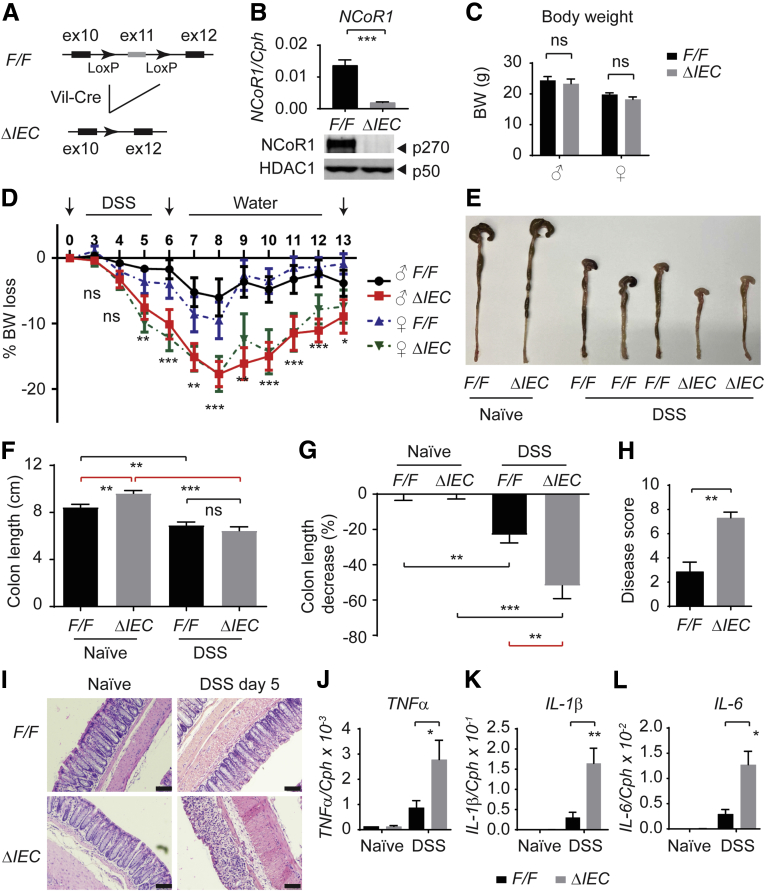
Figure 1.
Intestinal NCoR1 deletion mice are more sensitive to DSS-induced colitis. (A) An outline of the removal of exon 11 in the NCoR1 gene that leads to the creation of mice with an IEC-specific NCoR1 deletion (NCoR1ΔIEC). (B) RT-qPCR of NCoR1 concentrations in colon tissue from NCoR1F/F (F/F) and NCoR1ΔIEC (ΔIEC) and Western blot analysis using nuclear fractions isolated from ileum to examine NCoR1 and HDAC1 concentrations. (C) BW of adult mice at 8 weeks of age (n = 10 per group). (D) Kinetics of BW change (n = 10). Both male (♂) and female (♀) mice at 8 weeks of age were treated with either water (naïve) or 2.5% DSS dissolved in drinking water. After 6 days, mice were restored to regular drinking water. BW was monitored daily for 13 days (n = 10 per group). (E) Gross pictures of naïve (water) and DSS-treated mice of colons collected from mice (6 days of DSS treatment and 2 days of water). (F) Colon tissues were dissected on day 8 after 6 days of DSS treatment and 2 days of water, colon lengths were measured (n = 6). (G) The decrease of colon length of DSS-treated mice was described as the percentage change of colon lengths of DSS-treated over naïve mice (n = 6). (H) Pathologic colitis score. (I) Colon tissues were collected on DSS day 5. H&E staining showing damaged colon in NCoR1ΔIEC mice. Scale bar: 40 μm. Images were examined using a 20× Plan-Apochromat objective (numeric aperture, 0.8) on an upright Imager A2 microscope (Zeiss) with an Axiocam 506 color camera and ZEN2012 imaging software. (J–L) RT-qPCR of cytokine expression in colon tissues collected from both naïve and DSS-treated mice (DSS day 5, n = 6). Results were described as means ± SEM, Student t test analyses were performed, and P values smaller than .05 were considered statistically significant. *P < .05, **P < .01, and ***P < .001.