (Prey-IC-FLAG-GFP) is created to allow the detection of NIN/CIC-GFP combination, which produces a V5-FLAG-GFP peptide. b The performance of different SIMPL formats was experimentally assessed using the rapamycin-induced FRB/FKBP1A interaction in which the corresponding bait and prey constructs were transiently transfected. Bands of spliced products are highlighted with triangles and parental proteins are highlighted with asterisks. The densities of spliced bands (FRB-FKBP1A) were quantified with ImageJ and are presented as bar graphs above the blots. The blot is representative of three independent experiments. Source data are available in the Source Data file.